PROTECT Initiative: Advancing Children’s Medication Safety

The PRevention of Overdoses and Treatment Errors in Children Taskforce (PROTECT) Initiative is an innovative collaboration bringing together public health agencies, private sector companies, professional organizations, consumer/patient advocates, and academic experts to develop strategies to keep children safe from unintentional medication overdoses. Medication overdoses are a significant public health problem and often lead to emergency treatment and sometimes hospitalization.
Use of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications is increasing among people of all ages. Increasing medication use also increases the potential for unintentional overdoses. Children are especially vulnerable to unintentional overdoses, but overdoses can be prevented. Data from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-Cooperative Adverse Event Surveillance (NEISS-CADES) project estimates that each year in the United States:
- Approximately 35,000 emergency department (ED) visits result from unintentional medication overdoses among children under the age of 5;
- One out of every 250 two-year-olds is treated in an ED for an unintentional medication overdose;
- Over 90% of ED visits for unintentional medication overdoses among children under the age of 5 involve children who get into medicine on their own without caregiver oversight; and
- Approximately 5% of ED visits for unintentional medication overdoses among children under the age of 5 are due to medication errors. A common error is when caregivers measure and give too much medicine by mistake.

New approaches and innovations in child-resistant safety packaging can limit or prevent harm when a young child finds and tries to ingest medication on his or her own (unsupervised ingestions). Learn More about Safer Packaging.
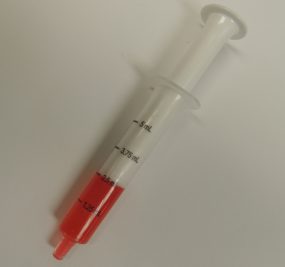
Standardizing and synchronizing the units of measure on dosing directions and on dosing devices can prevent caregiver dosing errors (e.g., milliliters (mL) should be used on both dosing directions and devices). Learn More about Safer Use.

All medicines should be stored up and away and out of sight of young children. Following a few simple steps every time medicines are used can decrease the chance of young children finding and ingesting medicines on their own. Learn More about Safer Storage.
