Diagnoses of HIV Infection in the United States and Dependent Areas 2020: Figures

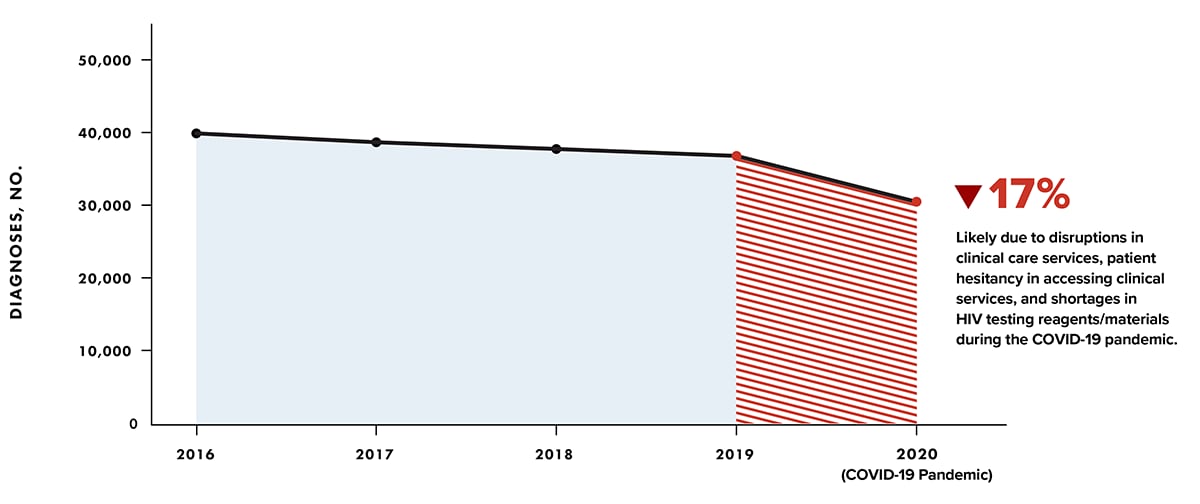
Note: Diagnoses of HIV infection reported to CDC through December 2021. The annual number of HIV diagnoses in 2020 was 17% lower than 2019. The decline in 2020 was larger than the average yearly decline (2%–3%) observed during 2016–2019.
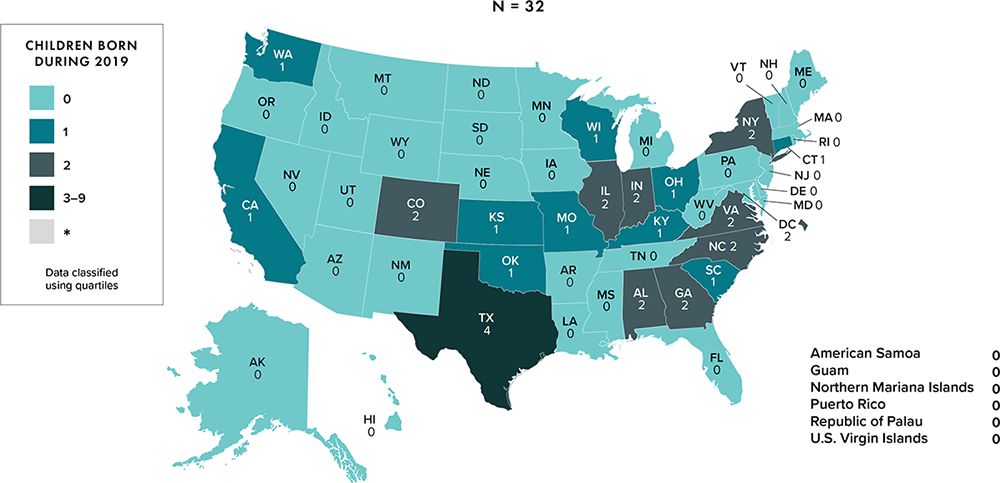
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting.
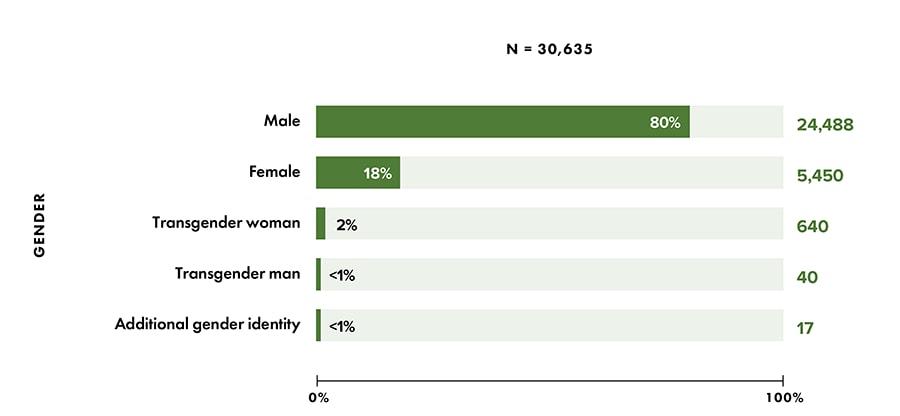
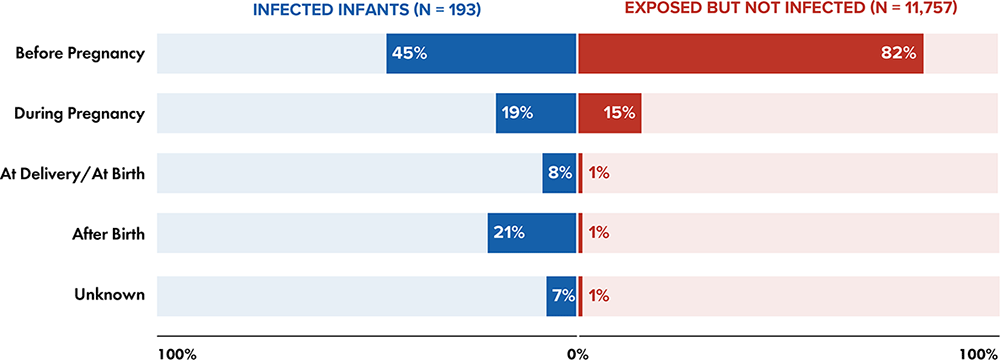
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
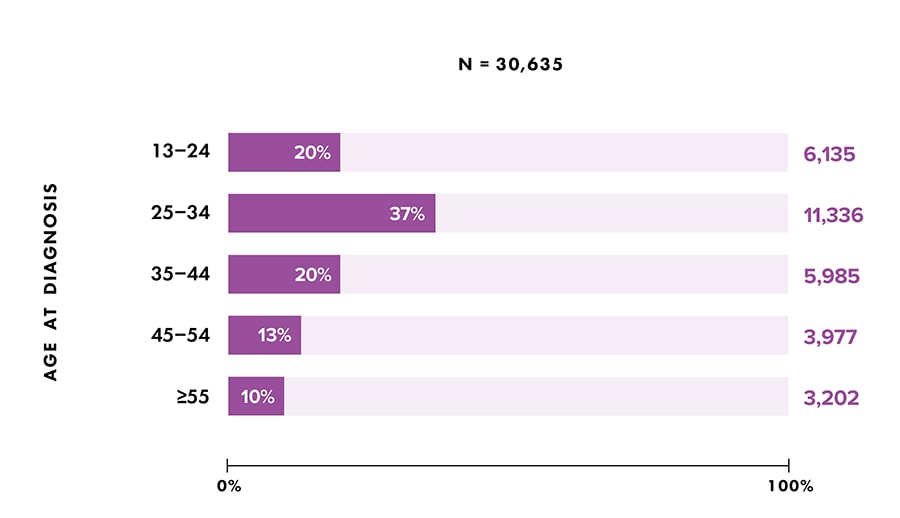
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
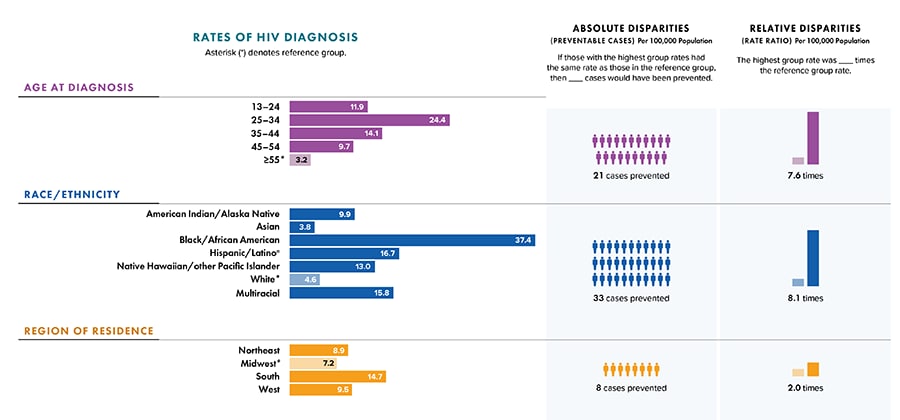
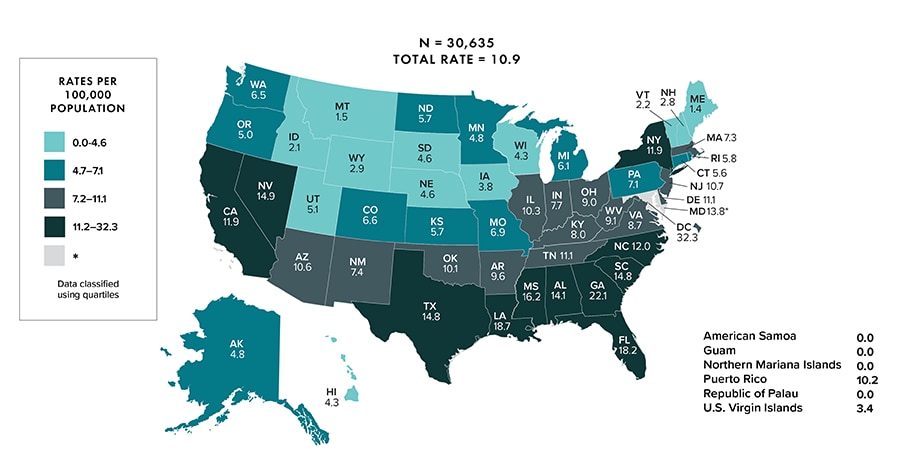
Note: Rates are per 100,000 population. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Absolute disparity measures the difference between rates in groups with the highest rates and a reference group (Ratehighest group − Ratereference group). Relative disparity (rate ratio) measures the rates in groups with the highest rates divided by a reference group (Ratehighest group ÷ Ratereference group).
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
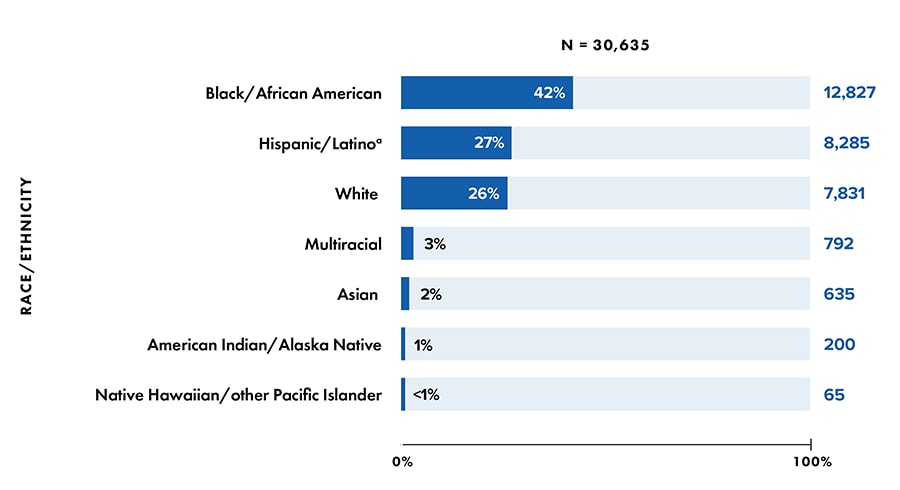
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
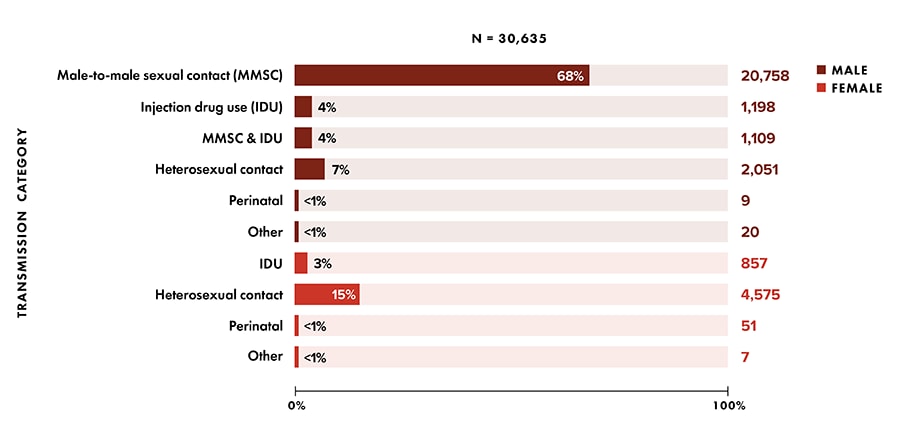
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. See section D4 in Technical Notes for more information on transmission categories.
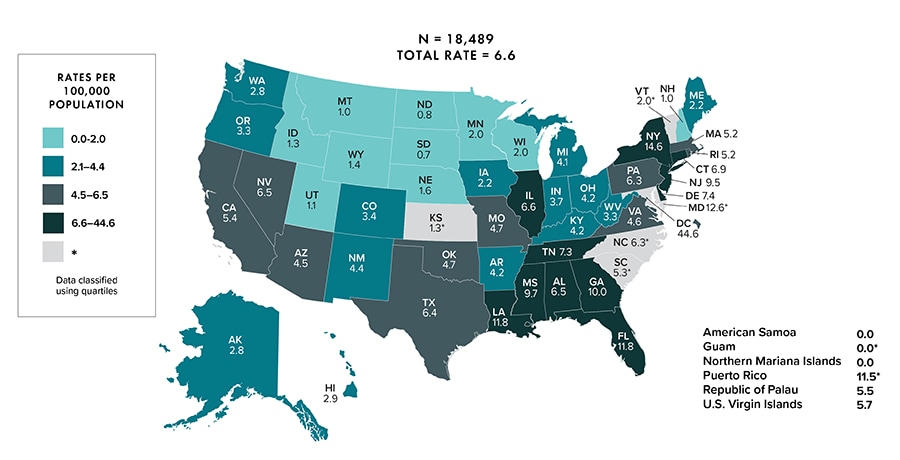
Note: Deaths of persons with a diagnosis of HIV infection may be due to any cause. Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
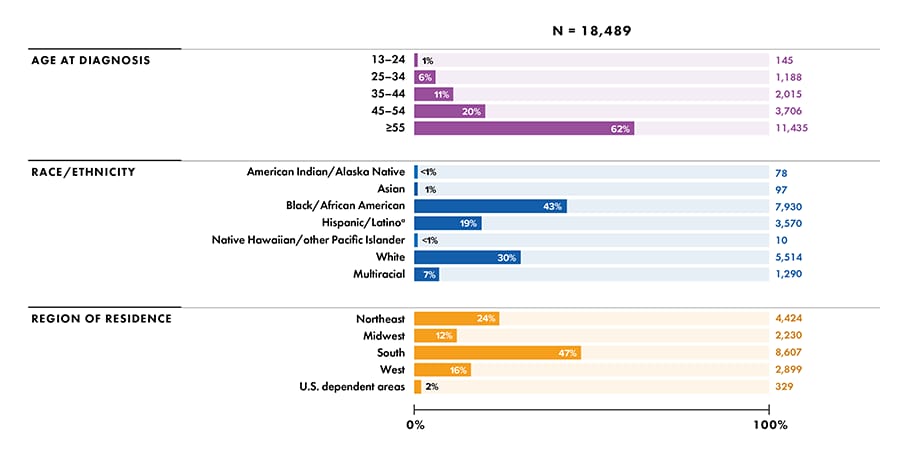
Note: Deaths of persons with a diagnosis of HIV infection may be due to any cause. Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Includes Asian/Pacific Islander legacy cases.
b Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
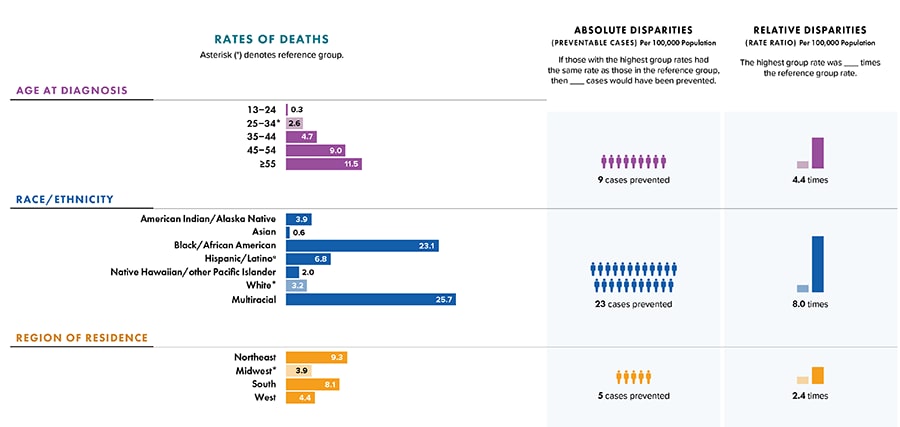
Note: Deaths of persons with a diagnosis of HIV infection may be due to any cause. Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Absolute disparity measures the difference between rates in groups with the highest rates and a reference group (Ratehighest group − Ratereference group). Relative disparity (rate ratio) measures the rates in groups with the highest rates divided by a reference group (Ratehighest group ÷ Ratereference group).
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
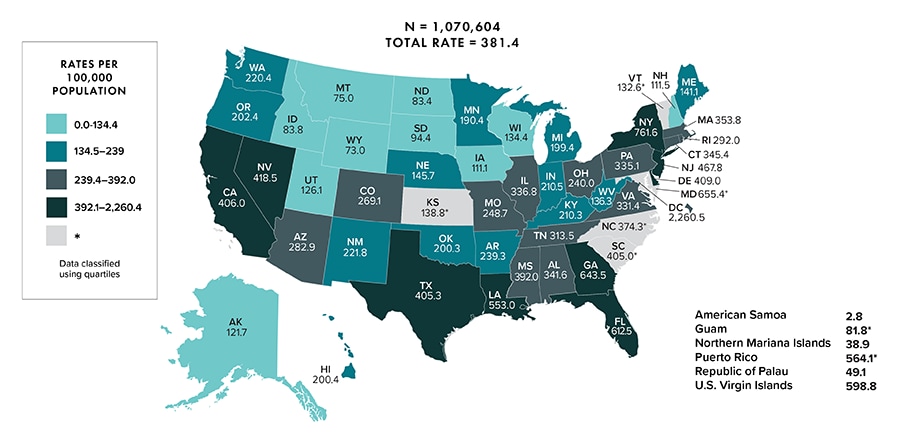
Note: Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Data are based on address of residence as of December 31, 2020 (i.e., most recent known address). Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting.
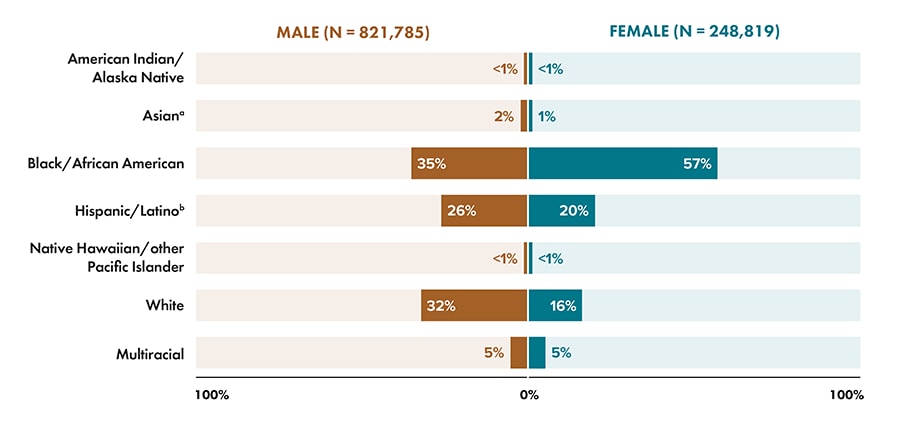
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
aIncludes Asian/Pacific Islander legacy cases.
bHispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
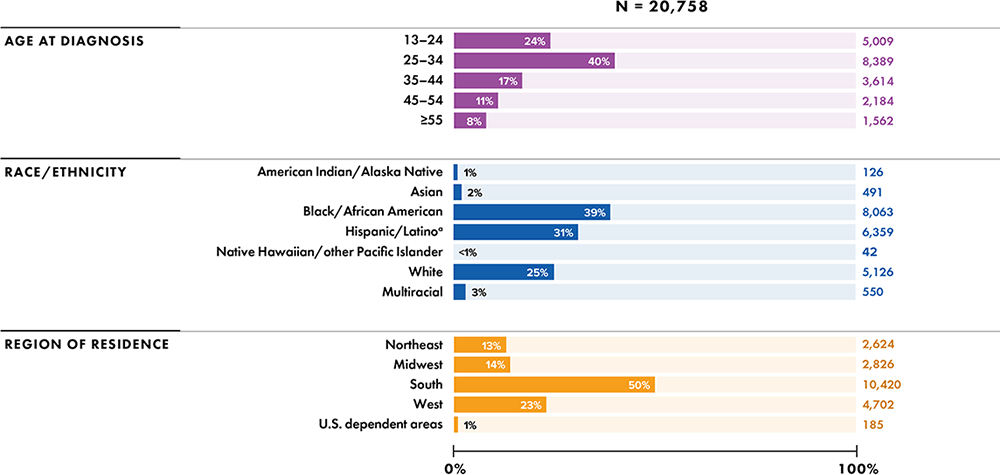
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
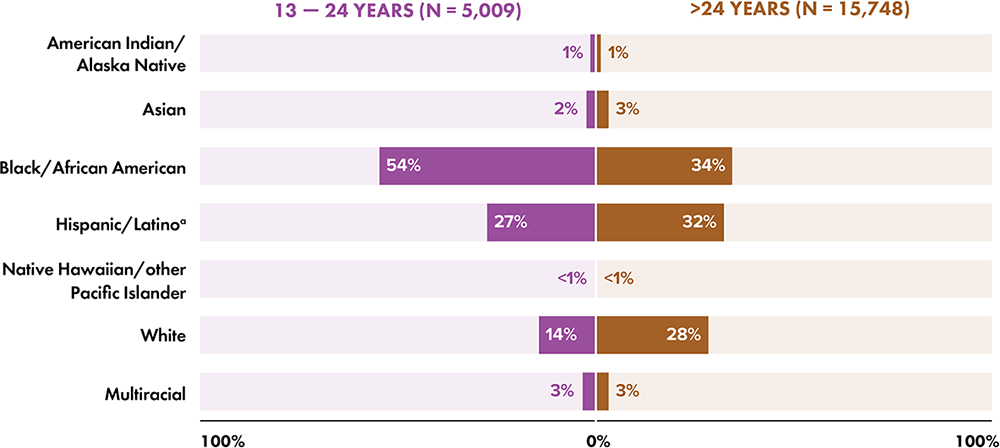
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
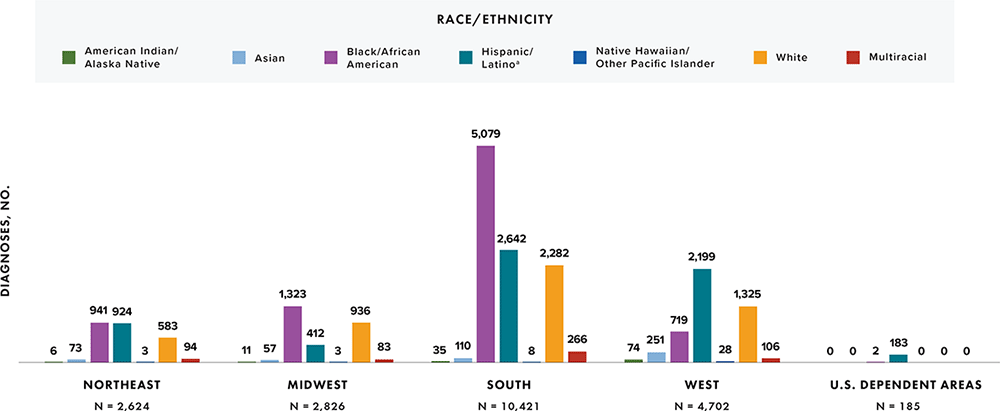
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
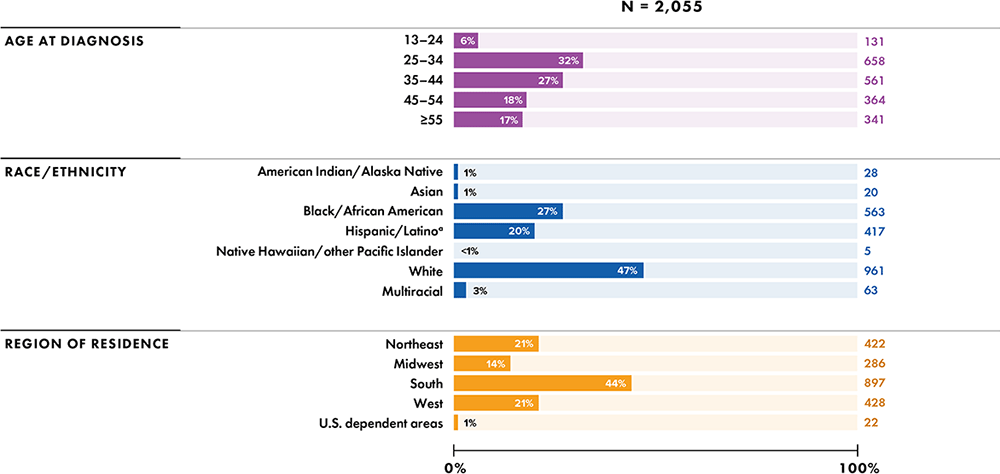
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
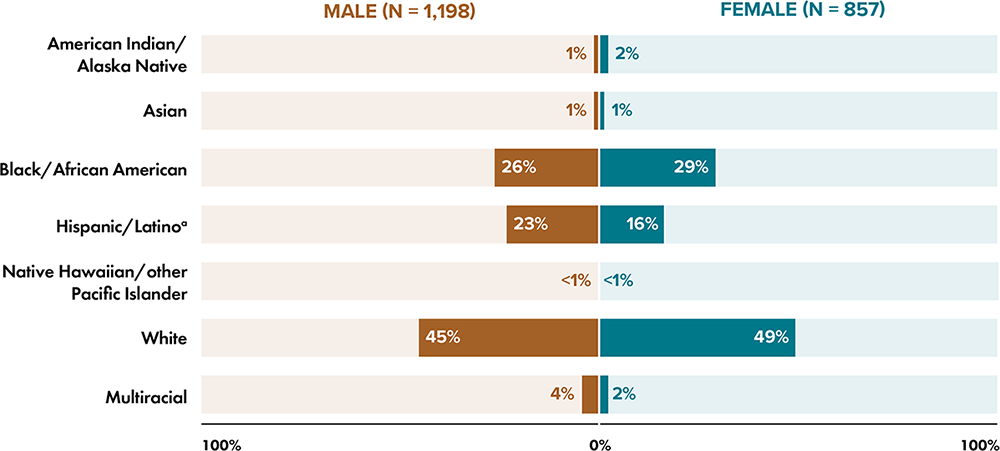
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
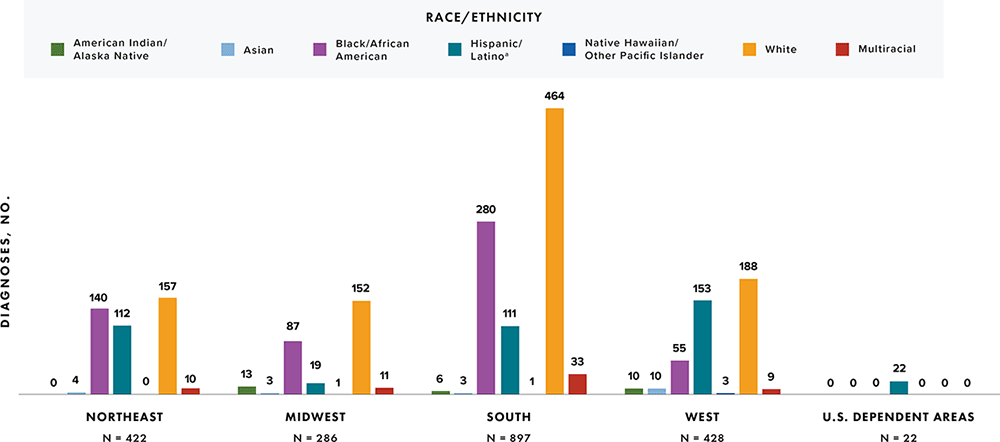
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
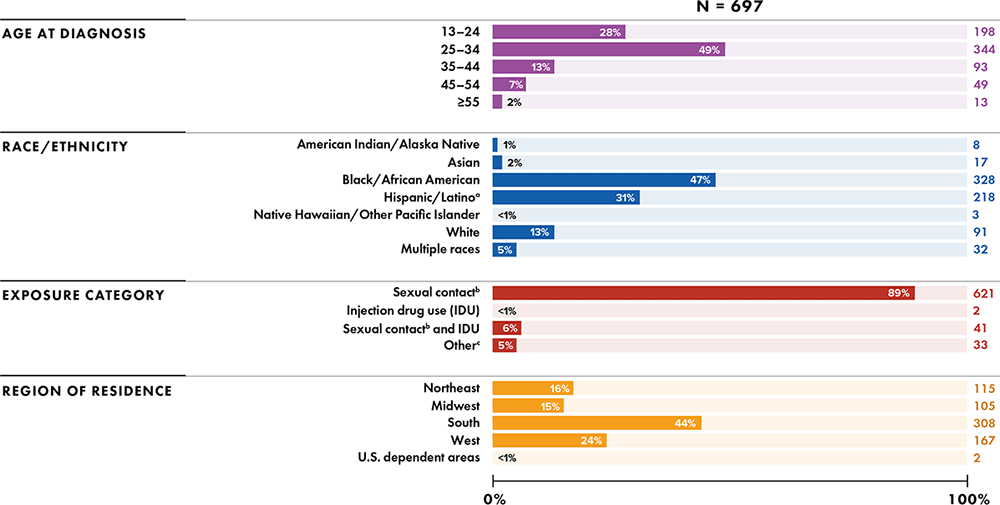
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
b For persons assigned “male” sex at birth, sexual contact with any person. For persons assigned “female” sex at birth, sexual contact with a person assigned “male” sex at birth.
c Other risk factors including perinatal, hemophilia, blood transfusion, and risk factor not reported or not identified. Data were not statistically adjusted to account for missing exposure category; therefore, case counts for “Other” might be high.
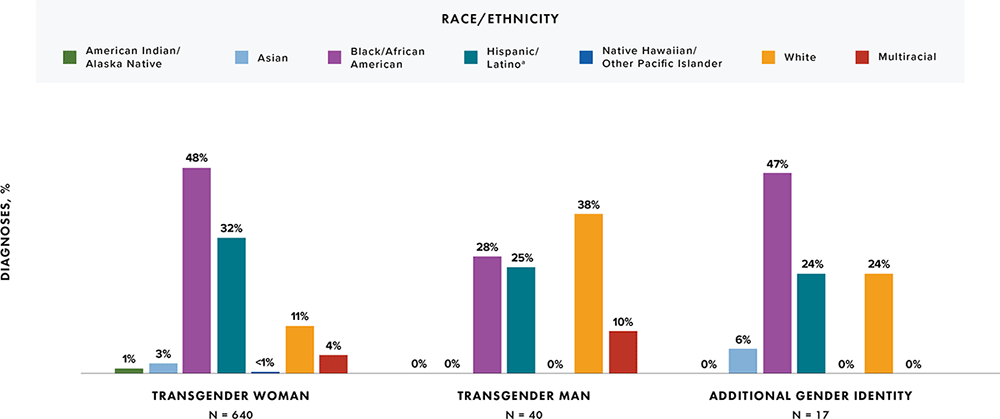
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
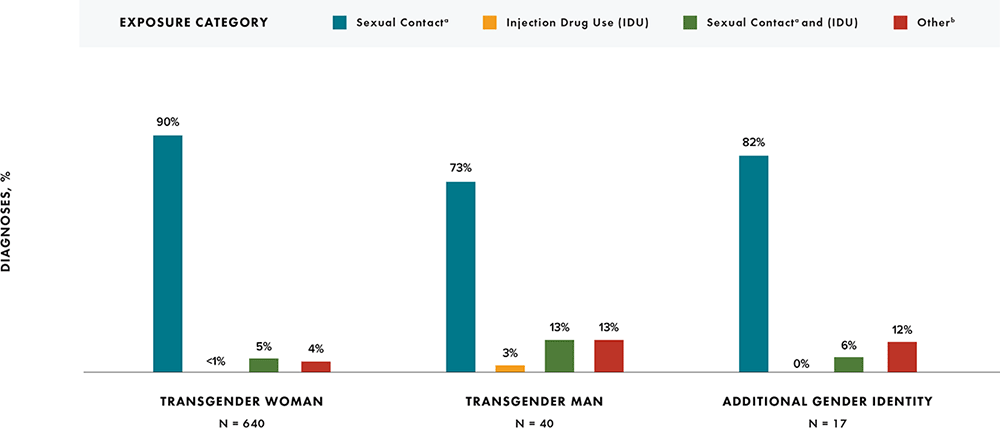
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a For persons assigned “male” sex at birth, sexual contact with any person. For persons assigned “female” sex at birth, sexual contact with a person assigned “male” sex at birth.
b Other risk factors including perinatal, hemophilia, blood transfusion, and risk factor not reported or not identified. Data were not statistically adjusted to account for missing exposure category; therefore, case counts for “Other” might be high.
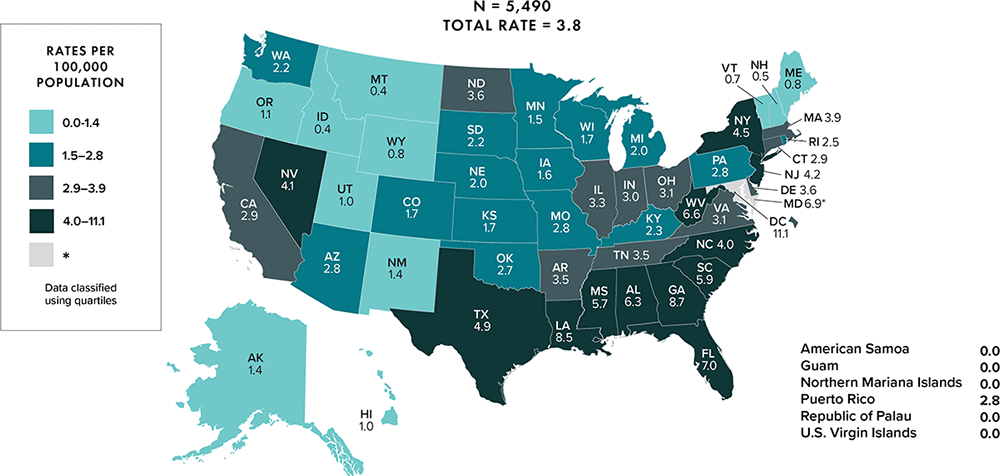
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting.
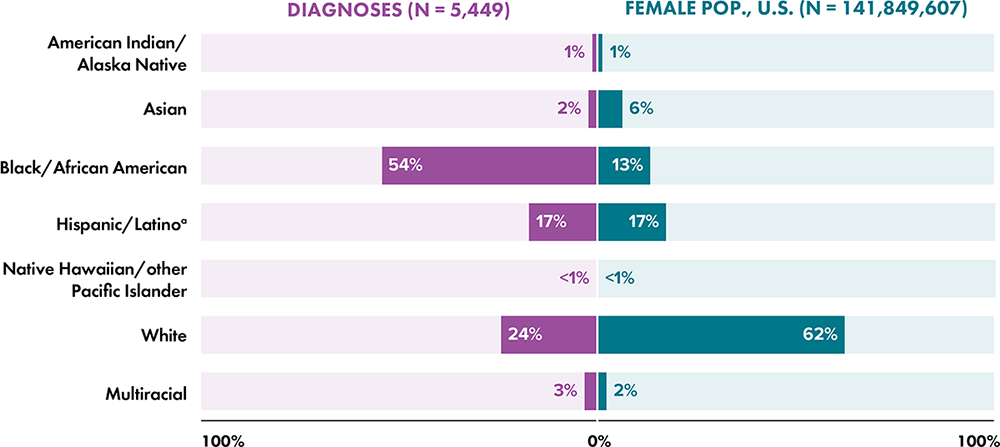
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
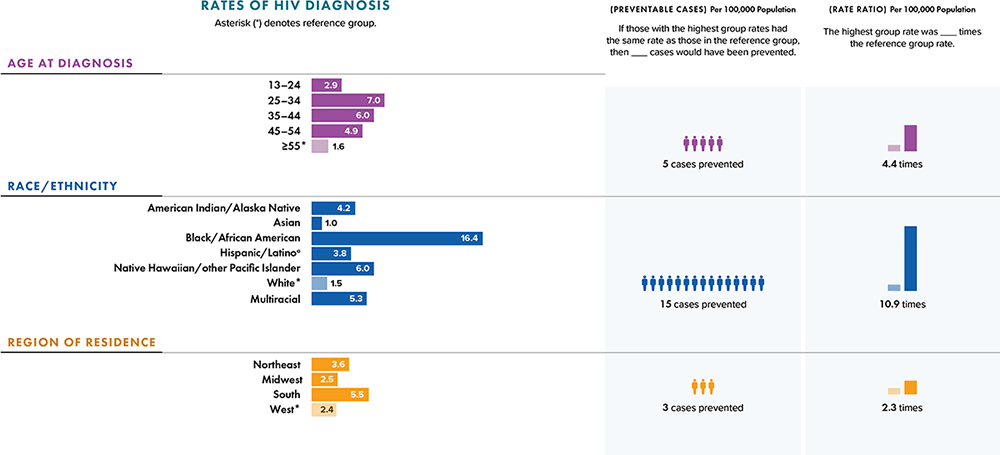
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Absolute disparity measures the difference between rates in groups with the highest rates and a reference group (Ratehighest group − Ratereference group). Relative disparity (rate ratio) measures the rates in groups with the highest rates divided by a reference group (Ratehighest group ÷ Ratereference group).
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
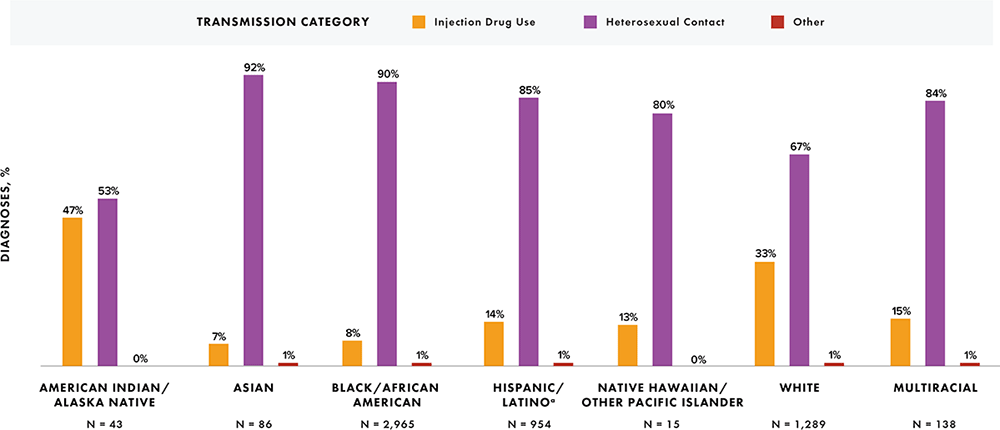
Note: Data have been statistically adjusted to account for missing transmission category. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
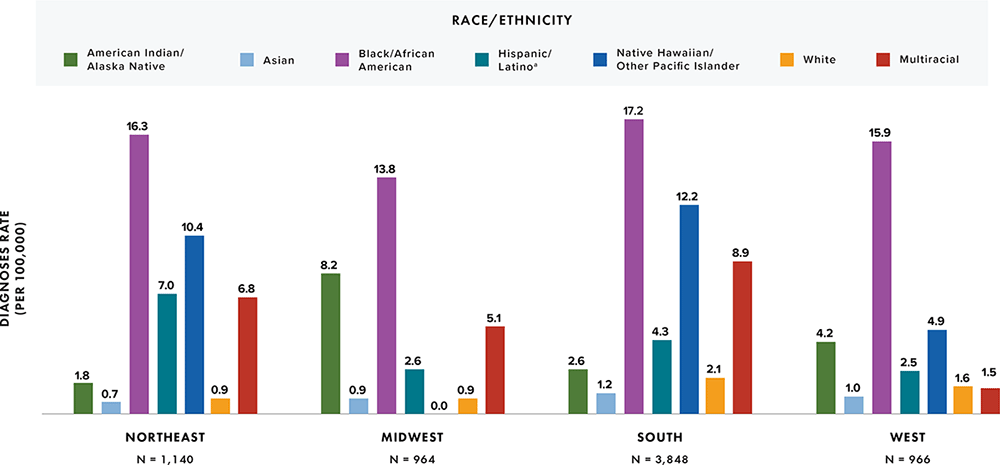
Note: Rates are per 100,000 population. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
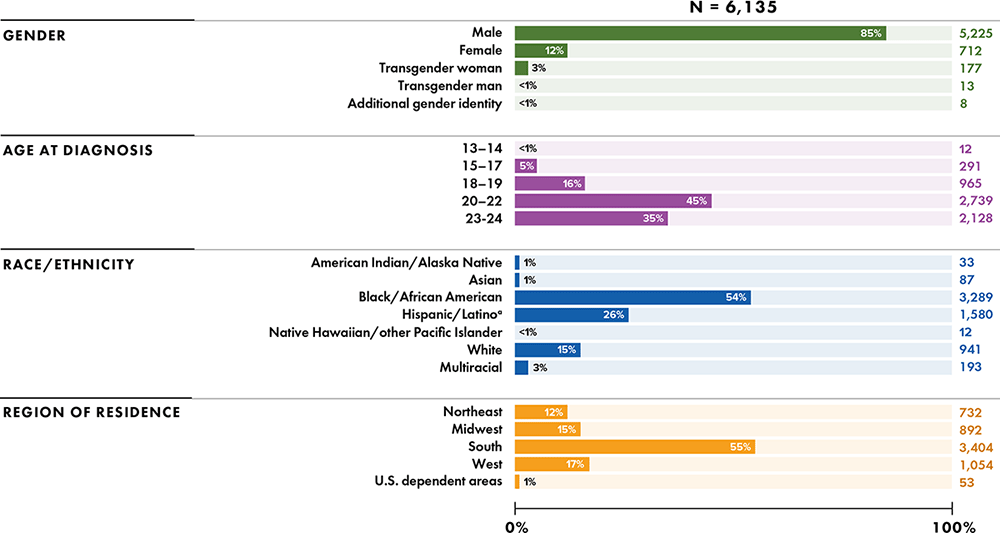
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
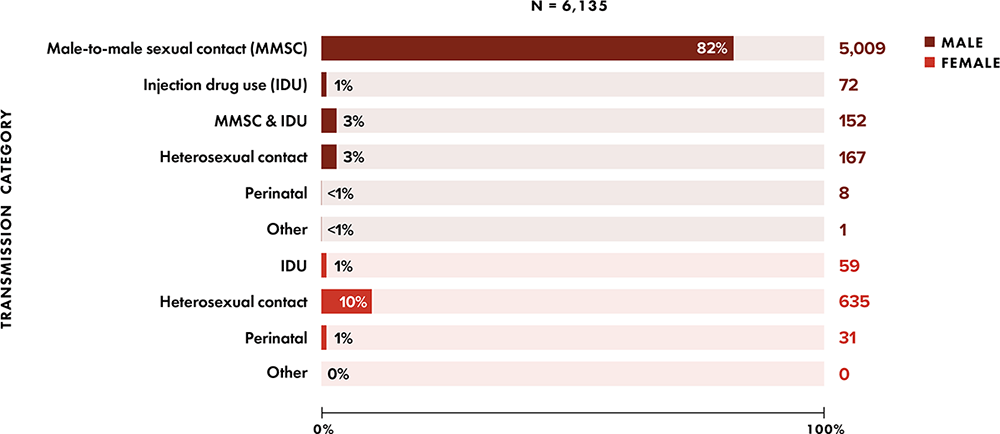
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
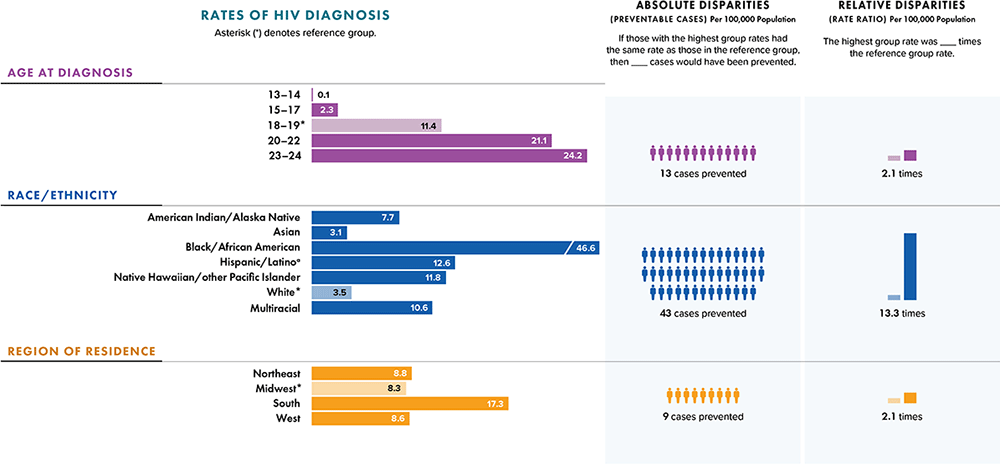
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions. Absolute disparity measures the difference between rates in groups with the highest rates and a reference group (Ratehighest group − Ratereference group). Relative disparity (rate ratio) measures the rates in groups with the highest rates divided by a reference group (Ratehighest group ÷ Ratereference group).
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
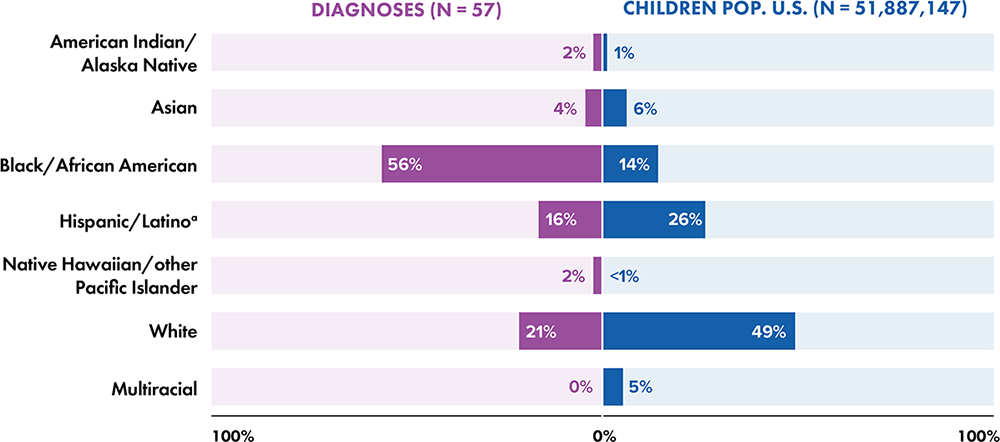
Note: Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
a Hispanic/Latino persons can be of any race.
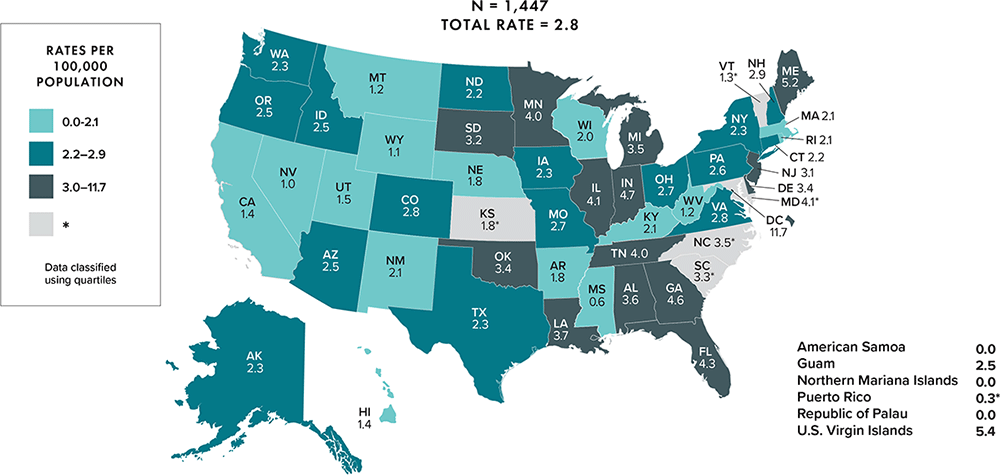
Note: Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Data are based on address of residence as of December 31, 2020 (i.e., most recent known address). Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.
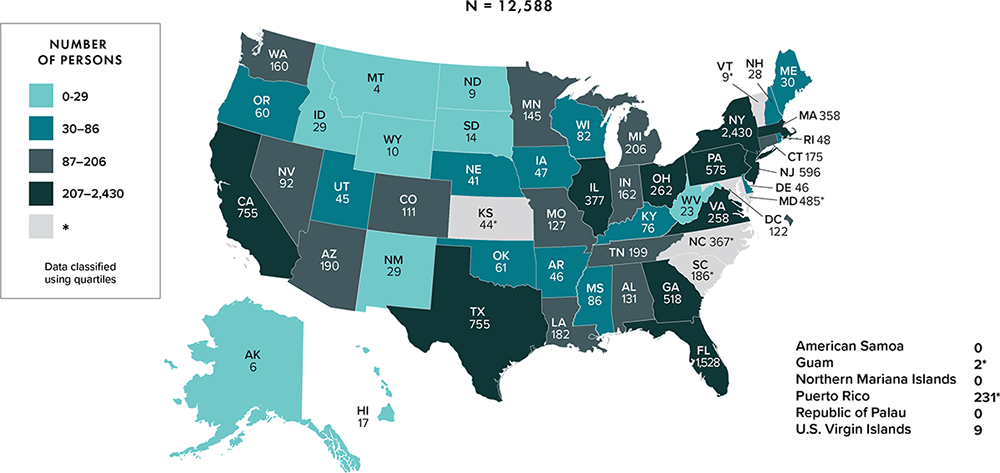
Note: Data for the year 2020 are preliminary and based on deaths reported to CDC as of December 2021. Data are based on address of residence as of December 31, 2020 (i.e., most recent known address). Asterisk (*) indicates incomplete reporting. Data for 2020 should be interpreted with caution due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on access to HIV testing, care-related services, and case surveillance activities in state/local jurisdictions.