Step 1 in the EGAPP Working Group Review Process
Download PDF (460 KB)
Overview | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4




|
Group
|
Topics
|
Evidence
Report |
Recommendation Statement
|
Dissemination
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGAPP Working Group (EWG) |
|
|
||
| EGAPP consultants and CDC-based staff |

|
|

|

|
| EWG members who serve on Technical Expert Panel |

|

|

|
|
| EWG who serve on the recommendation writing team |

|

|
||
| Stakeholders and interested public |

|

|
||
| Evidence-based Practice Centers (EPCs) and other review groups |

|

|
||
| Expert and/or peer reviewers |

|

|
||
| Industry/test developer* * invited comment on the final evidence report |

|

|
|

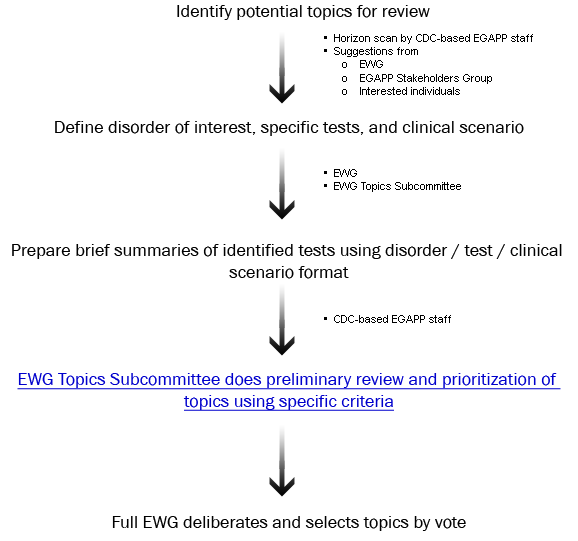
Summary: Process for identifying, prioritizing, and selecting tests and specific clinical scenarios for systematic review.
Who is involved: EGAPP Working Group (EWG) Topics Subcommittee, full EWG, CDC-based EGAPP staff, and interested public. See process diagram below for details.
Transparency: EGAPP welcomes suggestions on potential topics for review. Those submitting suggestions are
encouraged to include information on the disorder, the specific test(s), and the specific clinical
scenario(s) in which the test will be used. EGAPP Working Group members make final topic selections.
Products:
- List of topics
- Key questions and analytic framework for evidence reviews
Topic Selection Process

Summary: An evidence review involves many steps and is meant to synthesize available evidence on a particular disorder, test, and clinical scenario.
CDC commissions systematic evidence reviews using two strategies:
- Comprehensive Reviews are usually done in partnership with Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence-based Practice Centers (AHRQ EPCs). EPCs conduct comprehensive literature searches and evaluation, with detailed
documentation of methods and results. - Targeted and/or Rapid Reviews are conducted for topics with minimal literature to review and/or targeted questions to answer. These reviews are coordinated by CDC-based EGAPP staff in collaboration with technical contractors and expert core consultants.
Evidence reports, the products of these reviews, are detailed, systematic, objective assessments of the available scientific and
clinical evidence on a specific topic. Evidence reports are the basis for deliberations by the EGAPP Working Group as they develop
their Recommendation Statements.
Who is involved: CDC commissions the review, the EWG develops the key questions to be addressed, and the selected review team (e.g., EPC or other contracted group) conducts the review and produces a report. The review team establishes a Technical Expert Panel (TEP) to provide guidance, usually including topic experts and two to three EWG members.
Transparency: All EGAPP Working Group members, review team members, and consultants disclose potential conflicts of interest
for each topic considered. Evidence reports undergo external expert review. Reports or manuscripts published with CDC staff as authors may undergo CDC clearance.
Products:
Evidence reports posted on web sites (EGAPP or AHRQ)
Published summaries of evidence from the AHRQ EPCs or other contracted review group.
EGAPP EVIDENCE REVIEW PROCESS

Comprehensive EPC Reviews
Conducted by Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence-based Practice Centers
Technical Expert Panel (TEP) by EPC established to guide review
- The TEP includes topic experts and 2-3 EWG members to finalize key questions and guide the scope and content of the review.
Evidence report drafted
- Evidence reviewers solicit comments on draft evidence report from TEP, EWG, and expert reviewers selected by the EPC.
Final evidence report provided to AHRQ
- Reviewed and accepted by AHRQ
- Provided to CDC and EGAPP Working Group
- Posted on AHRQ web site and linked to from EWG website
Optional: EPC publishes summary manuscript in journal
Rapid and/or Targeted Reviews
Conducted by reviewers who may include:
- Core EGAPP consultants in with expertise in evidence-based review
- Consultants in specific topic areas (e.g., oncology)
- CDC-based technical EGAPP staff
TEP established to guide review
- The TEP includes topic experts and 2-3 EWG members to finalize key questions and guide the scope and content of the review.
Evidence report drafted
- Evidence reviewers solicit comments on draft evidence report from TEP, EWG, and expert reviewers selected by the review group.
Final evidence report provided to CDC and EWG
- Approved by EWG
- If CDC authors, cleared by CDC
- EWG provides final report to selected test developers for comment to aid in developing Recommendation Statement
- Final evidence report posted on EWG web site
- Evidence summary is prepared for submission to journal

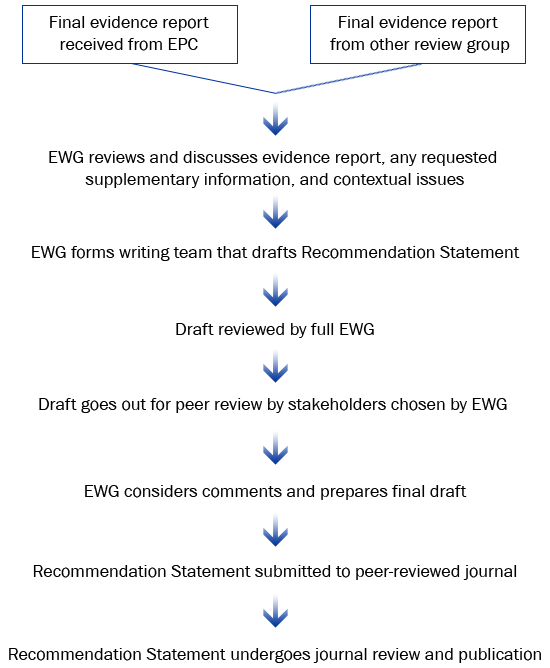
Summary: The EGAPP Working Group (EWG) reviews the evidence report, considers contextual issues, and may consider other
sources of evidence. A draft recommendation statement is developed, peer-reviewed, and submitted for publication.
EWG Recommendation Statements are based on CDC-commissioned evidence reports, other review of evidence as needed, the quality of available data, and potential clinical and social impact of using the test in practice.
Who is involved: EWG, with support from CDC-based EGAPP staff and consultants.
Transparency: Review of comments from industry and a range of stakeholders (e.g., from professional organizations, health plans, consumer groups, and public health programs).
Products:
Peer-reviewed, published EWG Recommendation Statements
Recommendation Statement Development Process

Summary: EGAPP initiative products are disseminated to stakeholders through publications, web sites, and presentations.
Who is involved: CDC-based EGAPP staff, EGAPP Stakeholders Group (ESG), EGAPP Working Group (EWG).
Transparency: Stakeholder peer review, CDC clearance.
Dissemination Processes for EGAPP Products and Informational Messages

Primary EGAPP products
Commissioned evidence reports
- Posted on EWG website or Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality website
EWG Recommendation Statements
- Published in peer-reviewed journal
- Free web access to article
- Journal may issue press release
EWG website
- Open access
Secondary EGAPP products
Announcements of EGAPP initiative primary products and other updates (CDC-based EGAPP staff)
- Posted on the website of the CDC Office of Public Health Genomics (OPHG), which supports the EGAPP initiative.
- Posted on the EWG website
- Distributed by e-mail across CDC and to EGAPP stakeholder list (approximately 400 genetic testing stakeholder organizations and individuals)
EGAPP informational messages incorporated into translational materials for providers and consumers (CDC-based EGAPP staff, ESG)
- Posted on CDC OPHG web pages
- Disseminated by various means through diverse EGAPP Stakeholders Group organizations
CDC Press Statements related to EGAPP (CDC-based EGAPP staff and CDC press office)
- Posted on CDC web pages for Media
EGAPP initiative web pages on CDC website (CDC-based EGAPP staff)
- Posted on CDC OPHG web pages
EGAPP initiative posters and presentations (CDC EGAPP staff, EWG, ESG)
Summary: Process for identifying, prioritizing, and selecting tests and specific clinical scenarios for systematic review.
Who is involved: EGAPP Working Group (EWG) Topics Subcommittee, full EWG, CDC-based EGAPP staff, and interested public. See process diagram below for details.
Transparency: EGAPP welcomes suggestions on potential topics for review. Those submitting suggestions are
encouraged to include information on the disorder, the specific test(s), and the specific clinical
scenario(s) in which the test will be used. EGAPP Working Group members make final topic selections.
Products:
List of topics
Key questions and analytic framework for evidence reviews