Transmission of Japanese Encephalitis Virus
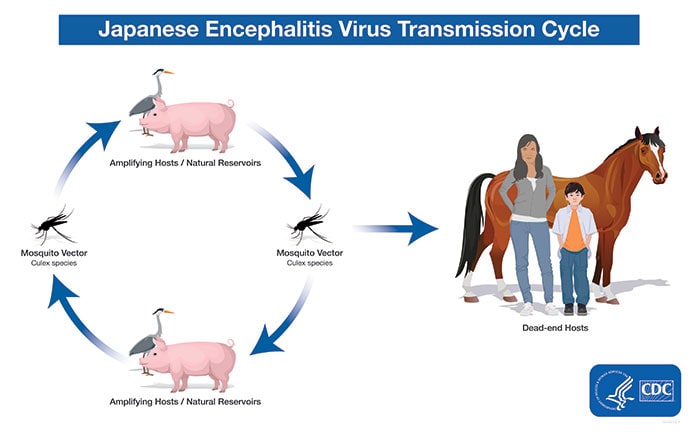
Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus, a flavivirus, is closely related to West Nile and St. Louis encephalitis viruses. JE virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected Culex species mosquitoes, particularly Culex tritaeniorhynchus.
The virus is maintained in a cycle between mosquitoes and vertebrate hosts, primarily pigs and wading birds (also referred to as amplifying hosts or natural reservoirs). Humans are incidental or dead-end hosts, because they usually do not develop high enough concentrations of JE virus in their bloodstreams to infect feeding mosquitoes.

JE virus transmission occurs primarily in rural agricultural areas, often associated with rice production and flooding irrigation. In some areas of Asia, these conditions can occur near urban centers.
In temperate areas of Asia, JE virus transmission is seasonal. Human disease usually peaks in the summer and fall. In the subtropics and tropics, transmission can occur year-round, often with a peak during the rainy season.
Risk areas and transmission season for Japanese encephalitis (JE), by country1,2,3
Country
Country
Risk areas
Risk areas
Transmission season
Transmission season
Comments
Comments
Australia
Australia
Outer Torres Strait Islands, Tiwi Islands, and some areas of mainland (parts of New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, and Northern Territory)
Outer Torres Strait Islands, Tiwi Islands, and some areas of mainland (parts of New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia, and Northern Territory)
November–May
November–May
Prior to 1999, 5 cases reported from Outer Torres Strait Islands and Far North Queensland mainland. No further cases reported until 2021. During 2021-2022 cases reported in rural areas of New South Wales, southern Queensland, southeastern South Australia, northern Victoria, and the Top End of the Northern Territory. Key risk locations are in the area surrounding the Murray River, and the Outer Torres Strait islands.
Prior to 1999, 5 cases reported from Outer Torres Strait Islands and Far North Queensland mainland. No further cases reported until 2021. During 2021-2022 cases reported in rural areas of New South Wales, southern Queensland, southeastern South Australia, northern Victoria, and the Top End of the Northern Territory. Key risk locations are in the area surrounding the Murray River, and the Outer Torres Strait islands.
Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with most cases reported July–November
Year-round with most cases reported July–November
Highest disease incidence in northwest Bangladesh
Highest disease incidence in northwest Bangladesh
Bhutan
Bhutan
Presumed widespread in nonmountainous areas
Presumed widespread in nonmountainous areas
Unknown
Unknown
Risk likely highest in southern districts that share similar ecologic conditions with bordering JE-endemic states of India
Risk likely highest in southern districts that share similar ecologic conditions with bordering JE-endemic states of India
Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam
Presumed widespread
Presumed widespread
Unknown
Unknown
Limited data but outbreak reported in 2013
Proximity to Sarawak, Malaysia suggests ongoing transmission likely
Limited data but outbreak reported in 2013
Proximity to Sarawak, Malaysia suggests ongoing transmission likely
Burma (Myanmar)
Burma (Myanmar)
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with most cases reported May–September
Year-round with most cases reported May–September
Greatest risk in delta and lowland areas
Greatest risk in delta and lowland areas
Cambodia
Cambodia
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with peak season May–October
Year-round with peak season May–October
Cases reported from majority of provinces, so transmission likely countrywide
Cases reported from majority of provinces, so transmission likely countrywide
China
China
All provinces except Xinjiang and Qinghai
All provinces except Xinjiang and Qinghai
Peak season June–October
Peak season June–October
India
India
Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Goa, Haryana, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Odisha, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Goa, Haryana, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Odisha, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal
Peak season May–November, especially in northern India; the season may be extended or year-round in some areas, especially in southern India
Peak season May–November, especially in northern India; the season may be extended or year-round in some areas, especially in southern India
Indonesia
Indonesia
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round, with peak season varying by island
Year-round, with peak season varying by island
Cases reported from many islands, including Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, Bali, Nusa Tenggara, and Papua, so transmission likely on all islands
Several traveler cases reported in recent years from Bali
Cases reported from many islands, including Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, Bali, Nusa Tenggara, and Papua, so transmission likely on all islands
Several traveler cases reported in recent years from Bali
Japan
Japan
All islands
All islands
June–October
June–October
Rare sporadic cases reported from all islands except Hokkaido
Enzootic transmission without reported human cases on Hokkaido
Rare sporadic cases reported from all islands except Hokkaido
Enzootic transmission without reported human cases on Hokkaido
Lao People’s Democratic Republic
Lao People’s Democratic Republic
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with peak season June–September
Year-round with peak season June–September
Malaysia
Malaysia
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round, with peak season in Sarawak from October–December
Year-round, with peak season in Sarawak from October–December
Much higher rates of disease reported from Sarawak than peninsular Malaysia
Much higher rates of disease reported from Sarawak than peninsular Malaysia
Nepal
Nepal
Southern lowlands (Terai), some hill and mountain districts
Southern lowlands (Terai), some hill and mountain districts
Peak season June–October
Peak season June–October
Highest rates of disease reported from southern lowlands (Terai)
Vaccine not routinely recommended for those trekking in high-altitude areas
Highest rates of disease reported from southern lowlands (Terai)
Vaccine not routinely recommended for those trekking in high-altitude areas
North Korea
North Korea
Presumed widespread
Presumed widespread
Unknown
Proximity to South Korea suggests peak transmission May–November
Unknown
Proximity to South Korea suggests peak transmission May–November
Pakistan
Pakistan
Unknown
Unknown
Unknown
Unknown
Very limited data
Previous case report and serosurvey data suggest transmission possible at least in Sindh Province
Very limited data
Previous case report and serosurvey data suggest transmission possible at least in Sindh Province
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea
Widespread
Widespread
Presumed year-round
Presumed year-round
Sporadic cases reported from Western Province, serologic evidence of disease from Gulf and Southern Highland Provinces, and 1 case reported from near Port Moresby, so transmission likely countrywide
Sporadic cases reported from Western Province, serologic evidence of disease from Gulf and Southern Highland Provinces, and 1 case reported from near Port Moresby, so transmission likely countrywide
Philippines
Philippines
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with peak season April–August
Year-round with peak season April–August
Human, animal, and mosquito studies have indicated transmission in 32 provinces, and transmission likely on all islands
Human, animal, and mosquito studies have indicated transmission in 32 provinces, and transmission likely on all islands
Russia
Russia
Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai
June–September
June–September
Cases previously reported from Primorsky Krai
Vaccine not routinely recommended
Cases previously reported from Primorsky Krai
Vaccine not routinely recommended
Singapore
Singapore
Presumed in focal areas
Presumed in focal areas
Year-round
Year-round
Very rare sporadic cases reported
Vaccine not routinely recommended
Very rare sporadic cases reported
Vaccine not routinely recommended
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Widespread except in mountainous areas
Widespread except in mountainous areas
Year-round with peak season November–February
Year-round with peak season November–February
Taiwan
Taiwan
Widespread
Widespread
Peak season May–October
Peak season May–October
Thailand
Thailand
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with peak season May–October, especially in northern Thailand
Year-round with peak season May–October, especially in northern Thailand
Highest rates of disease reported from Chiang Mai Valley
Several traveler cases reported in recent years from resort and coastal areas of southern Thailand
Highest rates of disease reported from Chiang Mai Valley
Several traveler cases reported in recent years from resort and coastal areas of southern Thailand
Timor-Leste
Timor-Leste
Presumed widespread
Presumed widespread
No data
Proximity to West Timor suggests year-round
No data
Proximity to West Timor suggests year-round
Viet Nam
Viet Nam
Widespread
Widespread
Year-round with peak season May–October, especially in northern Viet Nam
Year-round with peak season May–October, especially in northern Viet Nam
1 Destination and transmission season information should be considered in association with travel duration and activities when making decisions on vaccination.
2 Data are based on published and unpublished reports. Risk assessments should be performed cautiously, because risk can vary within areas and from year to year, and surveillance data regarding human cases and JE virus transmission are often incomplete. In some endemic areas, human cases among residents are limited because of vaccination or natural immunity among older people. However, because JE virus is maintained in an enzootic cycle between animals and mosquitoes, susceptible visitors to these areas still may be at risk for infection.
3 Outbreaks previously occurred in the Western Pacific Islands of Guam (1947–1948) and Saipan (1990), but as they are no longer considered risk areas, they are not included in the table.