Volume 29, Number 10—October 2023
Dispatch
Seafood-Associated Outbreak of ctx-Negative Vibrio mimicus Causing Cholera-Like Illness, Florida, USA
Figure
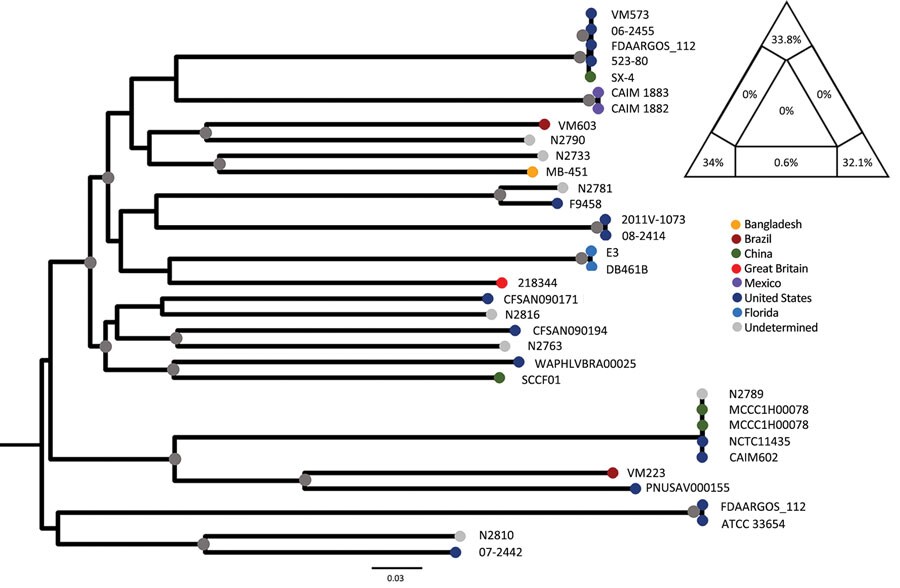
Figure. Maximum-likelihood tree of Vibrio mimicus strains. The tree was calculated by using 35 sequences; the best evolutionary model was selected by Bayesian information criterion. Nodes marked by a gray circle have bootstrap support (1,000 replicates) >90%. Scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site. The phylogenetic signal of the alignment was determined by likelihood mapping, as shown by the triangle in the top right corner. Likelihood mapping method is based on the analysis of maximum likelihoods for quartets of sequences randomly extracted from the alignment. There are only 3 possible fully resolved tree topologies deriving from 4 sequences (e.g., with 4 sequences named A,B,C, and D, sequence A can cluster with B and C with D; or A with C and D with B; or A with D and B with C); alternatively, if there is not enough information in the sequences, the result will be a star-like topology. The likelihoods of the 3 possible topologies are represented as 1 point in an equilateral triangle, in which each vertex represents 1 of the possible topologies. The triangle is partitioned in 7 regions: the region in the center represents completely unresolved quartets with star-like evolution topology; the 3 regions in the corners represent well-resolved topologies; the regions along the sides represent the situation in which it is difficult to decide between 2 of the 3 possible topologies. Percentages in the triangle reflect the number of quartets assigned to each region. A higher sum of the percentages in the triangle corners (completely resolved quartets) indicates a higher phylogenetic signal contained in the alignment. The alignment signal of >99% therefore shows a strong phylogenetic signal, which enables reliable calculation of the tree.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.