The University of Iowa Prevention Research Center for Rural Health
Populations of Focus: rural communities, micropolitan communities (10,000 to 50,000 residents) with growing Latinx, Black, refugee, and immigrant populations
Topic Areas: communities experiencing health disparities, social and structural determinants of health, physical activity, intervention adaptation, evaluation
Introduction, Mission, and Vision
The University of Iowa Prevention Research Center for Rural Health (UI PRC-RH) is one of 26 Prevention Research Centers (PRCs) supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for the 2019–2024 funding cycle. Each PRC is funded to establish and maintain their center and to conduct a core research project. PRCs may receive supplemental funding to conduct additional research projects and activities.
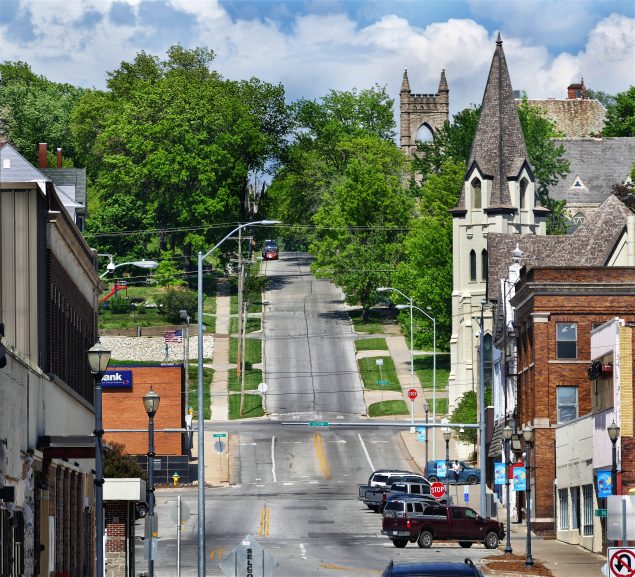

Ottumwa, IA. A micropolitan community and a UI PRC-RH partner.
UI PRC-RH’s mission is to address disparities in midwestern communities to promote well-being. The center works to advance health equity through collaborations that transform social, structural, and environmental conditions. The focus of the center’s work is on promoting health in rural and micropolitan communities – defined as a rural area with a population of at least 10,000 but less than 50,000.
Its three focus areas are:
- Rural and micropolitan area health disparities.
- Social and structural determinants of health.
- The development, testing, and adaptation of evidence-based interventions to promote health for rural and micropolitan communities.
UI PRC-RH supports public health capacity strengthening in micropolitan communities. These areas serve as community hubs for information, jobs, trade, and health and social services for both rural and micropolitan residents, an as a connector hub between rural/micropolitan and metropolitan communities.
Core Research
Each PRC uses a community-engaged approach to conduct one primary applied public health prevention research project called a core research project. Project activities include design, development, implementation, evaluation, and dissemination. PRCs use at least 50% of their CDC funding to conduct the project in partnership with communities.
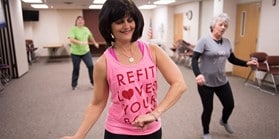
Active Ottumwa used local volunteers to support fun and free physical activity in the Ottumwa community.
UI PRC-RH’s core research project for the 2019–2024 funding cycle is strengthening community partnership capacity for evidence-based interventions.
Part I seeks to:
- Identify the facilitators and barriers to evidence-based interventions in micropolitan communities in Iowa.
- Adapt the Putting Public Health Evidence in Action training to help public health practitioners working in micropolitan areas to implement evidence-based interventions.
- Establish a learning collaborative to promote co-learning and sustained support for evidence-based interventions.
Part II builds on Active Ottumwa, a community-based peer-led physical activity intervention which was implemented in Ottumwa, Iowa. The aim of this project was to support accessible, affordable, and sustainable physical activity programs for adults in the community. Evaluation of the project found that residents had shifted from inactivity to light physical activity, like walking, after participating in these programs. Part II seeks to:
- Translate Active Ottumwa to “Active Iowa” by supporting adoption in other micropolitan communities.
- Create program materials (e.g., a manual of implementation, trainings) to support translation that fit the needs and resources of micropolitan communities across the state.
Additional Research
PRCs may receive supplemental funding to work on additional research projects each funding cycle. These Special Interest Projects (SIPs) focus on a variety of health topics or gaps in scientific evidence. PRCs can also conduct additional research as part of SIP Thematic Research Networks, which are groups of PRCs working together on related health topics.
PRC Vaccine Confidence Network (PRC VCN)
In April 2021, CDC funded a 12-month award to all 26 PRCs to form the PRC VCN in support of CDC’s Vaccinate with Confidence strategy for COVID-19. The goal was to reduce the incidence of COVID-19 in the United States. As part of this network, UI PRC-RH examined ways to increase vaccine uptake and reduce disparities in vaccination and COVID-19 infections in micropolitan communities.
UI PRC-RH’s strategy was to build trust and foster partnerships in communities where the center already had established relationships. It engaged with local community organizations to focus its work in areas that had significant need and no other large-scale vaccine confidence efforts.
Cancer Prevention and Control Research Network (CPCRN) Collaborating Center
UI PRC-RH became part of CPCRN in 2014 and focuses on sharing evidence-based interventions to address cancer disparities in rural communities in Iowa and across the United States. Its research seeks to:
- Expand existing national and local collaborations to accelerate the adoption of proven interventions for cancer screening and prevention in rural areas.
- Improve uptake of the human papillomavirus vaccine by adapting and testing proven interventions in small rural health systems.
- Reduce cancer risk by preventing rural adolescents and young adults from using cigarettes and e-cigarettes by adapting and testing of evidence-based interventions.
As part of the CPCRN network, UI CPCRN collaborates with the following workgroups: Rural Cancer, Cancer Survivorship, Scholars, Health Behaviors, and Health Equity & Social Determinants of Health.
Managing Epilepsy Well 2.0 (MEW) Network Collaborating Center
The MEW network works to improve the health and well-being of people living with epilepsy by developing self-management programs they can use. UI PRC-RH joined the network in 2019 and works to replicate an evidence-based intervention called SMART (Self-Management for People with Epilepsy and a History of Negative Health Events) in rural and underserved communities and to assess participants’ perceptions of the intervention.
SMART has been shown to reduce epilepsy-related complications and improve quality of life and physical and mental health functioning. It is an online, 12-week behavioral program delivered by peer educators (patients with epilepsy) and nurse educators. It was developed by researchers at Case Western Reserve University.
Examining the effectiveness and acceptability of SMART in rural and underserved communities will help guide its implementation and dissemination.

Location: Iowa City, Iowa
Principal Investigator: Rima Afifi, PhD, MPH
Email: rima-afifi@uiowa.edu
Deputy Director: Natoshia Askelson, PhD, MPH