Map Details – High Blood Pressure (HBP) Medication Non-Adherence and Pharmacies, by ZIP Code Tabulation Area (ZCTA/ZCTA Group), 2015–2017 Idaho Medicaid Patients
Impact Statement
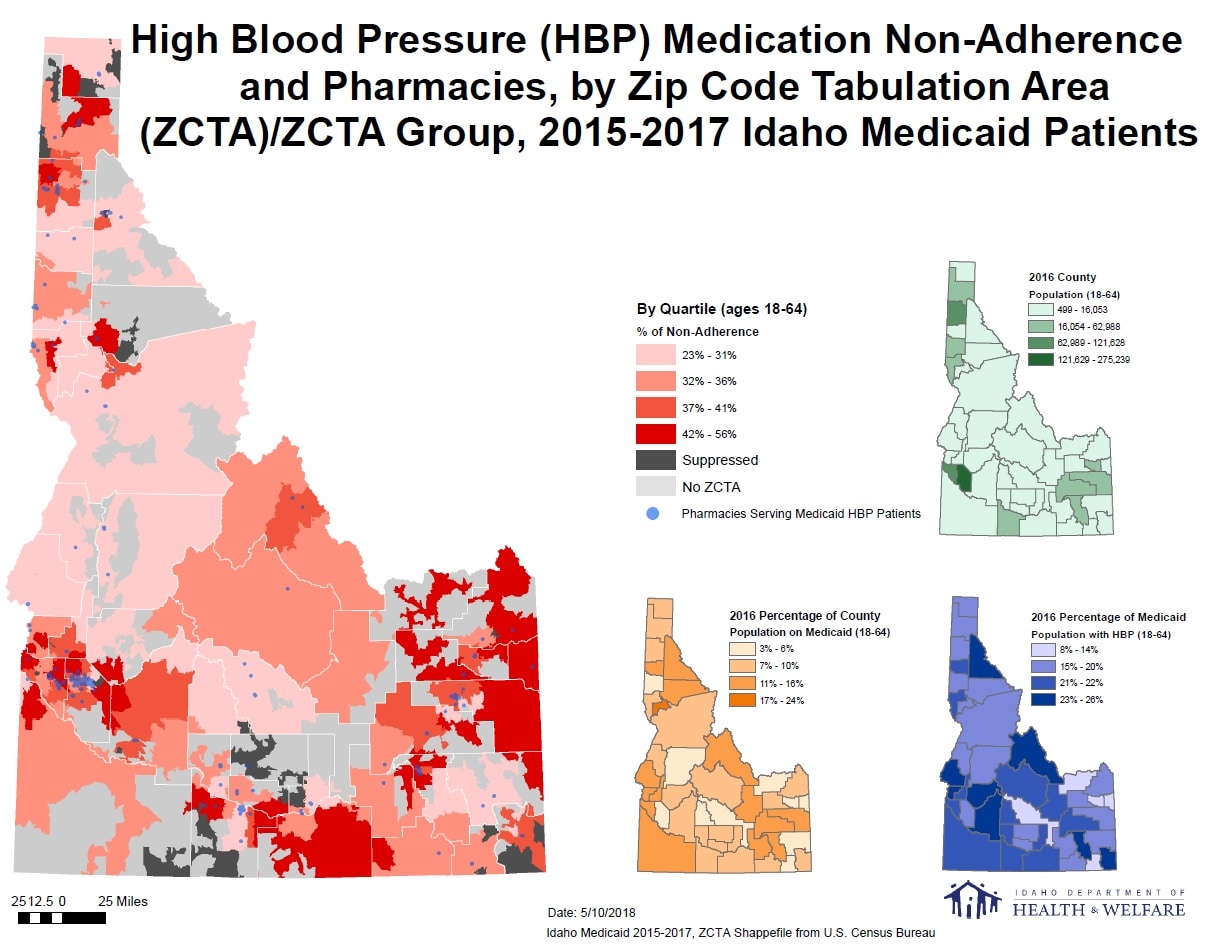
The map indicates variable but elevated rates of non-adherence within the state’s population centers (as indicated by clustering of pharmacy locations), with higher rates frequently seen in adjoining rural areas. This map suggests that abundant opportunities to improve non-adherence rates also exist outside of the state’s metro areas.
Major Findings
Estimates of health behaviors and/or conditions in rural areas of Idaho are frequently suppressed due to either statistical unreliability or potential for breaches in confidentiality. This map overcomes these issues by (1) aggregating over time and (2) aggregating over space in rural areas of the state to create rural ZCTA groups. The map indicates variable but elevated rates of non-adherence within the state’s population centers (as indicated by clustering of pharmacy locations), with higher rates frequently seen in adjoining rural areas. Improving access to effective services within Idaho population centers can positively impact overall Medicaid non-adherence rates. However, this map suggests that abundant opportunities to improve non-adherence rates also exist outside of the state’s metro areas.
How the map will be used, or has been used
These maps provide base-level understanding of access to blood pressure medication in relation to medication non-adherence rates. As a result of these maps, the Idaho Division of Public Health Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Program plans to work with the Idaho State University College of Pharmacy to conduct statewide assessment of pharmacy services with the state.