Skip directly to the search box, site navigation, or content.
NOTICE: The information on this page is no longer being updated and may have changed. The information is accurate only as of the last page update.
Investigation of Outbreak of Infections Caused by Salmonella Saintpaul
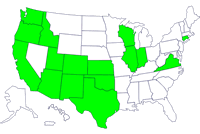
States with persons with the outbreak strain of Salmonella Saintpaul, by state of residence and onset of illness, April to June 2008.
Information updated June 7, 2008
Click Here for Advice to Consumers
CDC is collaborating with public health officials in many states, the Indian Health Service, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to investigate an ongoing multi-state outbreak of human Salmonella serotype Saintpaul infections. An epidemiologic investigation conducted by the New Mexico and Texas Departments of Health and the Indian Health Service using interviews comparing foods eaten by ill and well persons has identified consumption of raw tomatoes as the likely source of the illnesses in those states. The specific type and source of tomatoes is under investigation; however, the data suggest that large tomatoes, including Roma and round red, are the source.
Since mid-April, 145 persons infected with Salmonella Saintpaul with the same genetic fingerprint have been identified in 16 states: Arizona (12 persons), California (1), Colorado (1), Connecticut (1), Idaho (2), Illinois (17), Indiana (1), Kansas (3), New Mexico (39), Oklahoma (3), Oregon (2), Texas (56 persons), Utah (1), Virginia (2), Washington (1), and Wisconsin (3). These were identified because clinical laboratories in all states send Salmonella strains from ill persons to their State public health laboratory for characterization. Among the 73 persons who have been interviewed, illnesses began between April 16 and May 27, 2008. Patients range in age from 1 to 82 years; 49% are female. At least 23 persons were hospitalized. No deaths have been reported.
Only 3 persons infected with this strain of Salmonella Saintpaul were identified in the country during the same period in 2007. The previous rarity of this strain and the distribution of illnesses in all U.S. regions suggest that the implicated tomatoes are distributed throughout much of the country. Because of inherent delays in reporting and because many persons with Salmonella illness do not have a stool specimen tested, it is likely many more illnesses have occurred than those reported. Some of these unreported illnesses may be in states that are not on today’s map.
Clinical features of Salmonella Infection
Most persons infected with Salmonella develop diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps 12–72 hours after infection. Infection is usually diagnosed by culture of a stool sample. The illness usually lasts 4 – 7 days. Although most people recover without treatment, severe infections may occur. Infants, elderly persons, and those with impaired immune systems are more likely than others to develop severe illness. When severe infection occurs, Salmonella may spread from the intestines to the bloodstream and then to other body sites, and can cause death. In these severe cases, antibiotic treatment may be necessary.
Advice to consumers
At this time, FDA is advising U.S. consumers to limit their tomato consumption to those that are not the likely source of this outbreak. These include cherry tomatoes; grape tomatoes; tomatoes sold with the vine still attached; tomatoes grown at home; and raw red Roma, red plum, and round red tomatoes from specific sources listed at: http://www.fda.gov/oc/opacom/hottopics/tomatoes.html*. Consumers should be aware that raw tomatoes are often used in the preparation of fresh salsa, guacamole, and pico de gallo, are part of fillings for tortillas, and are used in many other dishes.
Customers everywhere are advised to:
- Refrigerate within 2 hours or discard cut, peeled, or cooked tomatoes.
- Avoid purchasing bruised or damaged tomatoes and discard any that appear spoiled.
- Thoroughly wash all tomatoes under running water.
- Keep tomatoes that will be consumed raw separate from raw meats, raw seafood, and raw produce items.
- Wash cutting boards, dishes, utensils, and counter tops with hot water and soap when switching between types of food products.
FDA recommends that U.S. retail outlets, restaurants, and food service operators offer only fresh and fresh cut red Roma, red plum, and round red tomatoes and food products made from these tomatoes from specific sources listed at: http://www.fda.gov/oc/opacom/hottopics/tomatoes.html#retailers*. Cherry tomatoes, grape tomatoes, and tomatoes sold with the vine still attached from any source may be offered.
FDA information on this investigation can be found at: http://www.fda.gov/oc/opacom/hottopics/tomatoes.html*
More information about Salmonella and this investigation can be found at:
- Salmonella FAQs
- New Mexico Department of Health Announces Link Between Tomatoes, Salmonella
 (PDF – 191 KB)
(PDF – 191 KB) - ADHS News Release - Tomatoes: Caution Urged*
- Texas Department of State Health Services - News Update, June 7, 2008*
- Kansas Identifies 3 Cases Linked to Multi-State Salmonella Outbreak*
Information on the safe handling of produce can be found at: www.cfsan.fda.gov/~dms/prodsafe.html.*
Previous Updates on this Outbreak
Error processing SSI file
Error processing SSI file
NOTICE: The information on this page is no longer being updated and may have changed. The information is accurate only as of the last page update.
Content Source: National Center for Zoonotic, Vector-Borne, and Enteric Diseases (ZVED)
Quick Links
Contact CDC

Error processing SSI file
s.pageName=document.title s.channel="Salmonella" s.hier1="NCEZID~DFWED~Salmonella~Saintpaul" s.prop22="NCEZID" s.prop23="DFWED" s.prop24="Salmonella" s.prop25="Saintpaul" Error processing SSI file