Water Management Gaps and Legionnaires’ Disease Outbreaks
Findings from a review of CDC-led Legionnaires’ disease outbreak investigations, 2015–2019

Take steps to improve water management in buildings and prevent outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease (LD).
- Building managers can increase use of programs that identify areas or devices in a building where Legionella might grow or spread to people (water management programs, or WMPs). We found that all deficiencies associated with LD outbreaks could have been prevented through effective use of such programs.
- Environmental health staff can collect and share data on common environmental and WMP deficiencies. This type of information sharing can improve WMP implementation.
Comprehensive water management programs can prevent problems associated with outbreaks.
We analyzed reports from CDC-led investigations of LD outbreaks to find deficiencies associated with outbreaks. We examined each deficiency by several criteria, including type of WMP deficiency and type of environmental deficiency (process, equipment, or human error or from unmanaged external change).
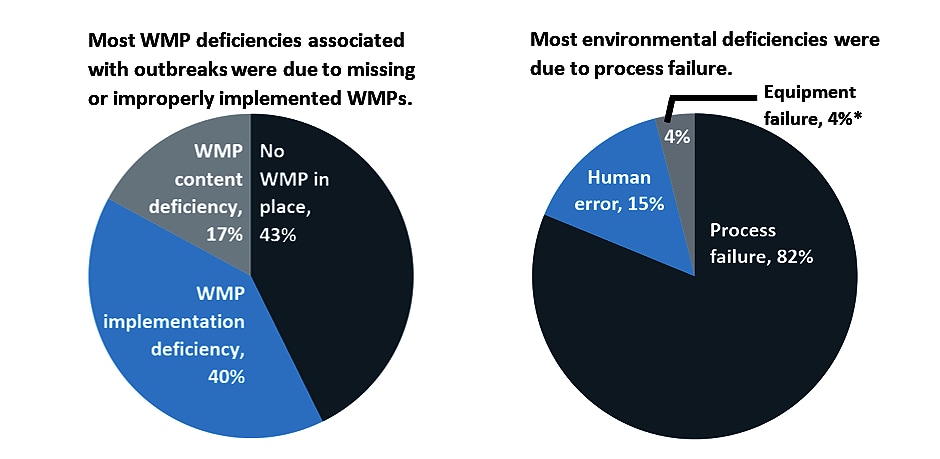
All of the deficiencies associated with outbreaks could have been prevented by comprehensive, properly implemented WMPs.
- The most common WMP deficiencies were that a building lacked a WMP (43%) or the WMP would have been adequate but was not followed (implementation deficiency, 40%). An example of an implementation deficiency would be not measuring water heater temperatures as called for in the WMP.
- Most environmental deficiencies (82%) were associated with a missing process or a process that could not prevent growth or spread of Legionella (process failure). The others were caused by human error or equipment failure.
EH practitioners play an important role in investigating and preventing LD outbreaks.
Information gathered by EH practitioners during LD outbreak investigations describes water system management practices and maintenance deficiencies.
We created a method that EH practitioners can use to collect this type of information to help address gaps and target water management priorities. EH practitioners, building managers, and other public health staff can share and use this information to identify common causes of LD outbreaks and improve the use and content of WMPs.
- Read the scientific articleexternal icon this summary is based on (includes abstraction method)
- Explore CDC’s Toolkit on Developing a Water Management Program to Reduce Legionella Growth and Spread in Buildings
- Discover CDC’s new Toolkit for Controlling Legionella in Common Sources of Exposure
- Take Preventing Legionnaires’ Disease: A Training on Legionella Water Management Programs (PreventLD Training)
- Find more Legionnaires’ Disease Resources for Environmental Health Professionals
* Note: Percentages do not add to 100 due to rounding.