Health Information & Privacy: FERPA and HIPAA | CDC
Download FERPA vs. HIPAA[PDF - 2 MB]
Health information is regulated by different federal and state laws, depending on the source of the information and the entity entrusted with the information. The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) are two examples of federal laws that regulate privacy and the exchange of specific types of information. The work of healthcare providers, school personnel, and others interacts with FERPA and HIPAA frequently, which is why it is important to understand these laws and know when they apply.
- Learn more about the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
- Learn more about the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA)

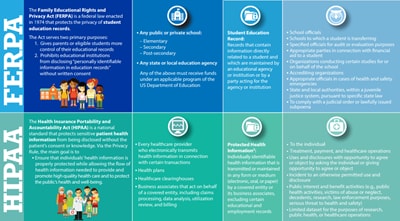
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a federal law enacted in 1974 that protects the privacy of student education records.
The Act serves two primary purposes:
- Gives parents or eligible students more control of their educational records
- Prohibits educational institutions from disclosing “personally identifiable information in education records” without written consent

Who must comply?

- Any public or private school:
- Elementary
- Secondary
- Post-secondary
- Any state or local education agency
Any of the above must receive funds under an applicable program of the US Department of Education
Protected Information

Student Education Record: Records that contain information directly related to a student and which are maintained by an educational agency or institution or by a party acting for the agency or institution
Permitted Disclosures 1

- School officials
- Schools to which a student is transferring
- Specified officials for audit or evaluation purposes
- Appropriate parties in connection with financial aid to a student
- Organizations conducting certain studies for or on behalf of the school
- Accrediting organizations
- Appropriate officials in cases of health and safety emergencies
- State and local authorities, within a juvenile justice system, pursuant to specific state law
- To comply with a judicial order or lawfully issued subpoena

The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a national standard that protects sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. Via the Privacy Rule, the main goal is to
- Ensure that individuals’ health information is properly protected while allowing the flow of health information needed to provide and promote high quality health care and to protect the public’s health and well-being.

Who must comply?

- Every healthcare provider who electronically transmits health information in connection with certain transactions
- Health plans
- Healthcare clearinghouses
- Business associates that act on behalf of a covered entity, including claims processing, data analysis, utilization review, and billing
Protected Information

Protected Health Information2: Individually identifiable health information that is transmitted or maintained in any form or medium (electronic, oral, or paper) by a covered entity or its business associates, excluding certain educational and employment records
Permitted Disclosures 1

- To the individual
- Treatment, payment, and healthcare operations
- Uses and disclosures with opportunity to agree or object by asking the individual or giving opportunity to agree or object
- Incident to an otherwise permitted use and disclosure
- Public interest and benefit activities (e.g., public health activities, victims of abuse or neglect, decedents, research, law enforcement purposes, serious threat to health and safety)
- Limited dataset for the purposes of research, public health, or healthcare operations
- Permitted disclosure means the information can be, but is not required to be, shared without individual authorization.
- Protected health information or individually identifiable health information includes demographic information collected from an individual and 1) is created or received by a healthcare provider, health plan, employer, or healthcare clearinghouse and 2) relates to the past, present, or future physical or mental health or condition of an individual; the provision of healthcare to an individual; or the past, present, or future payment for the provision of healthcare to an individual; and
(i) That identifies the individual, or
(ii) With respect to which there is a reasonable basis to believe the information can be used to identify the individual.
Laws and Guidance: Frequently Asked Questions. US Department of Education.
Health Information Privacy. US Department of Health and Human Services.
HIPAA Enforcement. US Department of Health and Human Services.