About Cholesterol
What is cholesterol?
Blood cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance made by your liver. Blood cholesterol is essential for good health. Your body needs it to perform important jobs, such as making hormones and digesting fatty foods. Your body makes all the blood cholesterol it needs, which is why experts recommend that people eat as little dietary cholesterol as possible while on a healthy eating plan.
Dietary cholesterol is found in animal foods, including meat, seafood, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Learn more about preventing high cholesterol by making healthy eating choices.
What do blood cholesterol numbers mean?
Cholesterol is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). When you go to a health care professional to get your cholesterol checked, this test (also called a lipid panel or lipid profile) will usually check the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in your body.
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol. Having high levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries and result in heart disease or stroke.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good” cholesterol. HDL is known as “good” cholesterol because high levels of it can lower your risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Triglycerides, a type of fat in your blood that your body uses for energy. The combination of high levels of triglycerides with low HDL cholesterol or high LDL cholesterol levels can increase your risk for heart attack and stroke.
- Total cholesterol, the total amount of cholesterol in your blood based on your HDL, LDL, and triglycerides numbers.
Learn more about LDL and HDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
What is high cholesterol?
If you are an adult or child, high cholesterol is having a total cholesterol above 200 mg/dL.1 This condition is also called hyperlipidemia.
Millions of people in the United States have high cholesterol. It can cause health problems.
Work with your health care team to prevent and manage high cholesterol by working toward optimal cholesterol levels.
What are signs and symptoms of high cholesterol?
High blood cholesterol doesn’t have symptoms, which is why getting your cholesterol levels checked is so important.
Knowing your cholesterol status can help you stay in control of your health. Learn about getting your cholesterol checked and why it is important.
What causes high cholesterol?
Certain health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and obesity, can raise your risk for high cholesterol. Lifestyle factors, such eating a diet high in saturated and trans fats and not getting enough activity, can also raise your risk for high cholesterol. Some people who have a family history of high cholesterol can also be at risk for high cholesterol. All these factors are called “risk factors.”
You can’t control some of these risk factors, such as your age or your family history. But you can take steps to lower your risk for high cholesterol by changing things you can control.
What problems does high cholesterol cause?
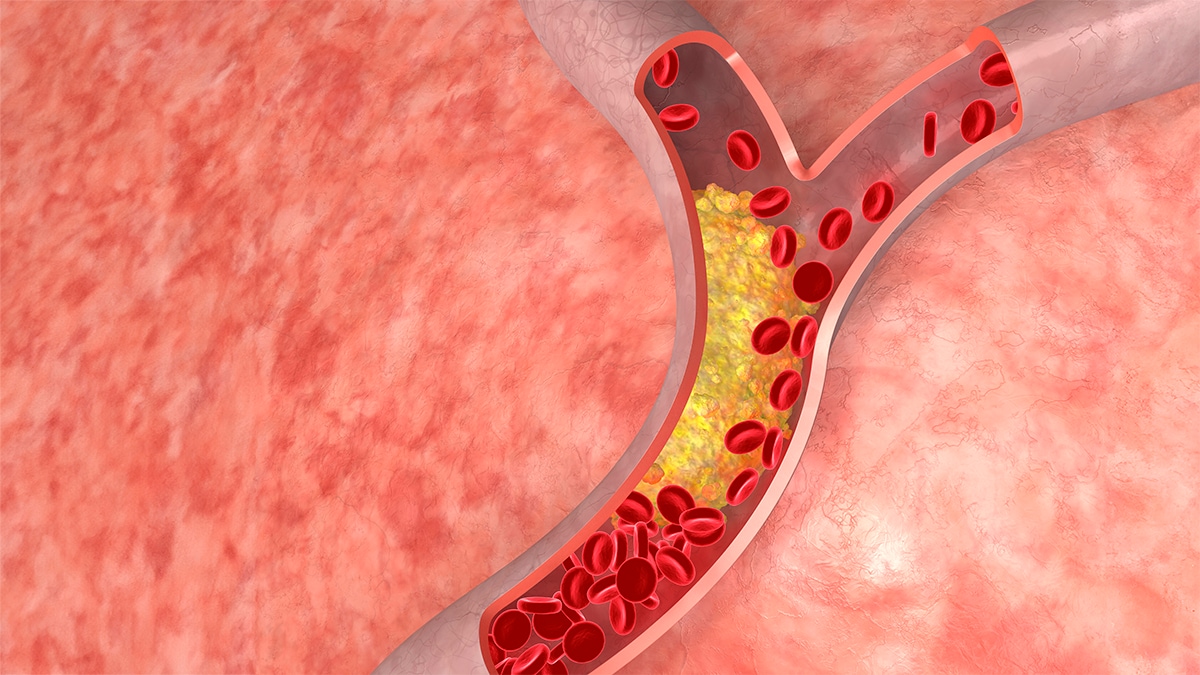
As cholesterol (plaque) builds up in the arteries, the arteries begin to narrow, which lessens or blocks the flow of blood.
Having high blood cholesterol can lead to a buildup called “plaque” on the walls of your arteries (a type of blood vessel).
As plaque builds up over time, the insides of your arteries narrow. This narrowing blocks blood flow to and from your heart and other organs. When blood flow to the heart is blocked, it can cause chest pain (also called angina) or a heart attack (also called myocardial infarction).
High cholesterol also increases your risk for heart disease and stroke, two leading causes of death in the United States.
How do I know if I have high cholesterol?
The only way to know whether you have high cholesterol is to get your cholesterol checked by your health care team. Talk with your health care team about how often you should have your cholesterol screened. Learn about getting your cholesterol checked and why it is important.
What can I do to prevent or manage high cholesterol?
Strong evidence shows that eating patterns that include less dietary cholesterol are associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. Learn how to prevent, treat, and manage high cholesterol.
Your overall risk for high cholesterol depends on many factors. Learn what increases your risk for high cholesterol.
More information
CDC
Other Organizations
- MedlinePlus: Cholesterol
- American Heart Association (AHA):
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA):
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI): High Blood Cholesterol—What You Need to Know
- Family Heart Foundation: What are the Risks of FH and High Lp(a)?
Reference
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139(25):e1082–e1143.
