Volume
8: No. 1, January 2011
Suggested citation for this article: Boles M,
Dent C, Dilley J, Maher JE, Boysun MJ, Reid T.
Regression model fitting with quadratic term leads to different conclusion
in economic analysis of Washington State smoking ban [response to letter]. Prev Chronic Dis 2011;8(1):A27.
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2011/jan/10_0222.htm. Accessed [date].
To the Editor:
We were interested to read Ma and McClintock’s letter (1) about our analysis
of taxable retail sales (TRS) data (2). Although we agree in general that
different models of data can lead to different conclusions, we disagree that our analysis misrepresents those data. Rather, we find the
reanalysis and presentation in their letter to be misleading.
Ma and McClintock reiterate our observation that the TRS data during this time
do not follow a linear trend — with an obvious upturn in 2006 through
2007 and a smaller downturn in 2002 through 2003 — and question our use of a
linear model to describe these data. In our analyses, we examined a segmented
regression approach (3) to address this nonlinearity, using a theoretical break
point at 2006 to delineate periods before and after passage of a smoke-free law
(SFL) in Washington. Ma and McClintock put forth a linear model with a quadratic
term to address the nonlinearity in these data, with no theoretical
justification for the mechanism that would drive such a function. The use of a
quadratic term suggests an exponential growth in TRS post-SFL, whereas we
suggest a theory-based, more moderate, and flexible linear growth function due
to the SFL. Although the figure presented by Ma and McClintock correctly
represents their model, it misrepresents our model as a single straight-line fit
when it actually has 2 linear segments (Figure).
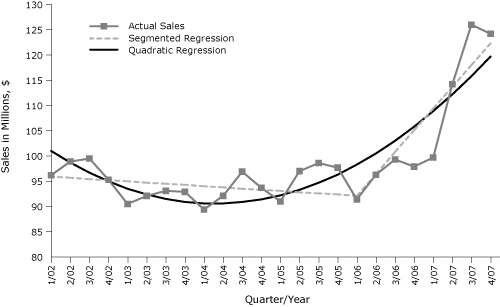
Figure. Segmented and quadratic regressions fit to
taxable retail sales in bars and taverns in Washington State after the
implementation of a smoke-free law, from the first quarter of 2002 (1/02)
through the fourth quarter of 2007 (4/07). Values are adjusted for inflation
to the Consumer Price Index (www.bls.gov/cpi/). [A tabular version of this figure is also available.]
In addition, Ma and McClintock’s contention that their model fits the data
better, supported by an improved R2 value, is incorrect. In
fact, the competing models, adjusted only for inflation — one with a quadratic term to specify the post-SFL
period and the other with a linear segmented term to model that period — have
nearly the same R2 value; our segmented model has a slightly
higher value, suggesting a better fit (0.888 vs
0.875, respectively).
Ma and McClintock state that their results suggest that “the smoking ban did
not affect the taxable sales revenue over the time.” This statement is
inaccurate in the context of the model they present. Rather, the quadratic term
in their model and the post-SFL segment term in our model both provide evidence
that TRS increased dramatically post-SFL.
Furthermore, Ma and McClintock present a table that is flawed. That table
contains projected TRS post-SFL “with and without a quadratic term.” The authors
contend that the difference between projected and actual sales using a model
with a quadratic term is large and opposite in sign to our estimated differences
without that term. The principal error in this table is that although the
“without quadratic term” column (our model projections) correctly reported the
forecasted trend by using the model fit to the pre-SFL values (the first segment
coefficient), the “with quadratic term” column actually uses the post-SFL
predicted values as the base, as if the quadratic term applied to that interval,
not to the values forecasted using a model fit to the data pre-SFL. In fact, it
is because the quadratic term overpredicts “exponential growth” post-SFL that
the residual values they present show the pattern they do. The comparison in
that table, and the conclusions reached by Ma and McClintock, are incorrect.
We also note for clarity that the raw data table presented by Ma and
McClintock do not agree completely with those we provided to them, possibly
because they used a different inflation adjustment than the one we provided to
them.
Given Ma and McClintock’s misunderstandings and misrepresentations of our
analysis, we stand firmly by our initial analysis and conclusions. As the
authors state, we provided raw TRS data. In addition, we communicated with them about
methods as an aid to their conducting a similar analysis
with data from their state. Their letter to the journal is the first indication
we received that they had concerns about our methods.
Myde Boles, PhD
Multnomah County Health Department and Oregon Public Health Division
Portland, Oregon
Clyde Dent, PhD
Multnomah County Health Department
Portland, Oregon
Julia Dilley, PhD, MES
Multnomah County Health Department and Oregon Public Health Division
Portland, Oregon
Julie E. Maher, PhD
Multnomah County Health Department and Oregon Public Health Division
Portland, Oregon
Michael J. Boysun, MPH
Washington State Department of Health
Portland, Oregon
Terry Reid, MSW
Washington State Department of Health
Portland, Oregon
Back to top
References
- Ma M, McClintock S. Regression model fitting with quadratic term
leads to different conclusion in economic analysis of Washington State
smoking ban [letter]. Prev Chronic Dis 2011;8(1).
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2011/jan/10_0213.htm.
- Boles M, Dilley J, Maher JE, Boysun MJ, Reid T. Smoke-free law
associated with higher-than-expected taxable retail sales for bars and
taverns in Washington State. Prev Chronic Dis 2010;7(4).
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2010/jul/09_0187.htm.
Accessed October 4, 2010.
- McGee VE, Carleton WT. Piecewise regression. J Am Stat Assoc
1970;65(331):1109-24.
Back to top
