The Costly Burden of Drug-Resistant TB Disease in the U.S.
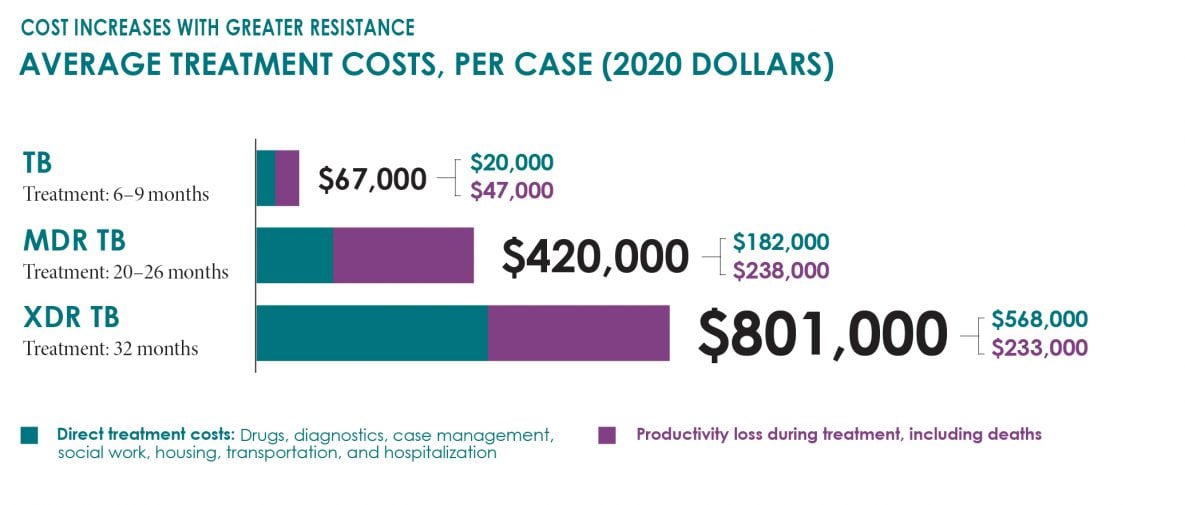
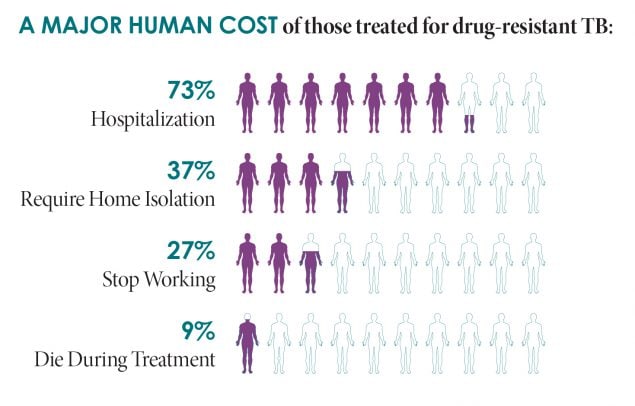
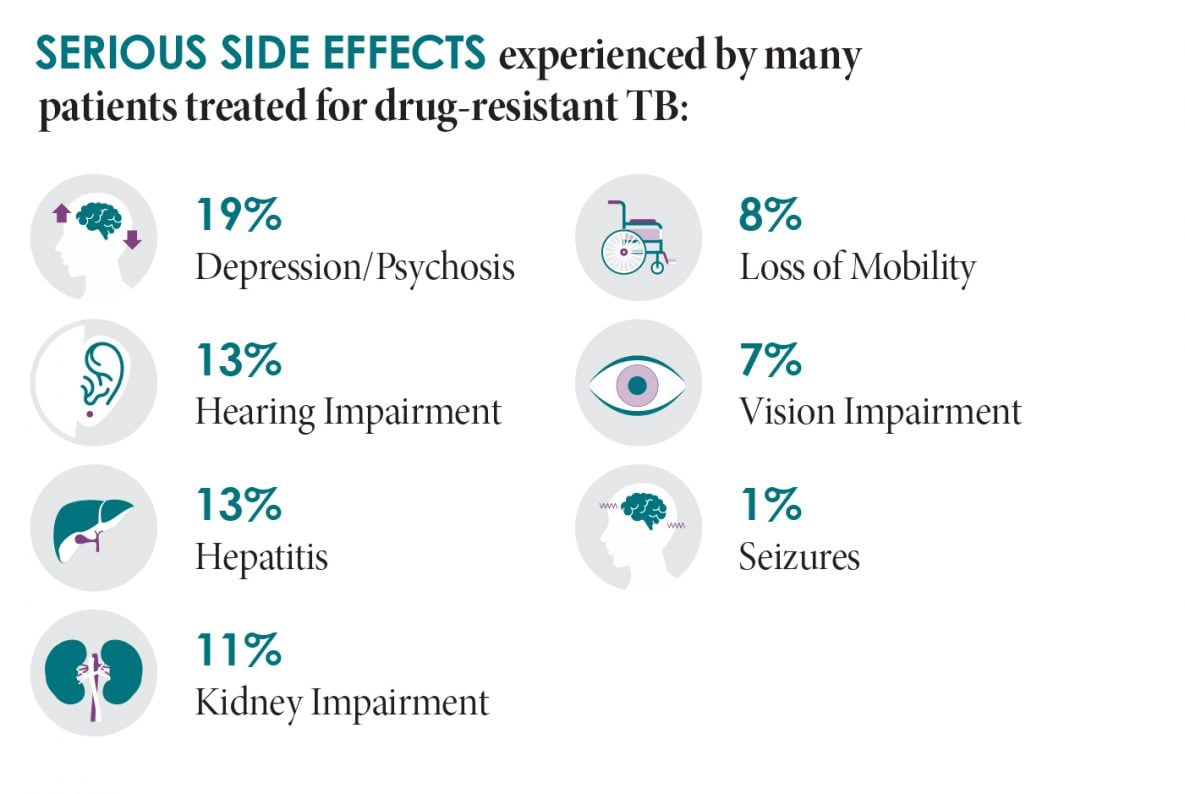
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) tuberculosis disease is a major health threat globally. Nearly half a million MDR TB1 cases are estimated to occur worldwide annually, including cases that are extensively drug-resistant (XDR).2 While MDR and XDR TB are relatively rare (fewer than 100 cases per year) in the United States, their treatment comes at a terrible price — it is very expensive, takes a long time to complete, disrupts lives, and has potentially life-threatening side effects. However, the number of drug-resistant cases in the United States remains stable due to effective control strategies.

1. Multidrug-resistant TB is resistant to at least two of the best and most important anti-TB drugs (isoniazid and rifampin).
2. Extensively drug-resistant TB is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin among first-line drugs, resistant to any fluoroquinolone and at least one second-line injectable drug.
Sources: Marks S et al. Treatment Practices, Outcomes, and Costs of Multidrug-resistant and Extensively Drug-resistant Tuberculosis in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20(5); Aslam et al. Number and Cost of Hospitalizations with Principal and Secondary Diagnoses of Tuberculosis, United States. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2018;22(12). Additional estimates for TB productivity losses due to premature deaths (see appendix); additional estimates for TB and XDR TB productivity losses due to premature deaths. Updated to 2020 dollars for medical costs using the Bureau of Economic Analysis Personal Consumption Expenditures separate indices for hospital and outpatient healthcare services and for productivity losses using the Bureau of Labor Statistics Private Sector Average Hourly Earnings of Production and Nonsupervisory Employees.
If you are a member of the news media and need more information, please visit www.cdc.gov/nchhstp/newsroom or contact CDC’s Media Office at 404-639-3286 or media@cdc.gov.