2011—2012 Recreational Water-associated Outbreak Surveillance Report Supplemental Figures
These tables provide supplemental information not published in Outbreaks of Illness Associated with Recreational Water — United States, 2011–2012 (MMWR Weekly).
Note: You can save these images by left-clicking, holding, and dragging each image to a folder on your computer.
Figure 1 — Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks, by Jurisdiction of Exposure* — United States, 2011–2012
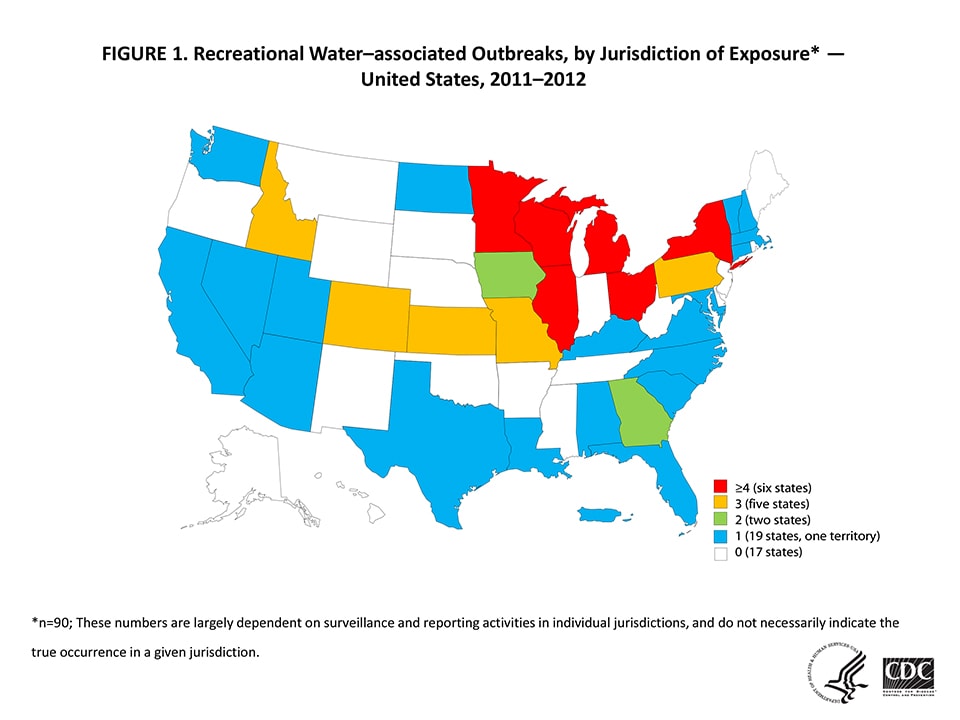
*n=90; These numbers are largely dependent on surveillance and reporting activities in individual jurisdictions, and do not necessarily indicate the true occurrence in a given jurisdiction.
Download PDF
Download CSV
Figure 2 — Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks, by Type of Exposure, Predominant Illness*, and Etiology — United States, 2011–2012
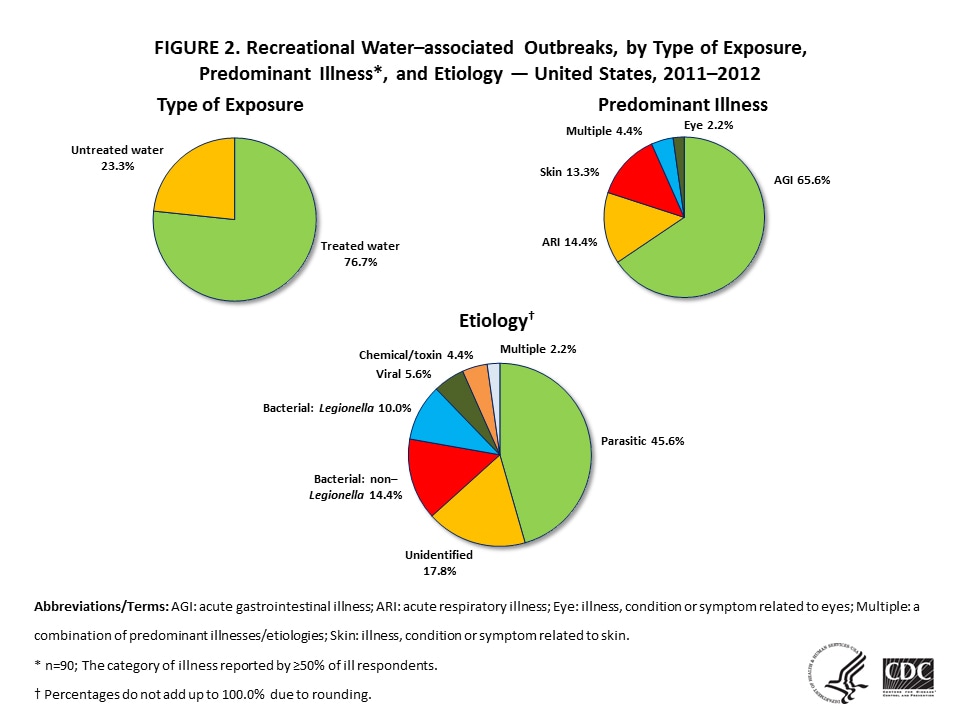
Abbreviations/Terms: AGI: acute gastrointestinal illness; ARI: acute respiratory illness; Eye: illness, condition, or symptom related to eyes; Multiple: a combination of predominant illnesses/etiologies; Skin: illness, condition, or symptom related to skin.
*n=90; The category of illness reported by ≥50% of ill respondents.
†Percentages do not add up to 100.0% due to rounding.
Download PDF
Download CSV
Figure 3 — Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks, by Predominant Illness* and Month — United States, 2011–2012
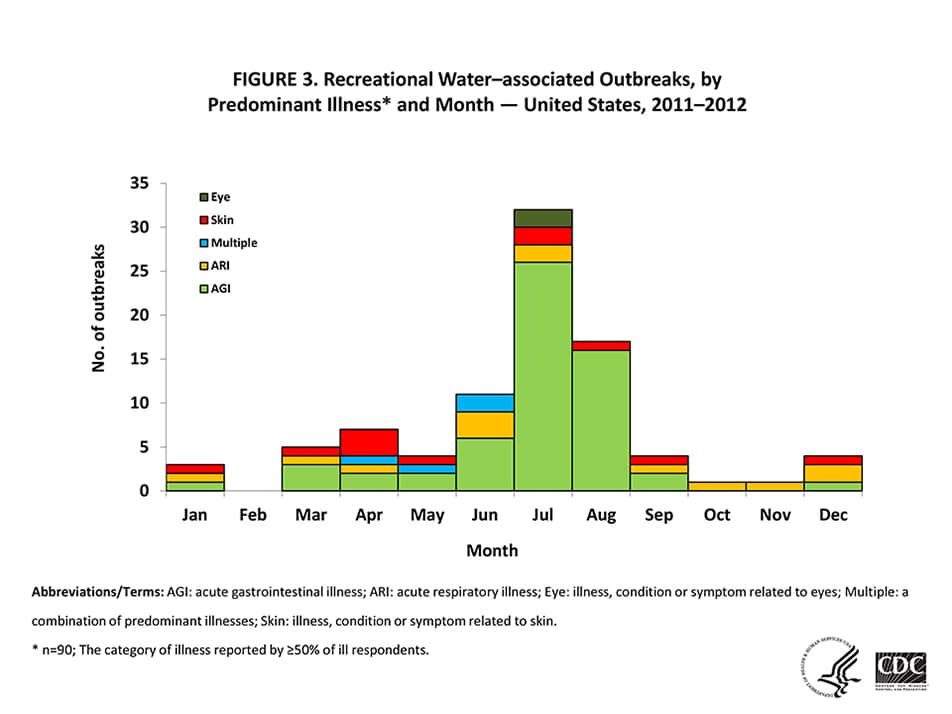
Abbreviations/Terms: AGI: acute gastrointestinal illness; ARI: acute respiratory illness; Eye: illness, condition or symptom related to eyes; Multiple: a combination of predominant illnesses; Skin: illness, condition, or symptom related to skin.
* n=90; The category of illness reported by ≥50% of ill respondents.
Download PDF
Download CSV
Figure 4 — Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks of Acute Gastrointestinal Illness (AGI), by Type of Exposure, Etiology, and Water Type — United States, 2011–2012
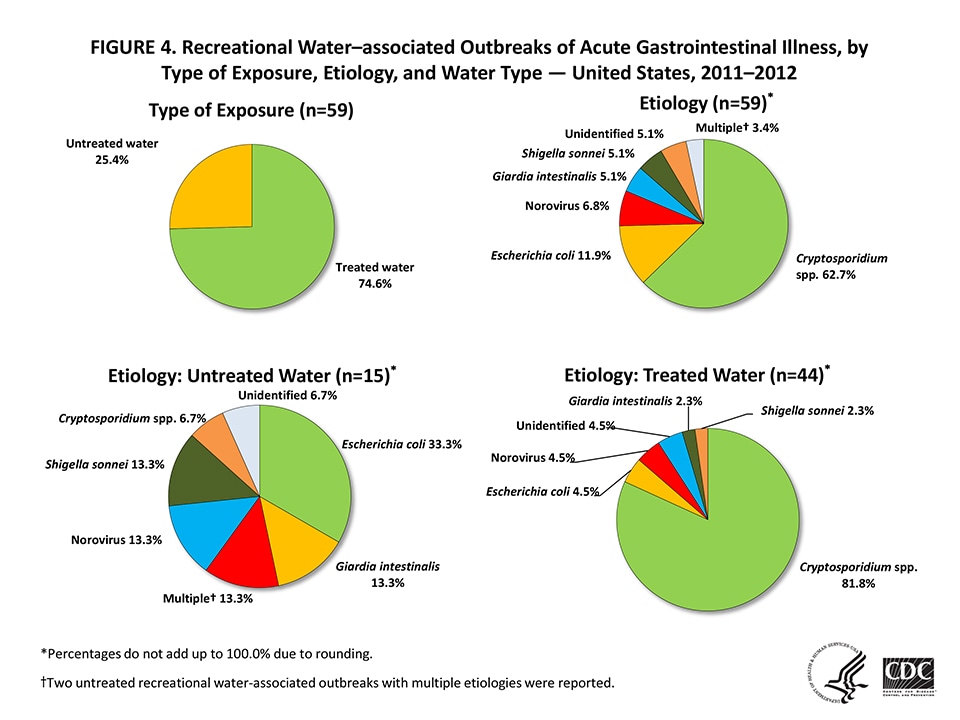
*Percentages do not add up to 100.0% due to rounding.
† Two untreated recreational water-associated outbreaks with multiple etiologies were reported.
Download PDF
Download CSV
- AGI Outbreaks, by Type of Exposure [CSV – 1kb]
- AGI Outbreaks, by Etiology [CSV – 1kb]
- AGI Etiology: Untreated water [CSV – 1kb]
- AGI Etiology: Treated water [CSV – 1kb]
Figure 5 — Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks, by Predominant Illness* and Year — United States, 1978–2012
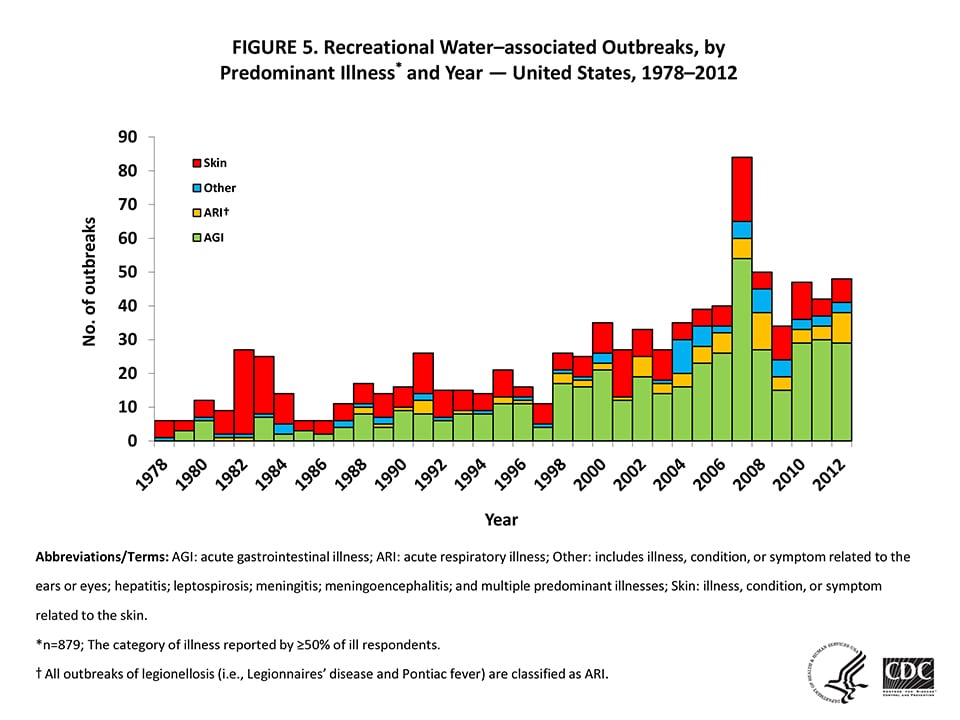
Abbreviations/Terms: AGI: acute gastrointestinal illness; ARI: acute respiratory illness; Other: includes illness, condition, or symptom related to the ears or eyes; hepatitis; leptospirosis; meningitis; meningoencephalitis; and multiple predominant illnesses; Skin: illness, condition, or symptom related to the skin.
*n=879; The category of illness reported by ≥50% of ill respondents.
†All outbreaks of legionellosis (i.e., Legionnaires’ disease and Pontiac fever) are classified as ARI.
Download PDF
Download CSV
Figure 6 — Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks of Acute Gastrointestinal Illness, by Type of Exposure* and Year — United States, 1978–2012
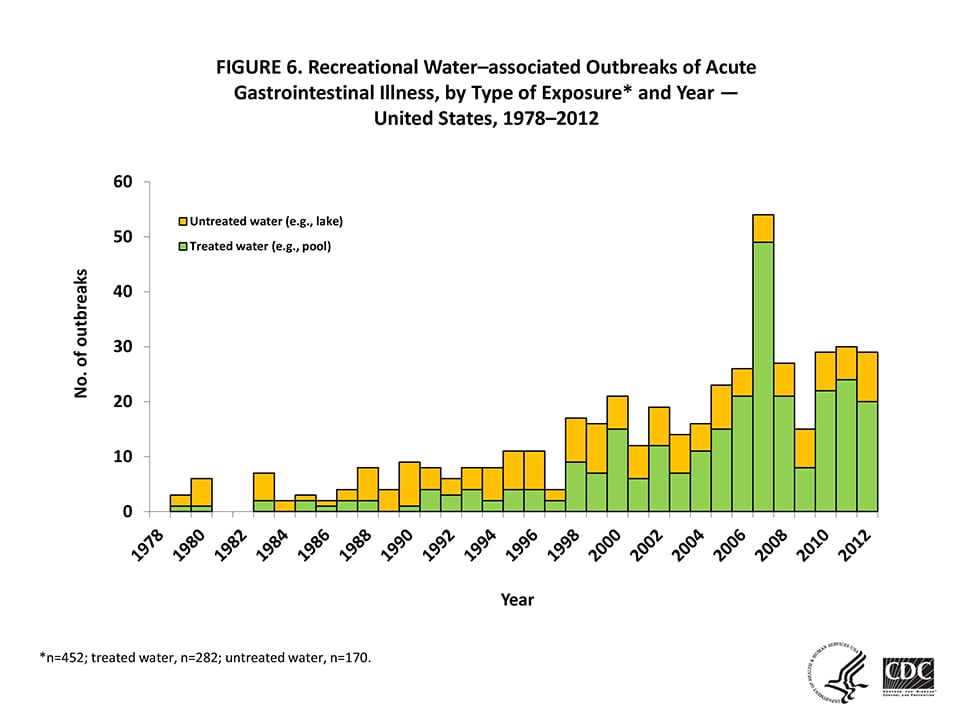
*n=452; treated water, n=282; untreated water, n=170.
Download PDF
Download CSV
Figure 7 – Recreational Water–associated Outbreaks of Acute Gastrointestinal Illness (AGI), by Type of Exposure and Etiology — United States, 2003-2012
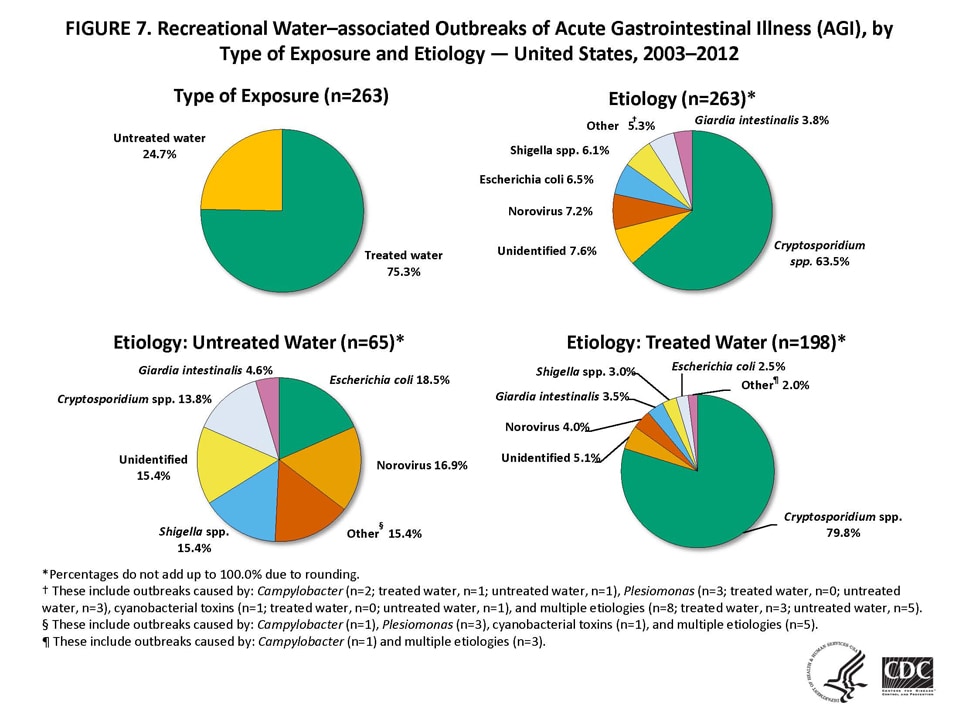
*Percentages do not add up to 100.0% due to rounding.
† These include outbreaks caused by: Campylobacter (n=2; treated water, n=1; untreated water, n=1), Plesiomonas (n=3; treated water, n=0; untreated water, n=3), cyanobacterial toxins (n=1; treated water, n=0; untreated water, n=1), and multiple etiologies (n=8; treated water, n=3; untreated water, n=5).
§ These include outbreaks caused by: Campylobacter (n=1), Plesiomonas (n=3), cyanobacterial toxins (n=1), and multiple etiologies (n=5).
¶ These include outbreaks caused by: Campylobacter (n=1) and multiple etiologies (n=3).