National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
NCHS Fact Sheet, December 2017
PDF Version pdf icon(PDF – 378 KB)
About NCHS
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) is the nation’s principal health statistics agency, providing data to identify and address health issues. NCHS compiles statistical information to help guide public health and health policy decisions.
Collaborating with other public and private health partners, NCHS uses a variety of data collection mechanisms to obtain accurate information from multiple sources. This process provides a broad perspective on the population’s health, influences on health, and health outcomes.
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is NCHS’ most in-depth and logistically complex survey, designed to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States. Annually, NHANES examines a nationally representative sample of 5,000 persons of all ages. To produce reliable statistics, the survey oversamples African American, Asian American, and Hispanic persons, and persons over age 60.
NHANES is the only national source of objectively measured health data capable of providing accurate estimates of both diagnosed and undiagnosed conditions. It is unique in that it combines personal interviews with standardized physical examinations, diagnostic procedures, and laboratory tests to determine the prevalence of major diseases and risk factors for diseases. Physical examinations are conducted in mobile examination centers that travel to 15 U.S. counties annually.
Examples of NHANES data
NHANES collects data on a variety of health-related topics, including:
Obesity Oral health
Diabetes Physical fitness and physical functioning
Nutrition Sexual behavior and sexually transmitted diseases
Kidney disease Environmental exposures
Infectious diseases Supplements and medications
NHANES data help produce national references for measurements such as height and weight (pediatric growth charts) and blood pressure.
Recent NHANES findings
Prevalence of hypertension among adults
Hypertension is a public health challenge in the United States because it directly increases the risk for cardiovascular disease.
- During 2015–2016, the prevalence of hypertension among adults was 29.0% and was similar among men (30.2%) and women (27.7%).
- Prevalence of controlled hypertension was 48.3% and increased with age for men but not women.
- From 1999 to 2016, hypertension prevalence was unchanged. For controlled hypertension, prevalence increased from 1999 to 2010 but then did not change through 2016.
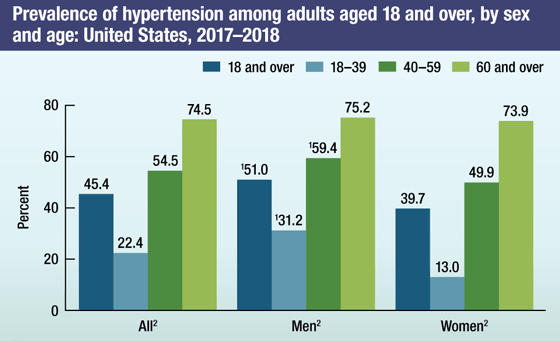 image icon
image icon
1Significant increasing trend for 1999–2010, p < 0.001.
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2016.
Adult obesity is associated with increased risk of a number of health conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, stroke, arthritis, and certain cancers. The prevalence of obesity was 39.8% among U.S. adults in 2015–2016.
NHANES data for 2015–2016 show differences by:
Age
- The prevalence of obesity among adults aged 40–59 (42.8%) was higher than among adults aged 20–39 (35.7%). No significant difference in prevalence was seen between adults aged 60 and over (41.0%) and younger groups.
Race and ethnicity
- The prevalence of obesity was lower among non-Hispanic Asian adults (12.7%), compared with all other race and Hispanic-origin groups. Hispanic (47.0%) and non-Hispanic black (46.8%) adults had a higher prevalence of obesity than non-Hispanic white adults (37.9%).
Sex
- The prevalence of obesity was 38.0% in non-Hispanic white, 54.8% in non-Hispanic black, 14.8% in non-Hispanic Asian, and 50.6% in Hispanic women.
- The prevalence of obesity was lower in non-Hispanic Asian men(10.1%) compared with non-Hispanic white (37.9%), non-Hispanic black (36.9%), and Hispanic (43.1%) men.
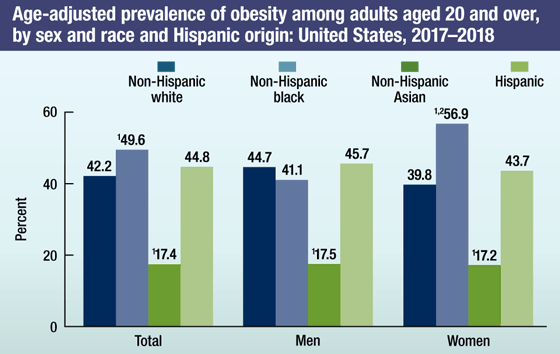 image icon
image icon
NOTES: All estimates are age adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 U.S. census population
using the age groups 20–39, 40–59, and 60 and over.
SOURCE: NCHS, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2015–2016.
Additional NHANES findings
Prevalence of obesity among youth
- The prevalence of obesity among U.S. youth aged 2–19 years was 18.5% in 2015–2016.
- Overall, the prevalence of obesity among adolescents (12–19 years) (20.6%) and school-aged children (6–11 years) (18.4%) was higher than among preschool-aged children (2–5 years) (13.9%).
Trends in adult and childhood obesity
From 1999–2000 through 2015–2016, a significantly increasing trend in obesity was observed in both adults and youth. The observed change in prevalence between 2013–2014 and 2015–2016, however, was not significant among either adults or youth.
NHANES cholesterol data in adults
- In 2015–2016, 24.4% of adults had high total cholesterol.
- Overall, prevalence was higher in adults aged 40–59 (17.1%) than in those aged 20–39 (7.9%) and 60 and over (12.5%). It was also higher in adults aged 60 and over than those aged 20–39.
- About 18.0% of adults (28.5% of men and 8.9% of women) had low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
- In men and women, low HDL cholesterol prevalence was higher in Hispanic adults than in non-Hispanic white, black, and Asian adults. In men, prevalence was higher in non-Hispanic white and Asian men than in non-Hispanic black men.
Challenges and future opportunities
- Due to the comprehensive nature of the interviews and examinations, as well as increasing challenges in reaching participants in the household, it is increasingly difficult to maintain survey response rates. In addition, the oversampling of some special populations increases the likelihood that interviewers will encounter linguistic and cultural barriers to participation.
- As health issues and biomedical science advance, a continuing need exists to develop new components in NHANES and related surveys to ensure that needed information can be collected using state-of-the art methods.
.
For more information about NCHS and its programs, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs.
For more information on NHANES, visit https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm.