Surveillance and Strategic Information
Download the complete slide set:
While the content is in the public domain and no copyright restriction applies, we do ask that users preserve the slides in their current format and cite CDC as the source.

Slide 1
Program Collaboration and Service Integration Surveillance and Strategic Information
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 2
Overview
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 3
NCHHSTP Mission
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 4
About NCHHSTP
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 5
Burden of disease
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon
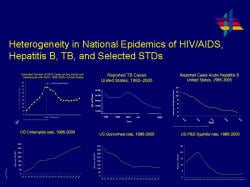
Slide 6
Heterogeneity in National Epidemics of HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B, TB,
and Selected STDs
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon
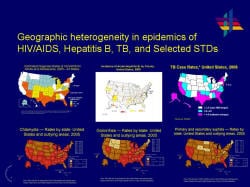
Slide 7
Geographic heterogeneity in epidemics of HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B, TB, and Selected STDs
Incidence of these diseases tends to be highest in Southern states.
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 8
HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis, STD and TB Common determinants
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 9
NCHHSTP Programs – Common Purposes and Strategies
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 10
CDC Goals and Strategic Imperatives
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 11
Program Collaboration and Service Integration (PCSI)
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 12
Program Collaboration and Service Integration (PCSI)
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 13
Levels of Integration of clinical preventive services in health care settings
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 14
NCHHSTP Consultation on PCSI, August 20-22 Overall meeting objectives
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon
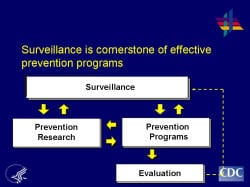
Slide 15
Surveillance is cornerstone of effective prevention programs
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 16
Surveillance / Strategic Information Gaps
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 17
NCHHSTP Consultation on PCSI, August 20 Surveillance Meeting Objectives
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 18
Key Questions
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon

Slide 19
Summary
PDF Filepdf icon or PPT Fileppt icon


