Persons using assistive technology might not be able to fully access information in this file. For assistance, please send e-mail to: mmwrq@cdc.gov. Type 508 Accommodation and the title of the report in the subject line of e-mail.
Sexual and Reproductive Health of Persons Aged 10--24 Years --- United States, 2002--2007
Summary
This report presents data for 2002--2007 concerning the sexual and reproductive health of persons aged 10--24 years in the United States. Data were compiled from the National Vital Statistics System and multiple surveys and surveillance systems that monitor sexual and reproductive health outcomes into a single reference report that makes this information more easily accessible to policy makers, researchers, and program providers who are working to improve the reproductive health of young persons in the United States. The report addresses three primary topics: 1) current levels of risk behavior and health outcomes; 2) disparities by sex, age, race/ethnicity, and geographic residence; and 3) trends over time.
The data presented in this report indicate that many young persons in the United States engage in sexual risk behavior and experience negative reproductive health outcomes. In 2004, approximately 745,000 pregnancies occurred among U.S. females aged <20 years. In 2006, approximately 22,000 adolescents and young adults aged 10--24 years in 33 states were living with human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS), and approximately 1 million adolescents and young adults aged 10--24 years were reported to have chlamydia, gonorrhea, or syphilis. One-quarter of females aged 15--19 years and 45% of those aged 20--24 years had evidence of infection with human papillomavirus during 2003--2004, and approximately 105,000 females aged 10--24 years visited a hospital emergency department (ED) for a nonfatal sexual assault injury during 2004--2006. Although risks tend to increase with age, persons in the youngest age group (youths aged 10--14 years) also are affected. For example, among persons aged 10--14 years, 16,000 females became pregnant in 2004, nearly 18,000 males and females were reported to have sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in 2006, and 27,500 females visited a hospital ED because of a nonfatal sexual assault injury during 2004--2006.
Noticeable disparities exist in the sexual and reproductive health of young persons in the United States. For example, pregnancy rates for female Hispanic and non-Hispanic black adolescents aged 15--19 years are much higher (132.8 and 128.0 per 1,000 population) than their non-Hispanic white peers (45.2 per 1,000 population). Non-Hispanic black young persons are more likely to be affected by AIDS: for example, black female adolescents aged 15--19 years were more likely to be living with AIDS (49.6 per 100,000 population) than Hispanic (12.2 per 100,000 population), American Indian/Alaska Native (2.6 per 100,000 population), non-Hispanic white (2.5 per 100,000 population) and Asian/Pacific Islander (1.3 per 100,000 population) adolescents. In 2006, among young persons aged 10--24 years, rates for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis were highest among non-Hispanic blacks for all age groups. The southern states tend to have the highest rates of negative sexual and reproductive health outcomes, including early pregnancy and STDs.
Although the majority of negative outcomes have been declining for the past decade, the most recent data suggest that progress might be slowing, and certain negative sexual health outcomes are increasing. For example, birth rates among adolescents aged 15--19 years decreased annually during 1991--2005 but increased during 2005--2007, from 40.5 live births per 1,000 females in 2005 to 42.5 in 2007 (preliminary data). The annual rate of AIDS diagnoses reported among males aged 15--19 years has nearly doubled in the past 10 years, from 1.3 cases per 100,000 population in 1997 to 2.5 cases in 2006. Similarly, after decreasing for >20 years, gonorrhea infection rates among adolescents and young adults have leveled off or had modest fluctuations (e.g., rates among males aged 15--19 years ranged from 285.7 cases per 100,000 population in 2002 to 250.2 cases per 100,000 population in 2004 and then increased to 275.4 cases per 100,000 population in 2006), and rates for syphilis have been increasing (e.g., rates among females aged 15--19 years increased from 1.5 cases per 100,000 population in 2004 to 2.2 cases per 100,000 population in 2006) after a significant decrease during 1997--2005.
Background
Early, unprotected sex among young persons can have negative consequences. Pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS), result in high social, economic, and health costs for affected persons, their children, and society.
CDC operates multiple nationally representative surveys and surveillance systems that track patterns of sexual risk behavior and reproductive health outcomes in the U.S. population. In addition, CDC's National Vital Statistics System (NVSS) provides information from vital records in the United States. These surveys, surveillance, and vital records systems collect information that includes age at initiation of sexual intercourse, frequency of sexual intercourse, number of sexual partners, contraceptive use and use of prevention services, pregnancies, births, abortions, cases of HIV/AIDS and other STDs, and reports of sexual violence.
Each source of information reports data separately and in different formats, which can make interpreting the data difficult. This report combines available data from multiple sources for the first time into a single report concerning the sexual and reproductive health of persons in the United States aged 10--24 years. The report addresses three main questions:
- How many young persons currently engage in sexual risk behaviors and experience related health outcomes?
- What are the greatest disparities in terms of age, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographic location?
- How do recent data compare with previously reported data, i.e., what are the historical trends?
This report includes the most recent data that were available when the report was produced. The findings can be used to guide the work of policy makers, researchers, and program providers.
Methods
This report was developed by CDC's Workgroup on Adolescent Sexual and Reproductive Health (the Workgroup), a voluntary effort formed in 2004 with participation of staff from five CDC divisions that address the sexual and reproductive health concerns of young persons. The workgroup meets approximately every 2 weeks and collaborates on projects that are of relevance to each of the divisions. For example, the Workgroup conducted an inventory of the adolescent sexual and reproductive health activities supported by CDC, convened an external expert panel to provide guidance on ways to strengthen those activities, and jointly maintains a website. To develop this report, Workgroup members selected the adolescent sexual and reproductive health indicators to be included; indicators were selected from among those already available in existing reports and on the basis of the collective judgment of Workgroup members regarding which were most helpful to assessing the magnitude of the problem, identifying high-risk groups, and monitoring trends. Published surveillance, survey, and statistical reports were reviewed, and relevant data were extracted. When data were not available from existing reports, Workgroup members collaborated with epidemiologists and analysts from the various surveillance and data systems to obtain the needed data.
Every effort was made to present the data in a consistent manner with regard to age groups, race/ethnicity, sex, and geographic location. Age categories ranged from 10 to 24 years, spanning preadolescence through young adulthood. For consistency, the term "youths" is used in this report for the youngest age group (aged 10--14 years), "adolescents" is used for those aged 15--19 years, and "young adults" is used for those aged 20--24 years. With a few exceptions, data for 5-year age groups are reported. The age group of adolescents aged 15--17 years sometimes was included to reflect the fact that consequences of poor reproductive health are likely to be more severe in this group than among persons aged 18--19 years because early pregnancy and poor health are likely to interrupt their schooling and to have greater social and economic impact. In addition, because limited data are available on the sexual behavior of persons aged 10--14 years, this age group is not represented in all data tables.
Whenever possible, five racial/ethnic categories (non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, Hispanic, Asian/Pacific Islander [API], and American Indian/Alaska Native [AI/AN]) were included. Residence was mapped at the level of the state, territory, or region of the United States for selected outcomes. Trends over time are depicted by the most recent available data and the 10-year period preceding that year; however, certain trend lines cover a period of >10 years. In addition, data on cases of HIV/AIDS are presented by the mode of HIV transmission.
Data from the following surveys, surveillance systems, and vital records system were used: the HIV/AIDS Reporting System, the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System--All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP), the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), the National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG), NVSS, the Nationally Notifiable Disease Surveillance System (NNDSS), the national Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS), and the National Vital Statistics System. Two data sources are used to report sexual behavior. NSFG collects data on a more extensive range of behavior variables and is used to describe current levels of sexual behavior and racial/ethnic disparities. YRBS data have been collected more frequently than NSFG (i.e., every 2 years) and are used to indicate trends over time. A description of each system follows (see Appendix for technical notes).
Descriptions of Data Systems
HIV/AIDS Reporting System
All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. territories conduct AIDS surveillance using a standardized, confidential name-based reporting system. Because successful treatment delays the progression of HIV infection to AIDS, surveillance data regarding only AIDS are insufficient to monitor trends in HIV incidence or to meet federal, state, or local data needs for planning and allocating resources for HIV prevention and care programs. For this reason, since 1985, an increasing number of states and U.S. territories also have implemented HIV case reporting as part of their comprehensive HIV/AIDS surveillance programs.
This report presents estimated numbers of reported cases of AIDS and AIDS prevalence (i.e., the number of persons living with AIDS) from the 50 states and the District of Columbia at the end of 2006. It also summarizes the estimated numbers of reported cases of HIV/AIDS (i.e., cases of HIV infection, regardless of whether they have progressed to AIDS) and estimated HIV/AIDS prevalence (i.e., the number of persons living with HIV/AIDS) at the end of 2006 from 38 areas that have had confidential name-based HIV infection reporting long enough (i.e., since at least 2003) to allow for stabilization of data collection and for adjustment of the data to monitor trends. These 38 areas include 33 states (Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming) and five U.S. territories (American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands). The 33 states represent approximately 63% of the epidemic in the 50 states and the District of Columbia.
The numbers of cases presented in this report are not reported case counts but rather point estimates, which are the result of adjusting reported case counts for reporting delays and for redistribution of cases in persons initially reported without an identified risk factor. CDC routinely adjusts data for the presentation of trends in the epidemic. To assess trends in cases, deaths, or prevalence, CDC uses adjusted data, presented by year of diagnosis instead of year of report, to eliminate artifacts of reporting in the surveillance system. Additional information about the HIV/AIDS surveillance system has been published previously (1--3) and is available at http://www.cdc.gov/hiv.
National Electronic Injury Surveillance System--All Injury Program
NEISS-AIP is a collaborative effort by CDC's National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission that collects data regarding nonfatal injuries (including sexual assault) in the United States. NEISS-AIP data provide information about what types of nonfatal injuries are observed in U.S. hospital emergency departments, how commonly they occur, whom they affect, and what causes them.
NEISS-AIP data are collected annually and represent all types and external causes of nonfatal injuries and poisonings treated in U.S. hospital emergency departments (EDs). NEISS-AIP data are collected from a nationally representative subsample (e.g., 63 in 2004, 62 in 2005, and 63 in 2006) of the 100 NEISS hospitals. The NEISS hospitals are a stratified probability sample of all U.S. hospitals (including U.S. territories) that have at least six beds and provide 24-hour emergency services and include very large inner-city hospitals with trauma centers and large urban, suburban, rural, and children's hospitals. Data from this ongoing surveillance system can be used to calculate weighted national estimates of nonfatal injuries. NEISS-AIP data are accessible through the interactive Web-based Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System (WISQARS) (available at http://www.cdc.gov/ncipc/wisqars). For all analyses described in this report using NEISS-AIP data, SUDAAN was used to account for the stratified clustered and weighted nature of the data, and a t-statistic was computed. A p value of <0.05 was used to determine statistical significance.
NEISS-AIP defines sexual assault as the use of physical force to compel another person to engage in a sexual act unwillingly, regardless of whether the act was completed. Sexual assault might involve an attempted or completed sexual act involving a person who is unable to 1) understand the nature of the act, 2) decline participation, or 3) communicate unwillingness to participate for whatever reason. It also includes abusive sexual contact, including intentional touching, either directly or through the clothing, of the genitalia, anus, groin, breast, inner thigh, or buttocks of any person against his or her will or of a person who is unable to consent (e.g., because of age, illness, disability, or the influence of alcohol or other drugs) or to refuse (e.g., because of the use of guns or other nonbodily weapons or because of physical violence, threats of physical violence, real or perceived coercion, intimidation or pressure, or misuse of authority). This category includes rape, completed or attempted; sodomy, completed or attempted; and other sexual assaults with bodily force, completed or attempted.
NEISS-AIP data are used by a broad audience, including the general public, media, public health practitioners and researchers, and public health officials. Additional information about NEISS-AIP and WISQARS has been published previously (4).
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
CDC's National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) has conducted a series of health and nutrition examination surveys since the early 1960s. The major objectives of the current NHANES are to estimate the number and percentage of persons in the U.S. population and designated subpopulations with selected diseases and risk factors; monitor trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of selected diseases; monitor trends in risk behaviors and environmental exposures; analyze risk factors for selected diseases; study the relationship between diet, nutrition, and health; explore emerging public health issues and new technologies; establish a national probability sample of genetic material for future genetic research; and establish and maintain a national probability sample of baseline information on health and nutritional status.
During 1971--1994, NHANES was conducted on a periodic basis. In 1999, NHANES was redesigned to become a continuous survey without a break between cycles. The procedures used to select the sample and conduct the interviews and examinations are similar to those of previous NHANES surveys. NHANES is composed of a series of cross-sectional, nationally representative health and nutrition examination surveys of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population. Samples are selected through a complex, multistage probability design. Certain populations (e.g., adolescents, non-Hispanic black, and Mexican-Americans) are oversampled by design to obtain more precise estimates for risk factors and health outcomes that might be unique to these subpopulations. Approximately 6,000 randomly selected persons of all ages across the United States are eligible to participate in NHANES each year; of these, approximately 80% participate in the survey and are interviewed in their homes. Approximately 75% participated in the health examination component of the survey conducted in mobile examination centers. STD evaluations that have been performed using specimens obtained at such examinations include seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) (using sera, among males and females), prevalence of chlamydia and gonorrhea (using urine, among males and females), and prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA (using self-collected vaginal swabs, among females).
This report summarizes data on seroprevalence of HSV-2 and HPV DNA prevalence that have been published previously (5--7). Additional information about NHANES is available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs.nhanes.htm.
National Survey of Family Growth
NSFG was conducted periodically through 2002 to collect data on factors that influence family formation and reproductive health in the United States, including marriage, divorce, cohabitation, contraception, infertility, pregnancy outcomes, and births. Cycles 1--6 of the survey were conducted in 1973, 1976, 1982, 1988, 1995, and 2002. Since 2006 (Cycle 7), NSFG has been conducted as a continuous survey, with interviews conducted 48 weeks every year. The survey results are used by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other agencies to plan health services and health education programs and to perform statistical studies of families, fertility, and health. NSFG data for 2002 are based on a nationally representative multistage area probability sample drawn from 120 areas across the country. The estimates are weighted to represent national estimates. The weights account for the different sampling rates and for nonresponse and are adjusted to agree with control totals provided by the U.S. Census Bureau (8).
NSFG data are derived from interviews that are conducted in person in the selected person's home. Data are collected from a nationally representative sample of women (since 1982) and men (since 2002) aged 15--44 years. Data are collected by Computer-Assisted Person Interviewing. The questionnaires are programmed into laptop computers and administered by a female interviewer. Some of the more sensitive questions, such as whether first intercourse was voluntary, are collected in a self-administered format using Audio Computer-Assisted Self-Interview.
This report used NSFG data from 2002, including some that have been published previously and some that have been tabulated for this report, to describe current levels of sexual risk behavior among adolescents and young adults and to identify disparities in these behaviors among racial/ethnic subpopulations. Because NSFG does not collect data concerning youths aged 10--14 years, information about the prevalence of sexual risk behavior and racial/ethnic disparities within this age group is not included in this report. Although NSFG collects data on race and ethnicity for all racial/ethnic populations, data are not presented separately for APIs and AI/ANs because of limited sample sizes for these two subpopulations. Unless indicated otherwise, data provided are for both married and unmarried respondents.
Detailed findings from the 2002 NSFG have been published previously (9--13). Additional information about NSFG methodology also has been published previously (8) and is available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nsfg.htm.
National Vital Statistics System
NVSS is the oldest example in the United States of intergovernment data sharing in public health, and the shared relationships, standards, and procedures form the mechanism by which official vital statistics for the United States are collected and disseminated. These data are provided through contracts between NCHS and vital registration systems operated in the various jurisdictions legally responsible for the registration of vital events (i.e., births, deaths, marriages, divorces, and fetal deaths) (14). In the United States, legal authority for the registration of these events resides individually with the 50 states, the District of Columbia, New York City, and five U.S. territories (American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands). These jurisdictions are responsible for maintaining registries of vital events and for issuing copies of birth, marriage, divorce, and death certificates. Detailed information about the national vital statistics system has been published previously (15).
Birth data presented in this report are based on 100% of the birth certificates registered in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Tables displaying data by state also provide separate information for five U.S. territories (American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands). Race and Hispanic origin are reported separately on the birth certificate. In tabulations of birth data by race and ethnicity, data for Hispanics are not further classified by race because the majority of Hispanic women are self-identified as white. Tables that present data by race/ethnicity include for five categories: non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, Hispanic, AI/AN, and API. Data for AI/AN and API births are not presented separately by Hispanic origin because the majority of these populations are non-Hispanic. Although data regarding prenatal care and mother's tobacco use during pregnancy were collected on both the 1989 and the 2003 revisions of the U.S. Standard Certificates of Live Birth, these data are not considered comparable between revisions and are presented in this report only for states that used the 1989 revision. Information on births by age, race, or marital status of the mother is imputed if it is not reported on the birth certificate. Births for which a particular characteristic is unknown (e.g., birth order or birth weight) are subtracted from the figures for total births that are used as denominators before percentages and percentage distributions are computed. Additional information about birth data has been published previously (16,17) and is available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/births.htm.
Pregnancy estimates are sums of live births, and estimates of fetal losses and induced abortions, and pregnancy rates are calculated based on several sources. Statistics for live births are based on complete counts of births provided by every state to NCHS through the Vital Statistics Cooperative Program of NVSS. Estimates of fetal losses are derived from pregnancy history data collected by NSFG (8). NSFG data used for these estimates are derived from surveys conducted during 1995 and 2002. Fetal loss estimates for persons aged <20 years are based on NSFG Cycles 3--6, which were conducted in 1982, 1988, 1995, and 2002. Data from the four most recent NSFG cycles have been combined in this way to increase statistical reliability because of the limited number of pregnancies to persons aged <20 years in the NSFG samples. Fetal loss estimates for adults aged 20--24 years are based on the proportions of pregnancies (live births plus fetal losses) that ended in fetal loss during the previous 5 years from the 1995 NSFG and during the previous 8 years from the 2002 NSFG (18,19). These proportions are applied to the actual numbers of live births in each population subgroup (by age and race) for each year to yield estimates of fetal losses that are summed to a national total. Estimates for induced abortions are obtained as described below. Rates are presented as the number of pregnancies per 1,000 women. The population denominators used for rates in this report are consistent with the 2000 census (20). Additional information about pregnancy estimates has been published previously (18,19).
Abortion Surveillance
Estimates of induced abortions are derived from abortion surveillance data reported to CDC's National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (NCCDPHP) (21). NCCDPHP collects information on the characteristics of women who obtain abortions based on information reported by age by central health agencies, such as state health departments and the health departments for 46 states, New York City, and the District of Columbia (reporting areas for 2004). Data by age were not available for California, Florida, New Hampshire, and West Virginia. National totals are derived from periodic surveys of abortion providers by the Guttmacher Institute, a nonprofit organization focused on sexual and reproductive health research, policy analysis, and public education (22). The estimated number of abortions published by NCCDPHP tends to be lower than the number published by the Guttmacher Institute; much of the difference reflects the absence of data for California, Florida, New Hampshire, and West Virginia. Although the Guttmacher Institute's abortion-provider surveys supply a more complete estimate of the number of abortions occurring, CDC's data surveillance system is able to obtain important information on the characteristics of women who obtain abortions, including age, marital status, race/ethnicity, number of prior births and abortions, and gestational age at abortion. The Guttmacher Institute's national totals are distributed by characteristics including age, race, Hispanic origin, and marital status according to CDC's tabulations, adjusted for year-to-year changes in the states that report comparable data (18). Abortion rates (number of abortions per 1,000 women in a given age group) are provided in this report and are based on revised population estimates consistent with the 2000 census (20).
Nationally Notifiable Disease Surveillance System
Surveillance data regarding nationally notifiable STDs are collected and compiled from reports sent by the STD control programs and health departments in the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and selected territories to CDC's National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention. An annual surveillance summary is published, which is intended as a reference document for policy makers, program managers, health planners, researchers, and others who are concerned with the public health implications of these diseases (23,24). Nationally notifiable disease surveillance incorporates data concerning three STDs for which federally funded control programs exist: chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis (see Appendix B for case definitions). These systems are an integral part of program management at all levels of STD prevention and control in the United States. Because many cases go undetected or unreported, the number of STD cases reported to CDC is less than the actual number of cases occurring in the United States population. The extent to which the magnitude and implications of incomplete reporting varies by disease has been reported elsewhere (25). Additional information about STD surveillance data is available at http://www.cdc.gov/std.
National Youth Risk Behavior Survey
The national Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) was developed in 1990 to monitor priority health risk behaviors that contribute to the leading causes of death, disability, and social problems among youth and adults in the United States. These behaviors, often established during childhood and early adolescence, include tobacco use; unhealthy dietary behaviors; inadequate physical activity; alcohol and other drug use; sexual behaviors that contribute to unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV infection; and behaviors that contribute to unintentional injuries and violence.
The biennial national YRBS used independent, three-stage cluster samples for the 1991--2007 surveys to obtain cross-sectional data representative of public and private school students in 9th--12th grades in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Sample sizes ranged from 10,904 to 16,296. School response rates ranged from 70% to 81%, and student response rates ranged from 83% to 90%; overall response rates for the surveys ranged from 60% to 70%. For each cross-sectional survey, students completed anonymous, self-administered questionnaires that included identically worded questions on sexual risk behaviors and violence.
In this report, YRBS data are used to indicate trends in sexual risk behaviors over time. Temporal changes were analyzed using logistic regression analyses, which controlled for sex, race/ethnicity and grade and simultaneously assessed significant (p<0.05) linear and quadratic time effects.*
National YRBS data usually are reported by the respondent's grade in school, rather than by age. To facilitate comparison with other data in this report that are reported by the respondent's age, the demographic characteristics of 2007 national YRBS respondents have been summarized (Table 1).
Additional information about YRBS has been published previously (26--28) and is available at http://www.cdc.gov/yrbs.
Results
Current Levels of Sexual Risk Behavior and Health Outcomes
Sexual Behaviors
NSFG data for 2002 were used to present the percentage of adolescents and young adults who engaged in a range of sexual risk behaviors (Tables 2 and 3). Among female adolescents aged 15--17 years, 30.0% reported ever having had sex, compared with 70.6% of those aged 18--19 years (Table 2). Among adolescent males aged 15--17 years, 31.6% reported ever having had sex, compared with 64.7% of those aged 18--19 years (Table 3). Among females aged 18--24 years, 9.6% who had sex by age 20 years reported having had nonvoluntary first intercourse. Having ever been forced to have intercourse was reported by 14.3% of females aged 18--19 years and 19.1% of females aged 20--24 years (Table 2). Among teenagers aged 15--19 years, 13.1% of females and 14.8% of males reported having had sex at age <15 years (Tables 2 and 3). The majority (58.7%) of females aged 15--19 years reported that their first sex partners were 1--3 years older than they were, and 22.4% reported that their first partners were ≥4 years older than they were (Table 2). Approximately three in 10 female and male adolescents aged 15--19 years reported having had two or more sexual partners (Tables 2 and 3).
Among never-married adolescents aged 15--19 years who were sexually active, 75.2% of females and 82.3% of males reported using a method of contraception at first intercourse. Condom use at first intercourse was reported by 67.5% of females and 70.7% of males (Tables 2 and 3). Adolescents also were likely to have used contraception at their most recent intercourse (83.2% of never-married females and 90.7% of never-married males). Never-married females aged 20--24 years were somewhat more likely than adolescent females to have used contraception at last sex (87.3%) (Table 2); never-married males aged 20--24 years were somewhat less likely than adolescent males to have done so (84.8%) (Table 3).
A substantial majority of adolescents aged 15--19 years (85.5% of females and 82.6% of males) reported having received formal instruction before reaching age 18 years on how to say no to sex, and 69.9% of adolescent females and 66.2% of adolescent males reported receiving instruction on methods of birth control (Tables 2 and 3). Among adolescents aged 18--19 years, 49.8% of females and 35.1% of males had talked with a parent before reaching age 18 years about methods of birth control. Approximately three fourths of adolescents aged 15--17 years (74.6% of females and 71.5% of males) reported having talked to their parents about at least one of five sex education topics included in the survey (Tables 2 and 3).
Use of reproductive and medical services varied by age. For example, 37.6% of females aged 15--17 years and 80.5% of females aged 20--24 years had received at least one family planning or medical service during the preceding 12 months (Table 2). Among males aged 15--19 years, 72.3% received at least one health or family planning service during the preceding 12 months, but that percentage decreased to 51.9% among young adult males aged 20--24 years (Table 3).
Pregnancies among adolescents are very likely to be unintended (unwanted or mistimed) at conception. Among females aged 15--17 years, 88.0% of births during the preceding 5 years were the result of unintended pregnancies (Table 2).
Pregnancy, Births, Birth Characteristics, and Abortions
In 2004, an estimated 2.4 million pregnancies occurred among U.S. females aged <25 years, with 30% of those pregnancies occurring among adolescent females aged 15--19 years and <1% among females aged aged <15 years (Table 4). The total number of pregnancies reported for U.S. females aged <25 years for 2004 included 1.5 million live births, 613,000 induced abortions, and 341,000 fetal losses (e.g., stillbirths and miscarriages; data not presented in table) (18). Among adolescents aged 15--19 years, 57% of pregnancies ended in a live birth, 27% ended in induced abortion, and 16% were fetal losses (18).
In 2006, a total of 435,436 births occurred to adolescent mothers aged 15--19 years (Table 4), with almost one third occurring among adolescents aged 15--17 years (preliminary data indicate that this number increased to 445,045 in 2007) (29). Initiation of prenatal care in the first trimester typically increases with age. In 2006, according to data for 32 states, the District of Columbia, and New York City, less than half of pregnant youths aged 10--14 years initiated prenatal care in the first trimester (Table 4). This proportion increased to 64.9% for those aged 15--17 years and 72.3% of those 18--19 years. A total of 92% of births among females aged 15--17 years and 81% among those aged 18--19 years were to unmarried mothers (data not presented in table). Mothers aged <15 years were more likely than adolescent females aged 15--19 years or young women aged 20--24 years to receive late or no prenatal care, to have a preterm or very preterm infant, and to have a low or very low birthweight infant. Smoking during pregnancy also typically increases with age through age 18--19 years. In 2006, on the basis of data for 33 states, the District of Columbia, and New York City, adolescents aged 15--17 years were three times more likely to smoke during pregnancy as youths aged 10--14 years (10.3 compared with. 3.3%).
In 2004, an estimated 199,000 abortions were reported for female adolescents aged 15--19 years, with more than one third occurring among adolescents aged 15--17 years and nearly two thirds among those aged 18--19 years (Table 4). Among young women aged 20--24 years, the estimated number of abortions was approximately twice that for adolescents aged 15--19 years. The abortion rates in 2004 varied substantially by age, with the rate for women aged 20--24 years (39.9 per 1,000 population) double the rate for adolescents aged 15--19 years (19.8 per 1,000) (18).
HIV/AIDS
In 2006, a total of 2,194 persons (668 females and 1,526 males) in the United States aged 10--24 years received a diagnosis of AIDS, and a cumulative total of 9,530 persons (3,914 females and 5,616 males) were living with AIDS. The majority of persons aged 10--24 years who received an AIDS diagnosis in 2006 were young adults aged 20--24 years (71% of females and 80% of males), and 72% of total diagnoses were received by males (1,526 of 2,194 total diagnoses). However, among persons aged 10--14 years, the majority of AIDS diagnoses (61%) were received by females.
The number of young persons living with HIV/AIDS† in the 38 areas with stable (i.e., confidential name-based) HIV reporting also is presented (Tables 4 and 5). In 2006, a total of 5,396 young persons (1,540 females and 3,856 males) received a diagnosis of HIV/AIDS, and a cumulative total of 21,890 young persons were living with HIV/AIDS in these 38 areas (9,024 females and 12,866 males). As with AIDS diagnoses, the majority of HIV/AIDS diagnoses occurred among young adults aged 20--24 years (1,049 [68%] of 1,540 females and 2,922 [76%] of 3,856 males) and were male (3,856 [71%] of 5,396 total diagnoses). Among youths aged 10--14 years, more diagnoses were received by females than by males (44 [70%] and 19 [30%], respectively).
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Adolescents and young adults aged 15--24 years have high rates for the most common STDs. Persons in this age group have been estimated to acquire nearly half of all incident STDs although they represent only 25% of the sexually active population (25). Reasons for the increased rates include biologic susceptibility, risky sexual behavior, and limited access to health care (23).
Cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis diagnosed in the United States are reported to CDC via NNDSS. Of these three STDs, for which federally funded ccontrol programs exist, chlamydia is the most frequently reported among all age groups of young persons. In 2006, among youths aged 10--14 years, 12,364 cases of chlamydia were reported in females and 1,238 in males; among adolescents aged 15--17 years, 130,569 cases were reported in females and 23,665 in males; among adolescents aged 18--19 years, 162,823 cases were reported in females and 35,155 in males; and among young adults aged 20--24 years, 284,763 cases were reported in females and 93,035 in males (Tables 4 and 5). Chlamydia screening is not recommended for males, so the consistently higher reported rates of chlamydia among females probably reflects compliance with recommendations for chlamydia screening for all sexually active females aged <26 years (30) and thus underestimates the disease burden among males. Population-based NHANES data demonstrate that prevalence of chlamydia among adolescents aged 14--19 years is somewhat greater among females (4.6%; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 3.7--5.8) than among males (2.3% [CI = 1.5--3.5]) (4). However, the trend is the opposite among young adults aged 20--29 years, for whom chlamydia prevalence is greater among males (3.2%; CI = 2.4--4.3) than among females (1.9%; CI = 1.0--3.4) (4).
Gonorrhea was the second most commonly reported STD in 2006. Among youths aged 10--14 years, 3,574 cases were reported in females and 675 cases in males; among younger adolescents aged 15--17 years, 30,703 cases were reported in females and 11,242 in males; among older adolescents aged 18--19 years, 35,701 cases were reported in females and 18,877 in males; among young adults aged 20--24 years, 61,665 cases were reported in females and 49,304 in males (Tables 4 and 5).
Of the three STDs for which federally funded control programs exist, primary and secondary syphilis is the least frequently reported STD. In 2006, among youths aged 10--14 years, 11 cases were reported in females and two in males; among younger adolescents aged 15--17 years, 96 cases were reported in females and 94 in males; among older adolescents aged 18--19 years, 137 cases were reported in females and 238 in males; and among young adults aged 20--24 years, 299 cases were reported in females and 1,083 in males.
NHANES data for 2003--2004 indicate that the prevalence of HPV DNA was 24.5% (CI = 19.6--30.5) among females aged 14--19 years and 44.8% (CI = 36.3--55.3) among females aged 20--24 years (Table 4). The overall prevalence of HPV DNA among females aged 14--24 years was 33.8%, representing approximately 7.5 million females with HPV infection in the United States (7). NHANES data for 1999--2004 indicated that prevalence of HSV-2 among persons aged 14--19 years was 2.3% (CI = 1.7--3.2) among females and 0.9% (CI = 0.5--1.5) among males (Table 5) (7).
Sexual Violence
During 2004--2006, an estimated 105,187 females and 6,526 males aged 10--24 years received medical care in U.S. EDs as a result of nonfatal injuries sustained from a sexual assault (data not presented). The rate was significantly higher (t = 5.75; p <0.001) among females aged 10--24 years than among males (114.8 and 6.8 ED visits per 100,000 population, respectively). Among females, rates were 90.0 per 100,000 females aged 10--14 years, 152.6 per 100,000 females aged 15--17 years, 163.7 per 100,000 females aged 18--19 years, and 97.1 per 100,000 females aged 20--24 years (Table 4). Nonfatal injury rates sustained from sexual assaults were significantly higher among females aged 15--17 years (t = 2.0; p<0.05) and 18--19 years (t = 2.44; p<0.05) than among females aged 20--24 years. Other differences between age groups for females were not statistically significant. Among males aged 10--14 years, the rate for nonfatal sexual assault--related injury was 11.1 ED visits per 100,000 population (Table 5). Estimates for other age groups of males (ages 15--17, 18--19, and 20--24 years) are not reported because of the limited sample size.
Disparities in Race/Ethnicity, Mode of Transmission for HIV/AIDS, and Geographic Residence
Sexual Behavior
Sexual risk behavior varied among non-Hispanic black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic white females and males (Tables 6--9). Among female adolescents aged 15--19 years, 40.4% of Hispanic females reported ever having had sex, compared with 46.4% of non-Hispanic white females and 57.0% of non-Hispanic black females (Table 6). Having first sex at age <15 years was reported by 22.9% of non-Hispanic black adolescent females aged 15--19 years, compared with 11.6% of non-Hispanic white females in the same age group. This estimate does not meet the NSFG standard of reliability for Hispanic females (see Appendix). Among adolescent females aged 15--19 years, Hispanics were more likely (35.2%) than non-Hispanic whites (19.6%) and non-Hispanic blacks (19.0%) to report having had sex for the first time with a partner who was substantially older (≥4 years). Among adolescent females aged 15--19 years, 40.8% of Hispanics reported using no method of contraception at last intercourse, compared with 25.2% of non-Hispanic blacks and 10.3% of non-Hispanic whites.
The majority (56.5%) of non-Hispanic black females aged 15--19 years reported having used at least one family planning or medical service during the preceding 12 months, compared with 41.2% of Hispanic females and 49.4% of non-Hispanic white females (Table 6). Among adolescent males aged 15--19 years, 29.6% of non-Hispanic blacks reported having had four or more lifetime partners, compared with 25.4% of Hispanic males and 12.1% of non-Hispanic white males (Table 7). Reported use of condoms at first and most recent intercourse was higher among non-Hispanic black males aged 15--19 years (85.3% and 86.1%, respectively) than non-Hispanic white males (68.6% and 69.2%, respectively) and Hispanic males (66.5% and 59.9%, respectively) in the same age group. Non-Hispanic blacks males aged 15--19 years were also more likely to report always using condoms during the previous 4 weeks than their non-Hispanic white and Hispanic counterparts (86.8% compared with 68.0% and 53.1%, respectively) (Table 7).
Among adolescents and young adults who reported being sexually active, non-Hispanic black females aged 20--24 years were more likely to have ever been tested for HIV, STDs, or both (62.4%, compared with 47.9% of Hispanic females and 45.4% of non-Hispanic white females) (Table 8). Among males aged 20--24 years, use of condoms at most recent intercourse also was higher among non-Hispanic black males (62.3%) than non-Hispanic white males and Hispanic males (46.5% and 47.3%, respectively) (Table 9).
Data from multiple studies for selected measures of pregnancies, births, birth characteristics, induced abortions, cases of HIV/AIDS, STDs, and sexual violence among persons aged 10--24 years are reported (Tables 10--15).
Pregnancy, Births, Birth Characteristics, and Abortions
Pregnancy rates varied by race and ethnicity (Tables 10, 12, and 14). In 2004, the highest pregnancy rates for adolescents aged 15--19 years were reported among Hispanic and non-Hispanic black adolescents (132.8 and 128.0, respectively), compared with 45.2 among non-Hispanic white adolescents (Table 12). Among young women aged 20--24 years, rates per 1,000 population were 259.0 among non-Hispanic black women and 244.8 among Hispanic women, compared with 122.8 among non-Hispanic white women (Table 14).
Birth rates also varied by race and ethnicity. Among females aged 10--24 years, birth rates were lowest among APIs and non-Hispanic whites in every age group and highest among non-Hispanic blacks and Hispanics (Tables 10, 12 and 14). The majority of births to adolescent mothers are nonmarital; in 2006, the proportion of births among unmarried adolescents aged 15--19 years ranged from 77.3% among APIs to 96.9% among non-Hispanic blacks (Table 12).
The risk for having a low and very low birthweight baby was highest among mothers in the youngest age group (age 10--14 years) and decreased linearly with age (Tables 10, 12, and 14). Non-Hispanic black mothers aged 15--19 years were more likely to have a low or very low birthweight infant than mothers in all other racial and ethnic populations. Similarly, the proportion of preterm and very preterm births was higher among non-Hispanic black mothers than among other groups (Table 12).
HIV/AIDS
Rates for AIDS and HIV/AIDS diagnoses and for living with AIDS and HIV/AIDS have been tabulated by age group, sex, and race/ethnicity (Tables 10--15). In 2006, non-Hispanic blacks experienced the highest rates of AIDS and HIV/AIDS diagnoses and the highest rate for living with AIDS and HIV/AIDS across all age groups. Rates among non-Hispanic blacks were three to five times higher than those among Hispanics, the population that had the second highest rates. For example, 141.7 per 100,000 non-Hispanic black males aged 15--19 years were living with HIV/AIDS compared with 39.8 per 100,000 Hispanic males that same age. Further, 129.5 per 100,000 non-Hispanic black females aged 15--19 years were living with HIV/AIDS compared with 40.2 per 100,000 Hispanic females aged 15--19 years. AI/ANs and non-Hispanic whites experienced the next highest rates, whereas API experienced the lowest rates of HIV/AIDS. For example, among males aged 15--19 years, the rates were 6.7 per 100,000 population for non-Hispanic whites, 7.3 per 100,000 population for AI/AN, and 4.7 per 100,000 population among APIs.
The frequency of HIV/AIDS diagnoses in 2006 by age, transmission category, sex and race/ethnicity has been calculated (Tables 16 and 17). Among females of all ages and racial/ethnic populations, the primary transmission category was heterosexual contact, followed by injection-drug use (IDU). Among males of all age groups and racial/ethnic populations, the primary transmission category was men who have sex with men (MSM). For non-Hispanic black males and for Hispanic males, the second most important transmission category was heterosexual contact; for non-Hispanic white males, it was IDU.
The frequency of persons aged 10--24 years who were living with HIV/AIDS in 2006 has been calculated by transmission category, age group, and sex (Table 18). The primary transmission category for persons aged 10--17 years was perinatal (92.5% among males aged 10--14 years and 90.1% among females aged 10--14 years). Among persons aged 20--24 years, the primary transmission category was MSM for males (74.9%) and heterosexual sex for females (78.7%). The frequency of persons aged 10--24 years who were living with AIDS in 2006 also has been calculated by transmission category, age group, and sex (Table 19). The patterns were similar to those for persons living with HIV/AIDS (i.e., the primary transmission category for youths and adolescents was perinatal transmission). Among males aged 20--24 years, the primary transmission category was MSM; among females, it was heterosexual.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Substantial disparities in STD rates exist among racial and ethnic populations (Tables 10--15). In 2006, rates for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis were highest among non-Hispanic blacks for all age groups. Among adolescents aged 15--19 years, the highest rates of chlamydia occurred among non-Hispanic black females (8,858.1 cases per 100,000 population), compared with non-Hispanic black males (2,195.4 cases per 100,000 population) and non-Hispanic white females (1,374.9 cases per 100,000 population) (Tables 12 and 13). A similar pattern among adolescents aged 15--19 years was recorded for gonorrhea, with the highest rates occurring among non-Hispanic black females (2,829.6 cases per 100,000 population), compared with non-Hispanic black males (1,467.6 cases per 100,000 population) and non-Hispanic white females (208.3 cases per 100,000 population) (Tables 12 and 13). The pattern varied slightly for syphilis, with non-Hispanic black males aged 20--24 years experiencing the highest rates (41.0 cases per 100,000 population), compared with non-Hispanic black females (14.8 cases per 100,000 population) and non-Hispanic white males (3.7 cases per 100,000 population) of the same age (Tables 14 and 15).
AI/AN and Hispanic young persons also experienced high rates of sexually transmitted diseases. For example, among females aged 20--24 years, rates for chlamydia were 5,008.5 cases per 100,000 population among AI/AN females and 3,301.5 cases per 100,000 population among Hispanic females, and gonorrhea rates were 634.8 cases per 100,000 population among AI/AN females and 326.7 cases per 100,000 population among Hispanic females (Table 14). Among males aged 20--24 years, syphilis rates were 6.3 cases per 100,000 population among AI/AN males and 9.2 cases per 100,000 population among Hispanic males (Table 15). Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis rates also are provided for youths aged 10--14 years (Tables 10 and 11), but the rates are substantially lower compared with older age groups. In this age group, the highest rates occurred among non-Hispanic black females: 462.2 cases per 100,000 population for chlamydia, 168.6 cases per 100,000 population for gonorrhea, and 0.6 cases per 100,000 population for syphilis.
Sexual Violence
During 2004--2006, among adolescents and young adults aged 10--24 years, an estimated 45,485 non-Hispanic white females, 24,121 black females (i.e., inclusive of Hispanic black and non-Hispanic black), and 10,733 Hispanic females (i.e., excluding Hispanic black) were treated in EDs of U.S. hospitals as a result of nonfatal injuries sustained from a sexual assault (Tables 10, 12, and 14). Among males aged 10--24 years, an estimated 2,361 non-Hispanic white, 1,663 black (including black Hispanic and non-Hispanic black), and 907 Hispanic (i.e., excluding Hispanic black) male adolescents and young adults were treated in EDs as a result of nonfatal injuries sustained from sexual assaults. Because of the low numbers and the high frequency of missing data concerning race/ethnicity, all estimates for males by age and race/ethnicity are unstable and not reported. For both females and males, 21% of the sexual assault injury cases are missing data on race/ethnicity, so rates by race/ethnicity were not calculated, and caution should be used when interpreting counts by race/ethnicity.
Geographic Distribution of Births, HIV/AIDS, and STD Cases
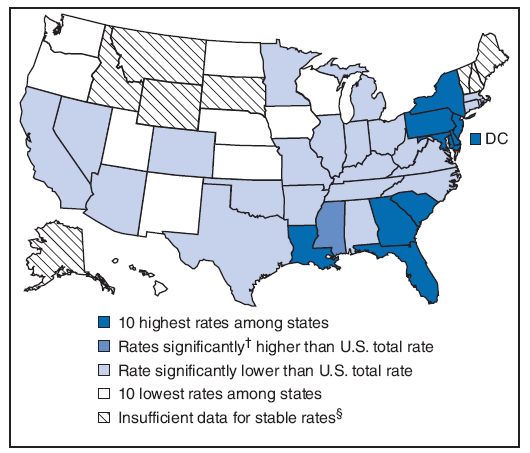
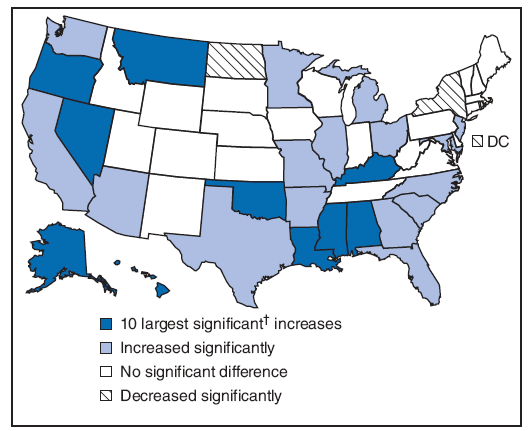
Birth rates for adolescents varied considerably by state (Table 20). Birth rates for adolescents were lower among states in the North and Northeast and higher among states in the South and Southwest. These geographic patterns largely reflect the composition (e.g., race/ethnicity and socioeconomic factors such as educational attainment) of each state's population (31). The number and rates of young persons living with HIV/AIDS in each of the 38 areas (i.e., 33 states and five U.S. territories) that had stable (i.e., confidential name-based) HIV reporting in 2006 has been calculated (Table 21), as has the number and rates of young persons living with AIDS in each of the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. territories in 2006 (Table 22). The highest rates of young persons living with AIDS were clustered in the eastern and southern regions of the United States (Figure 1). National rates have been calculated for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis (primary and secondary) by age group and region (Tables 23--25). Across all regions, overall rates for chlamydia and gonorrhea were higher among persons aged 18--19 years than among those aged 10--14, 15--17, and 20--24 years. Among persons aged 15--24 years, rates for syphilis increased with age group in all regions. Rates were higher for chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis in the South for all age groups, compared with other regions and with the U.S. total. However, variation in racial composition account for much of the difference by region (32).
Trends Over Time
Sexual Risk Behavior and Violence
YRBS data for 1991--2007 were used to describe trends in sexual risk behaviors and violence among high school students (9th--12th grades) (Table 26). During 1991--2007, the percentage of high school students who ever had sexual intercourse (i.e., sexual experience) decreased from 54.1% in 1991 to 47.8% in 2007. Logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear decrease during 1991-2007 among female students in 9th and 11th grade and among male students in 9th--12th grades. A significant quadratic trend also was detected among male students in 11th grade; the prevalence of sexual experience decreased during 1991--1997 and then leveled off during 1997--2007 (Table 26).
During 1991--2007, the percentage of high school students who had sexual intercourse for the first time before age13 years decreased from 10.2% in 1991 to 7.1% in 2007. Logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear decrease during 1991--2007 among female students in 9th grade, and among male students in 9th--12th grades. Statistically significant quadratic trends also were detected for high school students overall and for male students in 11th and 12th grades. Overall, the prevalence of having had sexual intercourse for the first time at age <13 years decreased during 1991--2005 and then leveled off during 2005--2007. Among male students in 11th grade, prevalence decreased during 1991--2001 and then increased during 2001--2007. Among male students in 12th grade, prevalence decreased during 1991--2001 and then leveled off during 2001--2007 (Table 26).
The percentage of high school students who had sexual intercourse with four or more persons during their life decreased from 18.7% in 1991 to 14.9% in 2007. Logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear decrease during 1991--2007 among female students in 9th--11th grade, and among male students in 9th--12th grades. Significant quadratic trends also were detected among male students in 11th--12th grade. Among both these groups, the prevalence of having had sexual intercourse with four or more persons decreased during 1991--1997 and then leveled off during 1997--2007 (Table 26).
The percentage of high school students who were currently sexually active (i.e., had sexual intercourse with at least one person during the 3 months before the survey) decreased from 37.5% in 1991 to 35.0% in 2007. Logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear decrease during 1991--2007 among female students in 9th grade. Significant quadratic trends were detected among male students in 9th and 11th grade. Among male students in 9th grade, prevalence was stable during 1991--1999 and then decreased during 1999--2007. Among male students in 11th grade, prevalence was stable during 1991--1997 and then increased during 1997--2007 (Table 26).
The percentage of currently sexually active high school students who reported that either they or their partner had used a condom during last sexual intercourse increased from 46.2% in 1991 to 61.5% in 2007. Logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear increase among female and male students in 9th--12th grades. Significant quadratic trends also were detected among high school students overall and female students in 10th grade; prevalence of condom use increased during 1991--2003 and then leveled off during 2003--2007.
During 1991--2007, the percentage of currently sexually active high school students who reported that either they or their partner had used birth control pills to prevent pregnancy before last sexual intercourse was stable overall and among female and male students in 9th--12th grades (Table 26).
During 1991-2007, the percentage of currently sexually active high school students who reported drinking alcohol or using drugs before last sexual intercourse was stable overall. Logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear increase among male and female students in 12th grade. Significant quadratic trends were detected among high school students overall and among male students in 9th and 10th grade. Overall, the prevalence of drinking alcohol or using drugs before the most recent sexual intercourse increased during 1991--2001 and then decreased during 2001--2007. Among male students in 9th and10th grade, the prevalence increased during 1991--1995 and then decreased during 1995--2007 (Table 26).
During 1999--2007, the prevalence of dating violence (i.e., having been hit, slapped, or physically hurt on purpose by their boyfriend or girlfriend during the 12 months before the survey) was stable overall and among male and female students in 9th--12th grades (Table 27).
During 2001--2007, the prevalence of ever having been physically forced to have sexual intercourse when they did not want to was stable overall and among female students in 9th--12th grades and male students in 9th, 11th and 12th grade. Among male students in 10th grade, logistic regression analyses also indicated a significant linear decrease during 2001--2007 and a significant quadratic trend; the prevalence was stable during 2001--2003 and then decreased during 2003--2007 (Table 27).
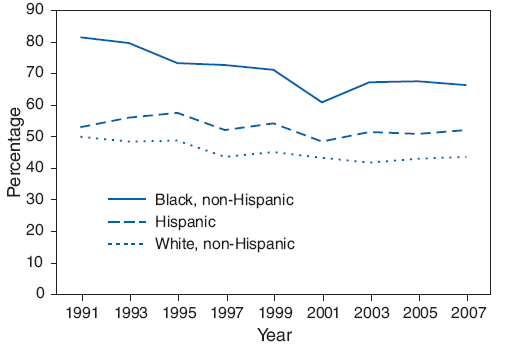
Trends in selected sexual risk behaviors were not consistent across racial/ethnic sub-groups (Table 28). During 1991--2007, logistic regression analyses indicated a significant linear decrease in the prevalence of sexual experience among non-Hispanic black (from 81.5% in 1991 to 66.5% in 2007) and non-Hispanic white students (from 50.0% in 1991 to 43.7% in 2007). Among Hispanic students, no significant change was detected. Among non-Hispanic black students, a significant quadratic trend also was detected; the prevalence of sexual experience decreased during 1991--2001 and then leveled off during 2001--2007 (Figure 2).
During 1991--2007, a significant linear decrease was detected in the prevalence of having had sexual intercourse with four or more persons during their life among non-Hispanic black (from 43.1% in 1991 to 27.6% in 2007) and non-Hispanic white students (from 14.7% in 1991 to 11.5% in 2007). Among Hispanic students, no significant change was detected.
During 1991--2007, a significant linear decrease in the prevalence of current sexual activity was detected among non-Hispanic black students (from 59.3% in 1991 to 46.0% in 2007). Among Hispanic and non-Hispanic white students, no significant change was detected.
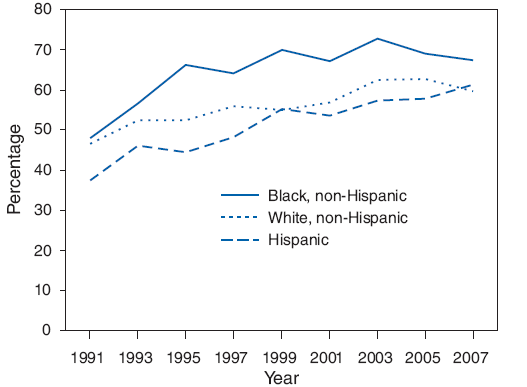
During 1991--2007, a significant linear increase in condom use was detected among currently sexually active non-Hispanic black (from 48.0% in 1991 to 67.3% in 2007), Hispanic (from 37.4% in 1991 to 61.4% in 2007), and non-Hispanic white (from 46.5% in 1991 to 59.7% in 2007) students (Figure 3). A significant quadratic trend also was detected among non-Hispanic black students; the prevalence of condom use increased during 1991--1999 and then leveled off during 1999--2007.
Pregnancy, Births, and Abortions
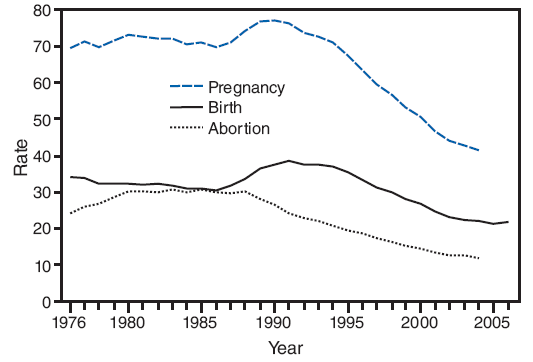
During 1990--2004, pregnancy rates for U.S. females aged 10--24 years declined among all age groups (Table 29). The rate for adolescents aged 15--17 years dropped 46%, from 77.1 per 1,000 population in 1990 to 41.5 in 2004, the most recent year for which national pregnancy rates are available. The rate for older adolescents aged 18--19 years decreased 31%, from a peak of 172.1 in 1991 to 118.6 in 2004. The 2004 rates for each of these age groups were lower than for any year during 1976--2004 for which a consistent series of estimates is available (19,20). During 1990--2004, pregnancy rates among women aged 20--24 years declined 18%, from 198.5 per 1,000 population in 1990 to 163.7 in 2004. Women aged 20--24 years continued to have the second highest pregnancy rates among all women of reproductive age (ages 10--49 years).
The declines in teenage pregnancy rates are reflected in reductions in both births and abortions (Figure 4; Tables 30 and 31). During 1991--2005, birth rates among females aged 15--19 years decreased 34% from a peak of 61.8 per 1,000 population in 1991 to 40.5 per 1,000 population in 2005. For adolescents aged 15--19 years and women aged 20--24 years, abortion rates have declined more steeply than birth rates. During 1990--2004, abortion rates for adolescents aged 15--19 years declined 51%, from 40.3 per 1,000 population in 1990 to 19.8 per 1,000 population in 2004. Among women aged 20--24 years, the rate declined 30% during the same period. Birth and abortion rates declined for non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, and Hispanic adolescents through 2004. During 1990--2004, both birth and abortion rates declined for non-Hispanic white adolescents (37% and 65%, respectively), for non-Hispanic black adolescents (46% and 43%, respectively), and for Hispanic adolescents (18% and 31%, respectively) (18,19).
Birth rates for persons aged 10--19 years declined during 1991--2005 (Table 30). The rate of decline during 1991--2005 was steeper for adolescents aged 10--14 years and for those aged 15--17 years than for adolescents aged 18--19 years. During 1991--2005, the annual decline in the rates for persons aged 15--17 years and 18--19 years averaged approximately 4% and 2%, respectively, but the decline has slowed in recent years. The long-term decline in birth rates for adolescents was interrupted in 2006, with a 3% overall increase compared with 2005. During 2005--2006, the birth rate for adolescents aged 15--17 years increased 3%, to 22.0 per 1,000 population; in 2007, the rate increased another 1% to 22.2 per 1,000 population (29). In 2006, the number of births to adolescents aged 15--17 years increased 4% to 138,943, approximately the same number as reported in 2002 (17). The birth rate for older adolescents aged 18--19 years (73.0 per 1,000 population) was 4% higher in 2006 than in 2005. The number of births to older adolescents (296,493) was 5% more in 2006 than in 2005 (16). The steepest declines in teenage birth rates during 1991--2005 were among non-Hispanic black adolescents (16). Overall, their rate declined 48% during this period, and for young black adolescents aged 15--17 years, the rate declined three fifths, from 86.1 per 1,000 population in 1991 to 34.9 per 1,000 population in 2005. However, the birth rate for non-Hispanic black adolescents increased 5% in 2006, the largest increase of any population group (17). Overall, the increase was broad-based geographically, with increases in birth rates in more than half of the states during 2005--2006 (Figure 5).
HIV/AIDS
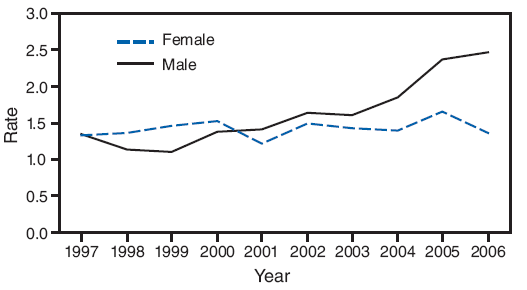
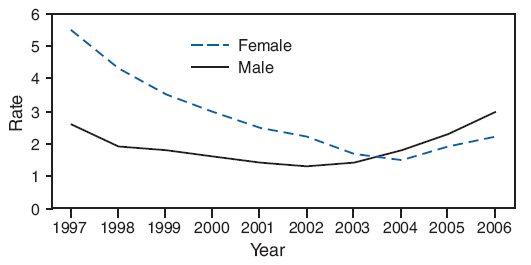
Trends for annual rates of AIDS diagnoses during 1997--2006 have been analyzed (Table 32). Among several groups (i.e., all youths aged 10--14 years, female adolescents aged 15--19 years, and women aged 20--24 years), rates either are relatively stable or decreased during this period. However, rates increased during the preceding 10 years among males aged 15--24 years. For example, during 1997--2006, the rate of AIDS diagnoses reported among males aged 15--19 years nearly doubled, from 1.3 cases per 100,000 population in 1997 to 2.5 cases per 100,000 population in 2006 (Figure 6).
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
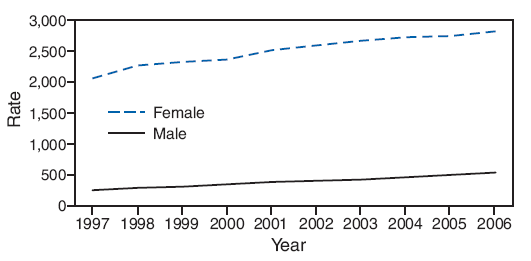
The number of cases of chlamydia that are reported have generally been increasing for all groups, with the exception of females aged 10--14 years since 2004 (Figure 7; Table 33). Greater implementation of chlamydia screening is believed to account for much of the increase, especially for cases among females. Furthermore, only since 2000 has chlamydia been reportable in all 50 states, contributing to earlier increases in national case rates (23).
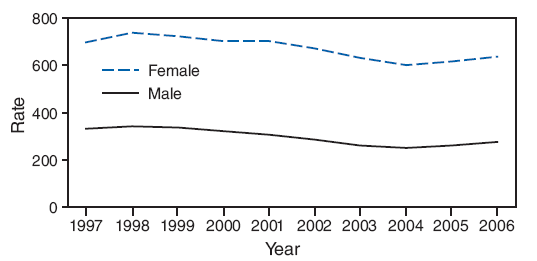
Gonorrhea rates decreased for >20 years until 1997; since 1997, rates have been stable, with some modest fluctuation among adolescents and young adults (Figure 8; Table 34). Gonorrhea infection rates among males aged 15--19 years ranged from 285.7 cases per 100,000 population in 2002 to 250.2 cases per 100,000 population in 2004 and then increased to 275.4 cases per 100,000 population in 2006. Rates of syphilis typically are lower among adolescents than among young adults aged 20--24 years. However, the rates for syphilis among adolescents and young adults have been increasing in recent years, (e.g., rates among females aged 15--19 years increased from 1.5 cases per 100,000 population in 2004 to 2.2 cases per 100,000 population in 2006), perhaps mirroring the national trend in syphilis rates that has been observed across the entire population (Figure 9; Table 35).
Sexual Violence
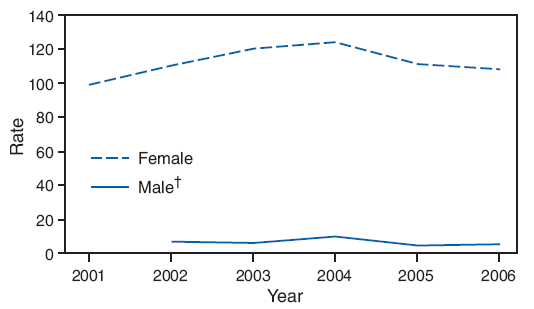
Rates of ED visits for nonfatal sexual assault related injuries for females aged 10--24 years were 99.2 per 100,000 population in 2001, 124.2 per 100,000 population in 2004, and 108 per 100,000 population in 2006 (Figure 8). A t-statistic indicated that the rates of sexual assault injuries for females aged 10--24 years did not differ significantly (t = 0.55; p = 0.58) during 2001--2006. Rates of nonfatal sexual assault injuries for females by smaller age categories have been calculated (Table 36). Analyses of rates of sexual assault injuries for females aged 10--14 years (t = 0.95; p = 0.34), 15--17 years (t = 0.07; p = 0.94), 15--19 years (t = 0.72; p = 0.47), and 20--24 years (t = 1.57; p= 0.12) during 2001--2006 indicated that rates have been relatively stable, and tests for trends were not statistically significant. In contrast, the rate for females aged 18--19 years increased significantly (t = 1.95; p<0.05) during 2001--2006 (from 103.9 per 100,000 population in 2001 to 169.9 per 100,000 population in 2006).
Among males aged 10--24 years, the rates for nonfatal sexual assault related injuries also have been relatively stable during 2001--2006 (6.7 per 100,000 population in 2002 and 5.3 per 100,000 population in 2006) (Figure 10). Consistent with females, the rates of nonfatal sexual assault injuries among males were not significantly different across the study period.
Conclusion
The data presented in this report indicate that the sexual and reproductive health of America's young persons remains an important public health concern: a substantial number of youths are affected, disparities exist, and earlier progress appears to be slowing and perhaps reversing. These patterns exist for a range of health outcomes (i.e., sexual risk behavior, pregnancy and births, STDs, HIV/AIDS, and sexual violence), highlighting the magnitude of the threat to young persons' sexual and reproductive health.
These findings underscore the importance of sustaining efforts to promote adolescent reproductive health. Effective screening, treatment, and referral services exist, and a growing number of evidence-based sexuality education, parent-child communication, and youth development programs are available to promote adolescent sexual and reproductive health. A key challenge is to ensure that these services are delivered so all youths can benefit. Continued support also is needed to monitor trends in sexual risk behavior and to promote research on new ways to help young persons achieve reproductive health.
The data presented in this report are subject to several limitations. First, self-reported data are subject to social desirability and response bias. Second, cases of disease often remain undetected and are unreported. Third, estimating pregnancy rates is challenging because of the difficulty in measuring the number of abortions and fetal losses. Finally, the data summarized in this report describe risk behaviors and negative reproductive health outcomes among young persons, but the data do not explain the causes of sexual risk behavior nor what interventions are most effective. Research is needed that identifies both the key determinants of sexual risk behavior and those interventions that are effective in reducing risk behavior.
Despite these limitations, understanding temporal trends and which subpopulations are at greatest risk is a critical first step that guides other public health action. Practitioners can use the information provided in this report when making decisions about how to allocate resources and identify those subpopulations that are in greatest need. Researchers can use the information provided in this report to guide future study on youths at highest risk to better understand the causes of sexual risk behavior and ways to reduce it. Finally, policy makers can use the information provided in this report to justify expanded funding of effective programs, new research on innovative intervention strategies, and continued monitoring of sexual risk behavior and reproductive health outcomes.
Acknowledgments
The following members of the Workgroup on Adolescent Sex and Reproductive Health Surveillance Review Subgroup participated in the preparation of this report: Janet Collins, PhD, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; Kathleen Ethier, PhD, Coordinating Center for Environmental Health and Injury Prevention; Lisa Romero, DrPH, Jenny Sewell, MPA, Division of Adolescent and School Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; Stephanie Bernard, PhD, Jennifer Galbraith, PhD, Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention, Lorrie Gavin, PhD, Division of Reproductive Health, Patricia Dittus, PhD, Nicole Liddon, PhD, Division of STD Prevention, National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention; Sara Harrier, MSW, Division of Violence Prevention National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, CDC; Kathryn Brown, MPH, Corinne David-Ferdon, PhD, Coordinating Center for Environmental Health and Injury Prevention. Additional assistance was provided by Kevin Fenton, MD, PhD, National Center for HIV/AIDS; John Lehnherr, Mary Brantley, MPH, Carla White, MPH, Catherine Lesesne, PhD, Taleria R. Fuller, PhD, Kelly Lewis, PhD, Trisha Mueller, MPH, Ndidi Nwangwu, MPH, Division of Reproductive Health; Howell Wechsler, EdD, Steve Kinchen, David Chyen, MS, Division of Adolescent and School Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion; Joyce C. Abma, PhD, Anjani Chandra, PhD, Brittany McGill, MPP, Michelle J. Osterman, MHS, National Center for Health Statistics; John Douglas, MD, Sharon Clanton, Matthew Hogben, PhD, Robert Nelson, Division of STD Prevention; Richard Wolitski, PhD, Rongping Zhang, MS, Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention, National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, CDC; Sharon G. Smith, PhD, Division of Violence Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
References
- CDC. Guidelines for national human immunodeficiency virus case surveillance, including monitoring for human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. MMWR 1999;48(No. RR-13).
- Glynn MK, Lee LM, McKenna MT. The status of national HIV case surveillance, United States 2006. Public Health Reps 2007;122(Suppl 1):63--71.
- CDC. HIV/AIDS surveillance report 2006, Vol. 18. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2008. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/surveillance/resources/reports.
- CDC. Web-based Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System (WISQARS). Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2003. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/ncipc/wisqars.
- Datta SD, Sternberg M, Johnson RE, et al. Gonorrhea and chlamydia in the United States among persons 14 to 39 years, 1999 to 2002. Ann Intern Med 2007;147:89--96.
- Dunne EF, Unger ER, Sternbreg M, et al. Prevalence of HPV infection among females in the United States. JAMA 2007;297:813--9.
- Xu F, Sternberg MR, Kottiri BJ, et al. Trends in herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 seroprevalence in the United States. JAMA 2006;296:964--73.
- Lepowski JM, Mosher WD, Davis KE, et al. National Survey of Family Growth, cycle 6: sample design, weighting, imputation, and variance estimation. Vital Health Stat 2006;2(142).
- Chandra A, Martinez GM, Mosher WD, Abma JC, Jones J. Fertility, family planning, and reproductive health of U.S. women: data from the 2002 National Survey of Family Growth. Vital Health Stat 2005;23(25).
- Martinez GM, Chandra A, Abma JC, Jones J, Mosher WD. Fertility, contraception, and fatherhood: data on men and women from Cycle 6 (2002) of the National Survey of Family Growth. Vital Health Stat 2006;23(26).
- Abma JC, Martinez GM, Mosher WD, Dawson, BS. Teenagers in the United States: sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing, 2002. Vital Health Stat 2004;23(24).
- Anderson JE, Chandra A, Mosher WD. HIV testing in the United States, 2002 [Advance data]. Vital Health Stat 2005;363.
- Mosher WD, Chandra A, Jones J. Sexual behavior and selected health measures: men and women 15--44 years, United States, 2002 [Advance data]. Vital Health Stat 2005;362.
- CDC. Technical appendix from vital statistics of the United States, 2004 natality. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2006. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/TechApp04.pdf.
- CDC. National vital statistic reports. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2009. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/nvsr.htm.
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Sutton PD, et al. Births: final data for 2005. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2007;56:(9).
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Sutton PD, et al. Births: final data for 2006. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2009;57(7).
- Ventura SJ, Abma JC, Mosher WD, Henshaw SK. Estimated pregnancy rates by outcome for the United States, 1990--2004. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2008:56(15).
- Ventura SJ, Mosher WD, Curtin SC, Abma JC, Henshaw S. Trends in pregnancies and pregnancy rates by outcome: estimates for the United States, 1976--96. Vital Health Stat 2000;21(56).
- CDC. U.S. census populations with bridged race categories. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2009. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/about/major/dvs/popbridge/popbridge.htm.
- CDC. Abortion Surveillance---United States, 2005. In: Surveillance Summaries, November 28, 2008. MMWR 2008;57(No. SS-13).
- Henshaw SK and Kost K, Trends in the characteristics of women obtaining abortions, 1974 to 2004. New York, NY: The Guttmacher Institute; 2008.
- CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2006. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2007.
- CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2007. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2008. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/std/stats07/surv2007final.pdf.
- Weinstock H, Berman S, Cates W. Sexually transmitted diseases among American youth: incidence and prevalence estimates, 2000. Perspect Sex Reprod Health 2004;36:6--10.
- CDC. Methodology of the Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System. MMWR 2004;53(No. RR-12).
- CDC. Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance---United States, 2007. MMWR 2008;57(No. SS-4).
- CDC. Trends in HIV- and STD-related risk behaviors among high school students---United States, 1991--2007. MMWR 2008;57:817--22.
- Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Ventura SJ. Births: Preliminary data for 2007. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2009. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr57/nvsr57_12.pdf.
- CDC. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2006. MMWR 2006;55(No. RR-11).
- Bauman, K.J. and Graf, N.L. Educational attainment: 2000. Census 2000 Brief C2KBR-24. Washington, DC: U.S. Census Bureau. 2003.
- Farley TA. Sexually transmitted diseases in the Southeastern United States: location, race, and social context. Sex Transm Dis 2006;33(Suppl 7):S58--64.