Increased SARS-CoV-2 Testing Capacity with Pooled Saliva Samples
Anne E. Watkins, Eli P. Fenichel
, Daniel M. Weinberger, Chantal B.F. Vogels, Doug E. Brackney, Arnau Casanovas-Massana, Melissa Campbell, John Fournier, Santos Bermejo, Rupak Datta, Charles S. Dela Cruz, Shelli F. Farhadian, Akiko Iwasaki, Albert I. Ko, Nathan D. Grubaugh
1, Anne L. Wyllie
1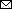
, and
the Yale IMPACT Research Team2
Author affiliations: Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut, USA (A.E. Watkins, D.M. Weinberger, C.B.F. Vogels, A. Casanovas-Massana, A.I. Ko, N.D. Grubaugh, A.L. Wyllie); Yale School of the Environment, New Haven (E.P. Fenichel); Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, New Haven (D.E. Brackney); Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven (M. Campbell, J. Fournier, S. Bermejo, R. Datta, C.S. Dela Cruz, S.F. Farhadian, A. Iwasaki, A.I. Ko); Howard Hughes Medical Institute, New Haven (A. Iwasaki)
Main Article
Figure 1

Figure 1. Effect of pooling on detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, by pool size and between samples tested. A) As the pool size increased, so did the Ct value (dotted lines connect pools comprising the same positive sample). Ct for positivity is set to 38. Samples falling on the x-axis indicated samples from which signal was not detected by reverse transcription quantitative PCR. B) As the pool size increased, so did the Ct. We equated this change by using linear regression (pool of 5 samples, dark blue, +2.2 Ct, 95% CI 1.4–3.0 Ct; pool of 10, light blue, +3.1 Ct, 95% CI 2.3–4.0 Ct; pool of 20, green, +3.6, 95% CI 2.7–4.4 Ct). Dashed lines indicate Ct 38 (cutoff for sample positivity). 1/5, pool of 5; 1/10, pool of 10; 1/20, pool of 20. Ct, cycle threshold.
Main Article
Page created: February 09, 2021
Page updated: March 18, 2021
Page reviewed: March 18, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
