
Monthy Case Studies - 2001
Case #73 - December, 2001
A 39-year-old man was seen by his health care provider for fever, chills, and headache he had been experiencing since a camping trip to South Carolina. The man recalled numerous tick bites during his trip. The physician requested a blood film examination. The following images (Figures A, B, and C) are of Giemsa stained blood smears from the patient. What is your diagnosis? Based on what criteria?
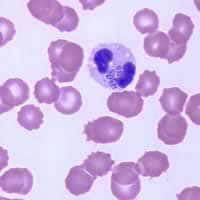
Figure A
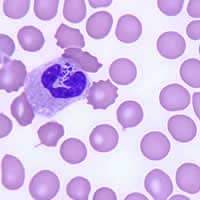
Figure B
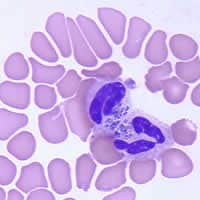
Figure C
Answer to Case #73
This was a case of ehrlichiosis, a bacterial disease that can be transmitted by certain tick vectors. Babesiosis may have been the presumed diagnosis given the clinical history and symptoms, however, no Babesia spp. were seen on the blood film. Serology and PCR may be useful to rule out babesiosis if blood smears are repeatedly negative. The cytoplasmic inclusions seen in the white blood cells shown in the image files, symptomology, and tick exposure indicate erlichiosis (Figures A, B, and C).
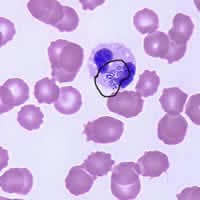
Figure A
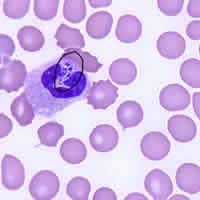
Figure B
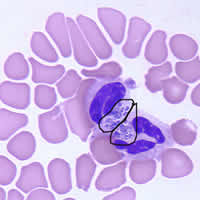
Figure C
More on: Ehrlichiosis
Images presented in the monthly case studies are from specimens submitted for diagnosis or archiving. On rare occasions, clinical histories given may be partly fictitious.
 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir


