Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Dispatch
Antigenic Characterization of Novel Human Norovirus GII.4 Variants San Francisco 2017 and Hong Kong 2019
Figure 2
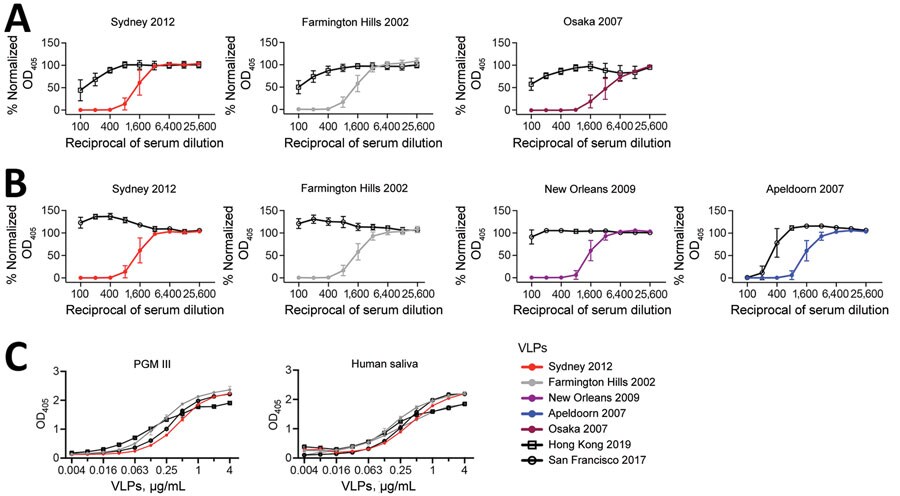
Figure 2. HBGA blockade and binding assays in a study of novel human norovirus GII.4 variants, San Francisco 2017 and Hong Kong 2019. A,B) Line graphs indicating normalized OD405 curves of GII.4 variants in HBGA blockade assays using mouse hyperimmune serum raised against currently circulating strains; A) Hong Kong 2019 VLPs against historical strains; B) San Francisco 2017 VLPs against historical strains. Normalized OD405 values were calculated by using values from positive and negative (serum only) control wells. C) OD405 curves of GII.4 variant VLPs in HGBA binding assays of Hong Kong 2019 and San Francisco 2017 VLPs and PGM III and human saliva, expressing the Lewisa, Lewisb, Lewisy, H type-1, and H type-2 HBGA carbohydrates. PGM III was used as a source of HBGA carbohydrates. Human saliva was collected from a healthy adult volunteer under US Food and Drug Administration, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research protocol no. CBER IRB 16–069B. HBGA, histo-blood group antigen; OD405, optical density at 405 nm; PGM, porcine gastric mucin; VLP, virus-like particles.