Diagnoses of HIV Infection in the United States and Dependent Areas 2020: National Profile

Data presented in this report are based on case data reported to CDC through December 31, 2021, and allows for a 12-month reporting delay and assessment of diagnosis, death, and prevalence for the year 2020. The statements in this section, unless otherwise indicated, are based on 12 or more cases. All rates are per 100,000 population.
When presenting rates by race/ethnicity, data are only provided for the United States (50 states and the District of Columbia) because denominator data are not available by race/ethnicity for all U.S. dependencies.
Please use caution when interpreting data for AGI persons, transgender men, American Indian/Alaska Native and Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander persons as many percentages and/or rates were based on small numbers.
For disparity measures, reference groups are based on the rate of the lowest group with more than five percent of cases.
Deaths of persons with diagnosed HIV infection may be due to any cause (i.e., may or may not be related to HIV infection). Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021.
Important note. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
Please read all titles and footnotes carefully to ensure a complete understanding of the displayed data. See Technical Notes for information on definitions and data specifications.
In 2020, in the United States and 6 dependent areas, there were 30,692 diagnoses of HIV infection (persons aged ≥13 years: 30,635) (Tables 1b, 3b). The overall HIV diagnosis rate was 9.2 (persons aged ≥13 years: 10.9) (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Rates of diagnoses of HIV infection among persons aged ≥13 years, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
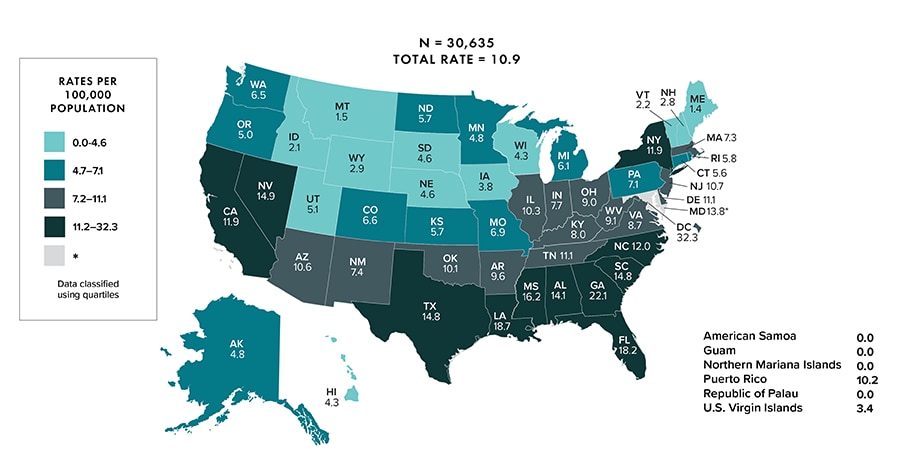
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting.
HIV diagnosis percentages and/or rates among persons aged ≥ 13 years were as follows:
- Gender (Figure 2):
- Male: 80%
- Female: 18%
- Transgender woman/girl: 2%
- Transgender man/boy: < 1%
- AGI: < 1%
Figure 2. Percentages of diagnoses of HIV infection among persons aged ≥13 years, by gender, 2020 (COVID-19 Pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
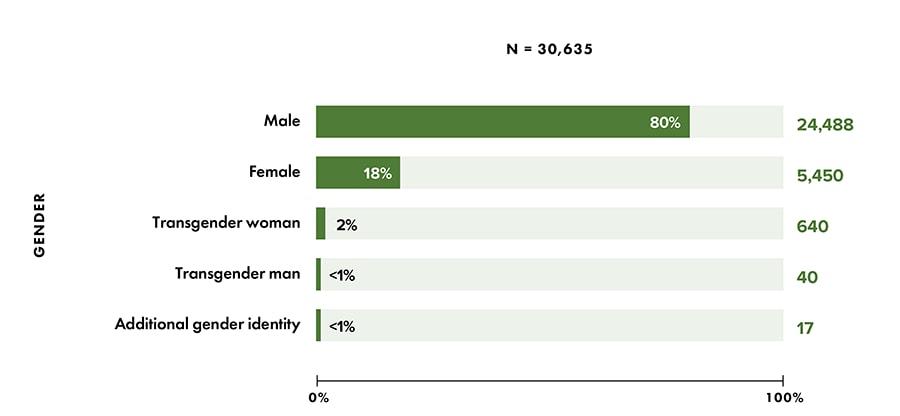
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
- Age group (Figure 3):
- 13–24 years: 20%
- 25–34 years: 37%
- 35–44 years: 20%
- 45–54 years: 13%
- ≥55 years: 10%
For additional data by 5-year age groups, see Table 3b.
Figure 3. Percentages of diagnoses of HIV infection among persons aged ≥ 13 years, by age at diagnosis, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
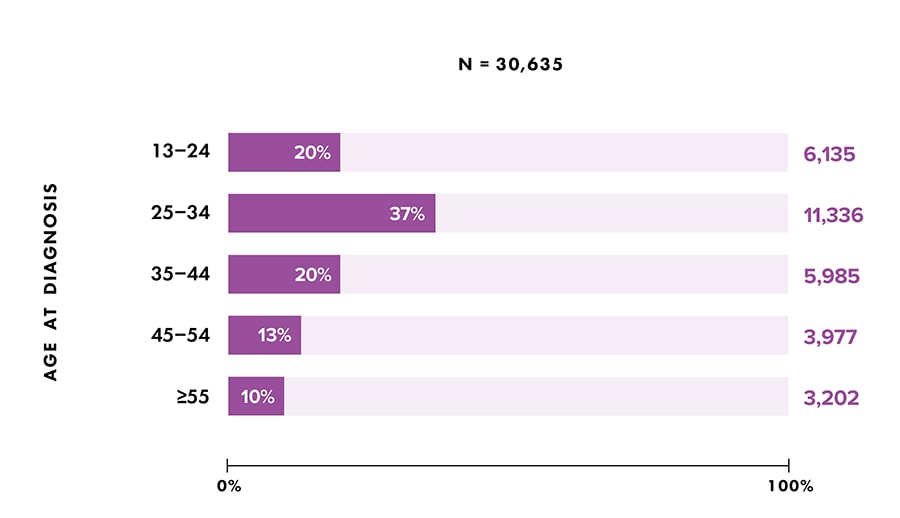
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
- Rates (U.S. only) (Figure 4):
- Highest: persons aged 25–34 years (24.4)
- Lowest: persons aged ≥ 55 years (3.2)
For additional data by 5-year age groups, see Table 3a.
-
- Disparities by age group:
- Absolute disparity (rate difference)—If persons aged 25–34 years had the same rate as persons aged ≥ 55 years, 21 cases per 100,000 population would have been prevented.
- Relative disparity (rate ratio)—Persons aged 25–34 years had a rate that was 7.6 times as high as persons aged ≥ 55 years.
- Disparities by age group:
- Rates (U.S. only) (Figure 4):
- Highest: Black/African American (37.4)
- Lowest: Asian (3.8)
- Disparities by race/ethnicity:
- Absolute disparity (rate difference)—If Black/African American persons aged ≥ 13 years had the same rate as White persons aged ≥ 13 years (4.6), 33 cases per 100,000 population would have been prevented.
- Relative disparity (rate ratio)—Black/African American persons aged ≥ 13 years had a rate that was 8.1 times as high as White persons aged ≥ 13 years.
- Disparities by race/ethnicity:
- Rates (U.S. only) (Figure 4):
- Highest: South (14.7)
- Lowest: Midwest (7.2)
- Disparities by region:
- Absolute disparities (rate difference): if the South had the same rate as the Midwest, 8 cases per 100,000 population would have been prevented.
- Relative disparities (rate ratio): the South had a rate that was 2.0 times as high as the Midwest.
- Disparities by region:
Figure 4. Rates and disparities of diagnoses of HIV infection among persons aged ≥ 13 years, by selected characteristics, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States
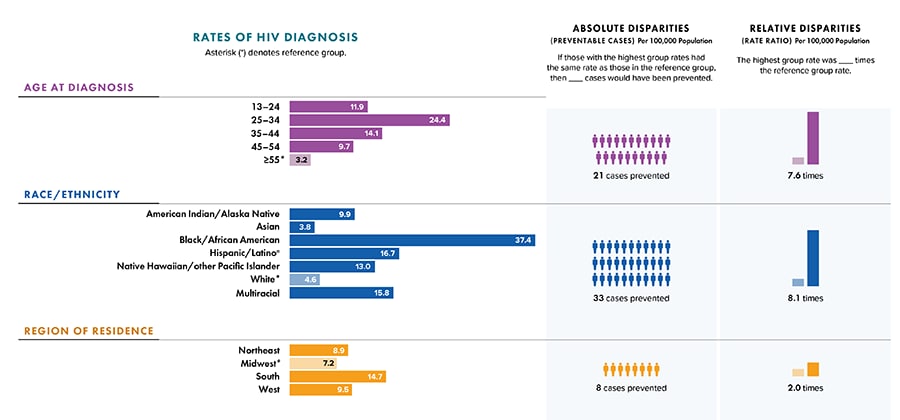
Note: Rates are per 100,000 population. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Absolute disparity measures the difference between rates in groups with the highest rates and a reference group (Ratehighest group − Ratereference group). Relative disparity (rate ratio) measures the rates in groups with the highest rates divided by a reference group (Ratehighest group ÷ Ratereference group).
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
- Race/ethnicity (Figure 5):
- American Indian/Alaska Native: 1%
- Asian: 2%
- Black/African American: 42%
- Hispanic/Latino: 27%
- Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander: < 1%
- White: 26%
- Multiracial: 3%
Figure 5. Percentages of diagnoses of HIV infection among persons aged ≥ 13 years, by race/ethnicity, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
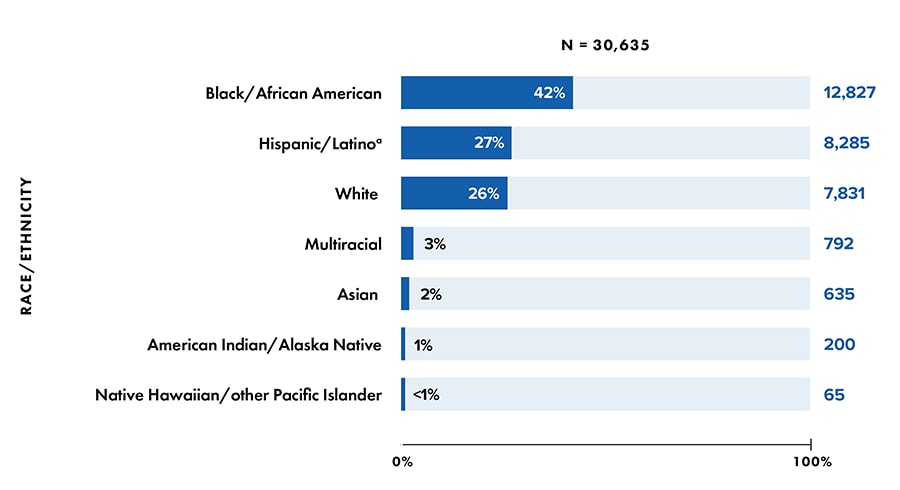
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
- Sex assigned at birth and transmission category—highest percentages (Figure 6, Table 1b):
- Overall: infections attributed to male-to-male sexual contact (MMSC) (68%)
- Among male sex at birth: MMSC (83%)
- Among female sex at birth: heterosexual contact (83%)
Figure 6. Percentages of diagnoses of HIV infection among persons aged ≥ 13 years, by sex assigned at birth and transmission category, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United Sates and 6 dependent areas
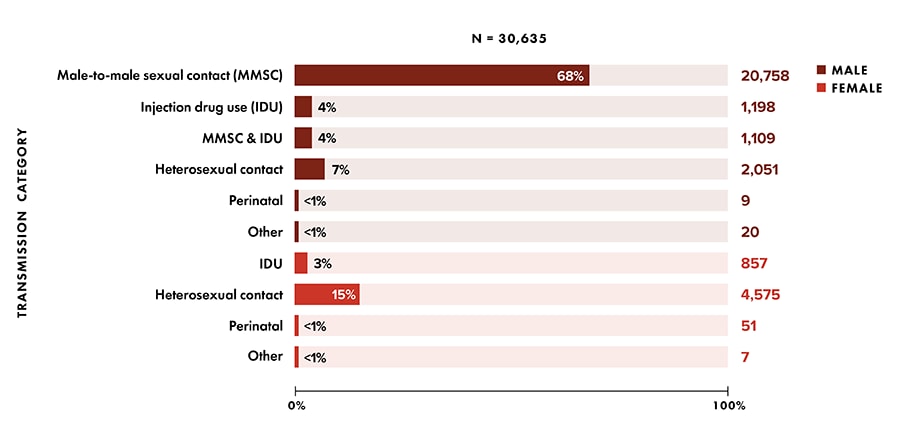
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. See section D4 in Technical Notes for more information on transmission categories.
- Gender and exposure category—highest percentages (Table 4b):
- Among transgender women: sexual contact (90%)
- Among transgender men: sexual contact (73%)
- Among AGI: sexual contact (82%)
- Region of residence, all persons (Table 1b):
- Northeast: 14%
- Midwest: 13%
- South: 51%
- West: 21%
- U.S. dependent areas: 1%
In 2020, in the United States and 6 dependent areas, there were 18,493 deaths among persons with diagnosed HIV infection (persons aged ≥13 years: 18,489) (Tables 12b). The overall rate of deaths was 5.6 (persons aged ≥13 years: 6.6) (Figure 7).
Figure 7. Rates of deaths of persons aged ≥13 years with diagnosed HIV infection, 2020—United States and 6 dependent areas
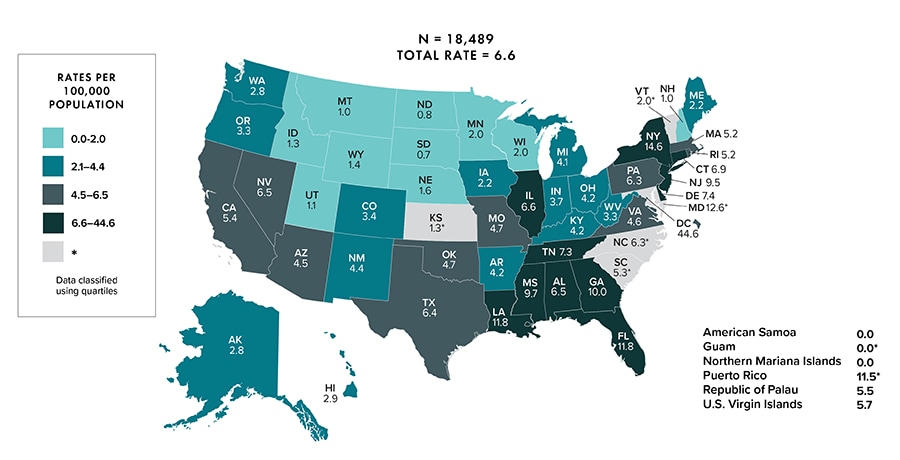
Note: Deaths of persons with a diagnosis of HIV infection may be due to any cause. Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
Deaths of persons aged ≥ 13 years with a diagnosis of HIV infection percentages and/or rates were as follows:
- Gender, all persons (Table 11b):
- Male: 74%
- Female: 24%
- Transgender woman/girl: 1%
- Transgender man/boy: <1%
- AGI: 0%
- Age group (Figure 8):
- 13–24 years: 1%
- 25–34 years: 6%
- 35–44 years: 11%
- 45–54 years: 20%
- ≥ 55 years: 62%%
For additional data by 5-year age groups, see Table 11b.
- Race/ethnicity (Figure 8):
- American Indian/Alaska Native: <1%
- Asian: 1%
- Black/African American: 43%
- Hispanic/Latino: 19%
- Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander: <1%
- White: 30%
- Multiracial: 7%
Figure 8. Percentages of deaths among persons aged ≥13 years with diagnosed HIV infection, by selected characteristics, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
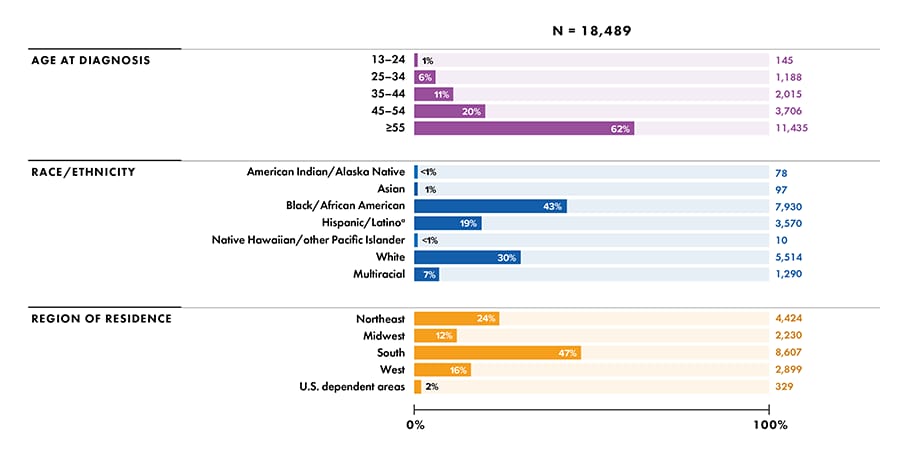
Note: Deaths of persons with a diagnosis of HIV infection may be due to any cause. Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Includes Asian/Pacific Islander legacy cases.
b Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
- Rates (U.S. only) (Figure 9):
- Highest: persons aged ≥55 years (11.5)
- Lowest: persons aged 13–24 years (0.3)
For additional rates by age group, see Table 11a.
-
- Disparities by age group:
- Absolute disparity (rate difference)—If persons aged ≥55 years had the same rate as persons aged 25–34 years, 9 cases per 100,000 population would have been prevented.
- Relative disparity (rate ratio)—Persons aged ≥55 years had a rate that was 4.4 times as high as persons aged 25–34 years.
- Disparities by age group:
- Rates (U.S. only) (Figure 9):
- Highest: Multiracial (25.7)
- Lowest: Asian (0.6)
- Disparities by race/ethnicity:
- Absolute disparity (rate difference)—If multiracial persons aged ≥13 years had the same rate as White persons aged ≥13 years (3.2), 23 cases per 100,000 population would have been prevented.
- Relative disparity (rate ratio)—Multiracial persons aged ≥13 years had a rate that was 8.0 times as high as White persons aged ≥13 years.
- Disparities by race/ethnicity:
- Rates (U.S. only) (Figure 9):
- Highest: Northeast (9.3)
- Lowest: Midwest (3.9)
- Disparities by region:
- Absolute disparities (rate difference): if the Northeast had the same rate as the Midwest, 5 cases per 100,000 population would have been prevented.
- Relative disparities (rate ratio): the Northeast had a rate that was 2.4 times as high as the Midwest.
- Disparities by region:
Figure 9. Rates and disparities of deaths of persons aged ≥ 13 years with diagnosed HIV infection, by selected characteristics, 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States
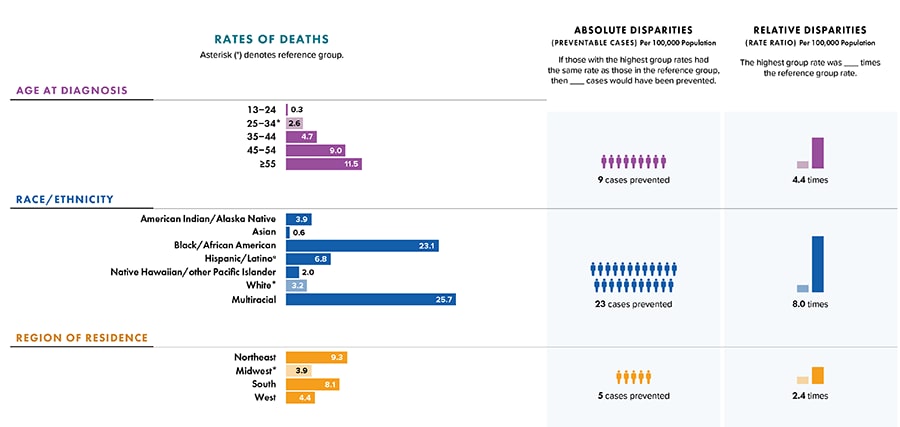
Note: Deaths of persons with a diagnosis of HIV infection may be due to any cause. Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Absolute disparity measures the difference between rates in groups with the highest rates and a reference group (Ratehighest group − Ratereference group). Relative disparity (rate ratio) measures the rates in groups with the highest rates divided by a reference group (Ratehighest group ÷ Ratereference group).
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
- Sex assigned at birth and transmission category—highest percentages (Table 11b):
- Overall: infections attributed to MMSC (43%)
- Among male sex at birth: MMSC (56%)
- Among female sex at birth: heterosexual contact (66%)
- Gender and exposure category—highest percentages (Table 14b):
- Among transgender women: sexual contact (68%)
- Among transgender men: sexual contact (67%)
- Among AGI: no deaths
- Region of residence, all persons (Table 11b):
- Northeast: 24%
- Midwest: 12%
- South: 47%
- West: 16%
- U.S. dependent areas: 2%
At year-end 2020 in the United States and 6 dependent areas, 1,072,051 persons were living with diagnosed HIV infection (persons aged ≥13 years: 1,070,604) (Table 15b, 17b). The overall rate of persons living with diagnosed HIV infection was 321.9 (persons aged ≥13 years: 381.4) (Figure 10).
Figure 10. Rates of persons aged ≥ 13 years living with diagnosed HIV infection, year-end 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
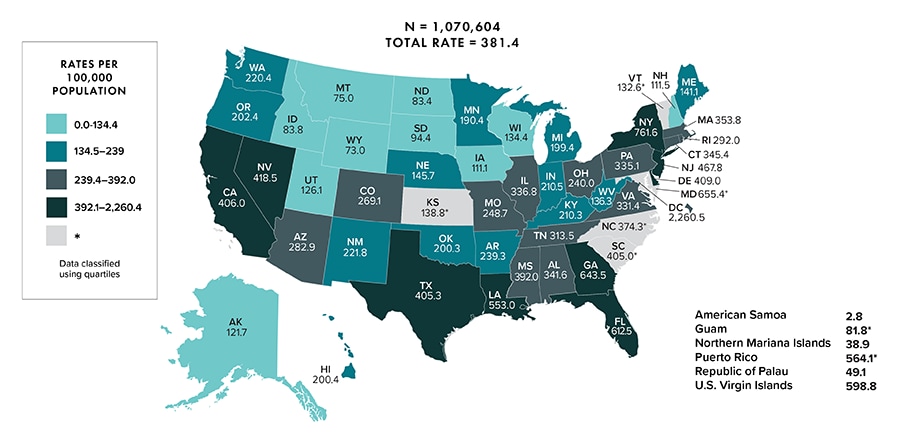
Note: Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Data are based on address of residence as of December 31, 2020 (i.e., most recent known address). Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting.
Persons living with diagnosed HIV infection percentages and/or rates were as follows:
- Gender (Table 15b):
- Male: 76%
- Female: 23%
- Transgender woman/girl: 1%
- Transgender man/boy: <1%
- AGI: <1%
- Age group (Table 15b):
- 13–24 years: 3%
- 25–34 years: 15%
- 35–44 years: 19%
- 45–54 years: 24%
- ≥55 years: 39%
For additional data by 5-year age groups, see Table 15b.
- Race/ethnicity (Figure 11):
- American Indian/Alaska Native: <1%
- Asian: 2%
- Black/African American: 40%
- Hispanic/Latino: 24%
- Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander: <1%
- White: 29%
- Multiracial: 5%
- Sex assigned at birth and race/ethnicity, persons aged ≥13 years (Figure 11):
- Highest among male sex at birth: Black/African American (35%)
- Highest among female sex at birth: Black/African American (57%)
Figure 11. Percentages of persons aged ≥13 years living with diagnosed HIV infection, by sex assigned at birth and race/ethnicity, year-end 2020 (COVID-19 pandemic)—United States and 6 dependent areas
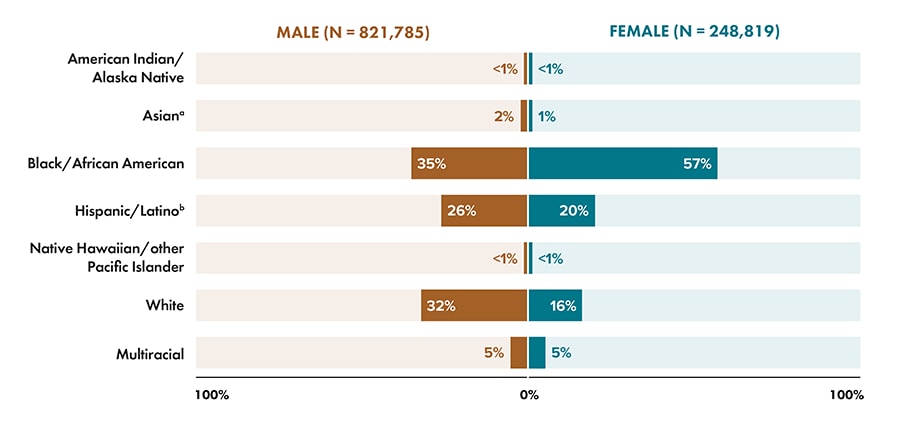
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
aIncludes Asian/Pacific Islander legacy cases.
bHispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
- Rates (U.S. only) (Table 15a):
- American Indian/Alaska Native: 133.5
- Asian: 83.6
- Black/African American: 1,038.0
- Hispanic/Latino: 401.4
- Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander: 152.6
- White: 155.5
- Multiracial: 693.7
- Sex assigned at birth and transmission category, persons aged ≥13 years—highest percentages (Table 17b):
- Overall: infections attributed to MMSC (56%)
- Among male sex at birth: MMSC (74%)
- Among female sex at birth: heterosexual contact (77%)
- Gender and exposure category, persons aged ≥13 years—highest percentages (Table 18b):
- Among transgender women: sexual contact (85%)
- Among transgender men: sexual contact (75%)
- Among AGI: sexual contact (87%)
- Region of residence (Table 15b):
- Northeast: 22%
- Midwest: 12%
- South: 45%
- West: 20%
- U.S. dependent areas: 2%
- Rates (U.S. only) (Table 15b):
- Highest: Northeast (421.4)
- Lowest: Midwest (185.8)