About National HIV Behavioral Surveillance (NHBS)
In 2003, CDC created NHBS to conduct bio-behavioral surveillance among persons at high risk for HIV infection.
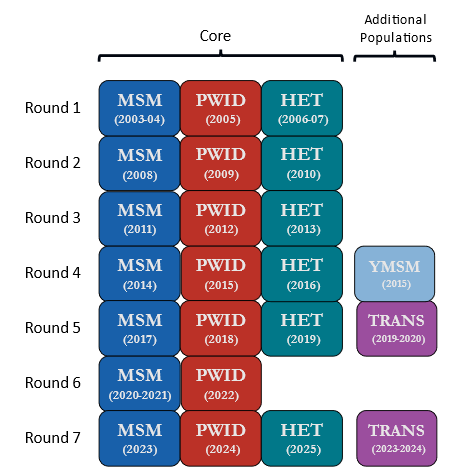
Surveillance is conducted in rotating, annual cycles in three different populations at increased risk for HIV:
- Gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men; known as the MSM cycle
- Persons who inject drugs; known as the PWID cycle
- Heterosexually active persons at increased risk for HIV infection; known as the HET cycle
These three annual cycles are considered a round. In addition to the core cycles, a limited number of project areas conducted surveys in other key populations.
Before each NHBS cycle, formative assessment is conducted to learn more about each local population and to inform operational procedures. Venue-based, time-space sampling (VBS) is used during the MSM cycles. Project area staff identify venues frequented by MSM (e.g., bars, clubs, organizations, and street locations) as well as days/times when men frequent those venues. Venues (and specific day/time periods) for recruitment are chosen randomly each month. Respondent-driven sampling (RDS) is used during the PWID and HET cycles. Project area staff select a small number of initial participants, or “seeds,” who complete the survey and recruit their peers to participate. Recruitment and interviewing then continue until the target sample size is reached.
Trained interviewers in all NHBS project areas use a standardized, anonymous questionnaire to collect information on HIV-related risk behaviors, HIV testing, and the use of HIV prevention services. HIV testing is offered to all participants regardless of their self-reported HIV status. During each cycle, a minimum of 500 eligible persons from each participating project area are interviewed and offered HIV testing.
NHBS data are used to provide a behavioral context for trends seen in HIV surveillance data. They also describe populations at increased risk for HIV infection and thus provide an indication of the leading edge of the epidemic. Through systematic surveillance in groups at high risk for HIV infection, NHBS is critical for monitoring the impact of the National HIV/AIDS Strategy, which focuses on decreasing HIV incidence, improving linkage to care, and reducing disparities.