Volume 29, Number 9—September 2023
Dispatch
Fatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Neonate Caused by Cronobacter sakazakii Sequence Type 64 Strain of CRISPR Sublineage b
Figure 1
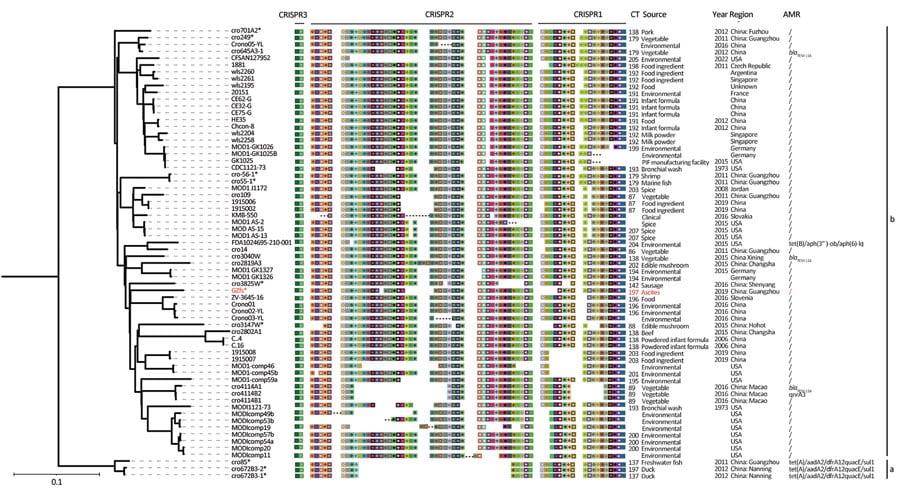
Figure 1. Multilocus sequence typing phylogenetic tree based on whole-genome sequencing single-nucleotide polymorphisms of a Cronobacter sakazakii ST64 strain from a fatal case of necrotizing enterocolitis in a 17-day-old male neonate, China, compared with reference strains. Asterisks indicate newly sequenced strains in this study; red text indicates isolate from the neonate. CRISPR spacers arrangement, CT, source, year, region and genes are listed next to corresponding strains. Color schemes in CRISPR arrays are provided at the spacer level to illustrate differences among strains by using CRISPRStudio software (https://www.semanticscholar.org). Ellipsis in spacers indicate partial CRISPR arrays without determined end (incomplete CRISPR arrays). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. AMR, antimicrobial resistance; CR, CRISPR type; CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; ST, sequence type.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.